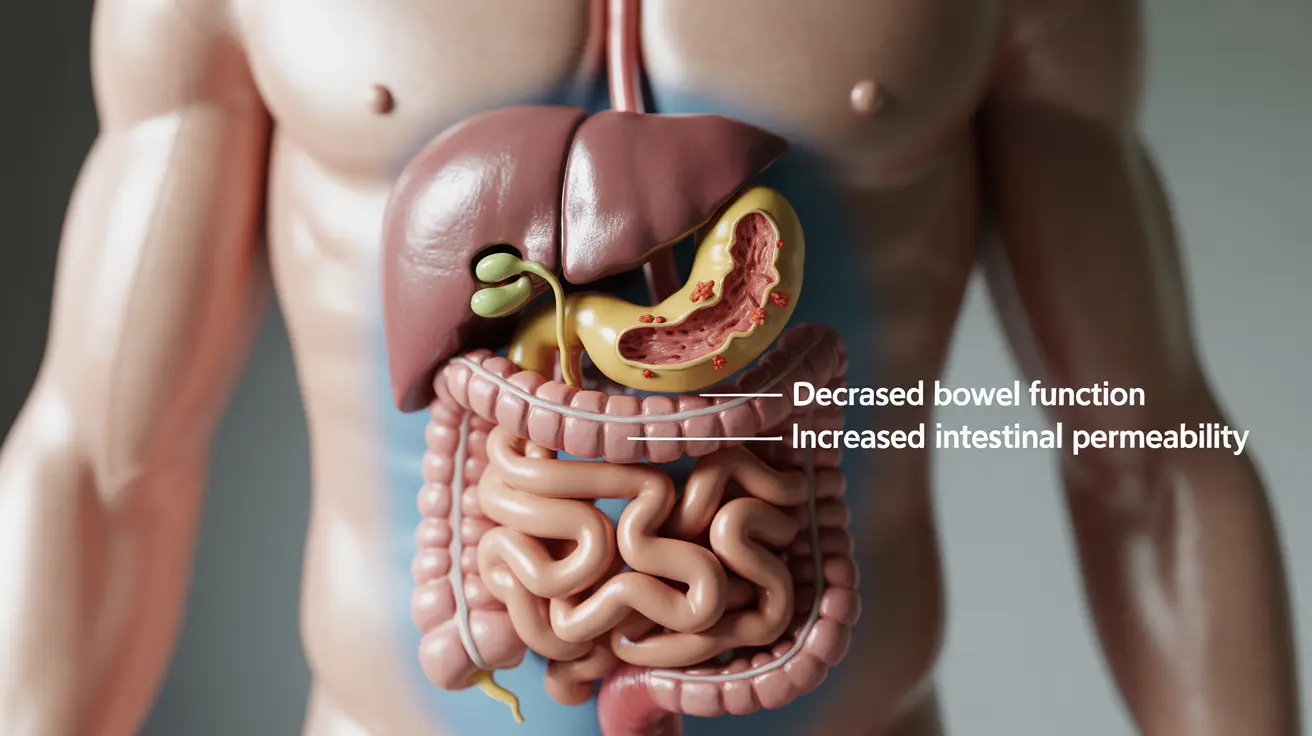
Living with HIV can bring various health challenges, including changes in digestive function that may affect bowel movements and overall gastrointestinal health. Many people with HIV experience digestive issues, particularly diarrhea, which can significantly impact quality of life and overall health management.
Understanding the connection between HIV and digestive symptoms is crucial for effective management and maintaining optimal health. These symptoms can result from various factors, including the virus itself, medications used in treatment, or opportunistic infections that may develop when the immune system is compromised.
Why HIV Affects Digestive Health
HIV directly impacts the immune system, which plays a vital role in maintaining digestive health. When HIV weakens immune function, it can disrupt the delicate balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to various gastrointestinal symptoms including changes in bowel movements.
The virus can also directly affect the cells lining the digestive tract, causing inflammation and interfering with normal absorption of nutrients and water. This inflammatory process can lead to loose stools, increased frequency of bowel movements, and other digestive discomfort.
Additionally, people with HIV are more susceptible to opportunistic infections that can affect the digestive system. These infections, caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi, can cause severe diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms that may persist without proper treatment.
Medication-Related Digestive Side Effects
Antiretroviral therapy (ART), while essential for managing HIV, can sometimes cause digestive side effects as the body adjusts to treatment. These medications work by suppressing viral replication, but they can temporarily disrupt normal digestive processes.
Most medication-related digestive symptoms are temporary and typically improve within a few weeks as the body adapts to treatment. However, some individuals may experience ongoing symptoms that require management strategies or medication adjustments.
Protease inhibitors, a class of HIV medications, are particularly associated with digestive side effects. Newer formulations and combination therapies have reduced these issues, but they can still occur in some patients.
