Understanding the visual signs and symptoms of HIV in men is crucial for early detection and treatment. While HIV affects all genders, certain symptoms may present differently in males, and recognizing these signs can lead to faster diagnosis and better health outcomes.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand what to look for, when symptoms typically appear, and when to seek medical attention. Remember that HIV symptoms can vary greatly between individuals, and some people may not show any visible signs in the early stages.
Early HIV Symptoms in Men: The First Signs
The initial symptoms of HIV infection in men typically appear within 2-4 weeks after exposure. These early signs often resemble flu-like symptoms and may include:
- Fever and chills
- Night sweats
- Muscle aches and joint pain
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headache
These symptoms usually last for several days to a few weeks and may resolve on their own, which is why many people mistake them for a common cold or flu.
Understanding HIV-Related Skin Changes
Common Skin Manifestations