Managing Chronic Digestive Issues
Effective management of HIV-related digestive problems involves multiple approaches tailored to individual needs. Dietary modifications often play a crucial role in symptom management and can significantly improve quality of life.
The BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) can help firm up loose stools and provide easily digestible nutrients. Avoiding dairy products, high-fat foods, caffeine, and artificial sweeteners may also reduce symptoms in many individuals.
Probiotics can help restore healthy gut bacteria balance, which is particularly important for people with HIV. These beneficial bacteria support digestive health and may help reduce the frequency and severity of digestive symptoms.
Staying hydrated is essential, as digestive issues can lead to fluid and electrolyte loss. Clear liquids, electrolyte solutions, and gradual reintroduction of solid foods can help maintain proper hydration and nutrition.
Preventing and Treating Dehydration at Home
Dehydration is a serious concern when experiencing frequent loose stools or diarrhea. Home management strategies can effectively prevent mild to moderate dehydration and support recovery.
Oral rehydration solutions, available over-the-counter or homemade with water, salt, and sugar, help replace lost fluids and electrolytes. These solutions are more effective than water alone for maintaining proper hydration.
Small, frequent sips of clear liquids throughout the day are better tolerated than large amounts consumed at once. Coconut water, clear broths, and diluted fruit juices can also contribute to hydration while providing some nutrients.
Avoiding alcohol and caffeine is important, as these substances can worsen dehydration. Ice chips or popsicles may be easier to tolerate when nausea accompanies digestive symptoms.
Recognizing When to Seek Medical Attention
While many digestive issues can be managed at home, certain symptoms require prompt medical evaluation. Understanding when to contact healthcare providers is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring appropriate treatment.
Severe dehydration signs include dizziness, dry mouth, decreased urination, and fatigue. Blood in stool, severe abdominal pain, or high fever accompanying digestive symptoms warrant immediate medical attention.
Persistent symptoms lasting more than a few days, or symptoms that worsen despite home management, should be evaluated by healthcare providers. Changes in HIV viral load or CD4 count may also be related to digestive issues.
Rapid weight loss, inability to keep fluids down, or signs of severe malnutrition require professional medical intervention. Early treatment of complications can prevent more serious health problems.
Long-term Health Considerations
Chronic digestive issues can affect HIV management by interfering with medication absorption and overall nutritional status. Working closely with healthcare providers to address these symptoms is essential for optimal HIV treatment outcomes.
Regular monitoring of nutritional status, including vitamin and mineral levels, may be necessary for individuals with ongoing digestive symptoms. Nutritional supplements might be recommended to address specific deficiencies.
Maintaining open communication with healthcare teams about digestive symptoms ensures that treatment plans can be adjusted as needed. This collaborative approach helps optimize both HIV management and overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do people with HIV experience diarrhea and what causes it?
People with HIV experience diarrhea due to several factors. The virus itself weakens the immune system and can directly affect digestive tract cells, causing inflammation. HIV also increases susceptibility to opportunistic infections from bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi that can cause severe digestive symptoms. Additionally, the virus disrupts the normal balance of gut bacteria, further contributing to digestive issues.
Can HIV medications cause diarrhea and how long does it typically last?
Yes, HIV medications, particularly antiretroviral therapy (ART), can cause diarrhea as a side effect. This typically occurs as the body adjusts to new medications and usually improves within 2-4 weeks of starting treatment. Protease inhibitors are especially associated with digestive side effects. If symptoms persist beyond a month or are severe, healthcare providers may adjust medications or recommend management strategies.
What are the best ways to manage and treat chronic diarrhea related to HIV?
Management involves dietary modifications such as following the BRAT diet, avoiding dairy, high-fat foods, caffeine, and artificial sweeteners. Probiotics can help restore healthy gut bacteria. Anti-diarrheal medications may be recommended by healthcare providers. Staying hydrated with electrolyte solutions is crucial. Working with healthcare teams to address underlying causes, including medication adjustments or treating opportunistic infections, is essential for long-term management.
How can dehydration from HIV-related diarrhea be prevented and treated at home?
Prevention involves drinking small, frequent amounts of clear liquids throughout the day. Oral rehydration solutions are more effective than water alone. Coconut water, clear broths, and diluted fruit juices can help maintain hydration. Avoid alcohol and caffeine, which worsen dehydration. Ice chips or popsicles may be easier to tolerate. Monitor for signs of severe dehydration and seek medical care if symptoms worsen.
When should someone with HIV seek medical help for diarrhea symptoms?
Seek immediate medical attention for severe dehydration signs (dizziness, dry mouth, decreased urination), blood in stool, severe abdominal pain, or high fever. Contact healthcare providers if symptoms persist more than a few days, worsen despite home treatment, or are accompanied by rapid weight loss or inability to keep fluids down. Any concerns about medication absorption or changes in HIV management should also prompt medical consultation.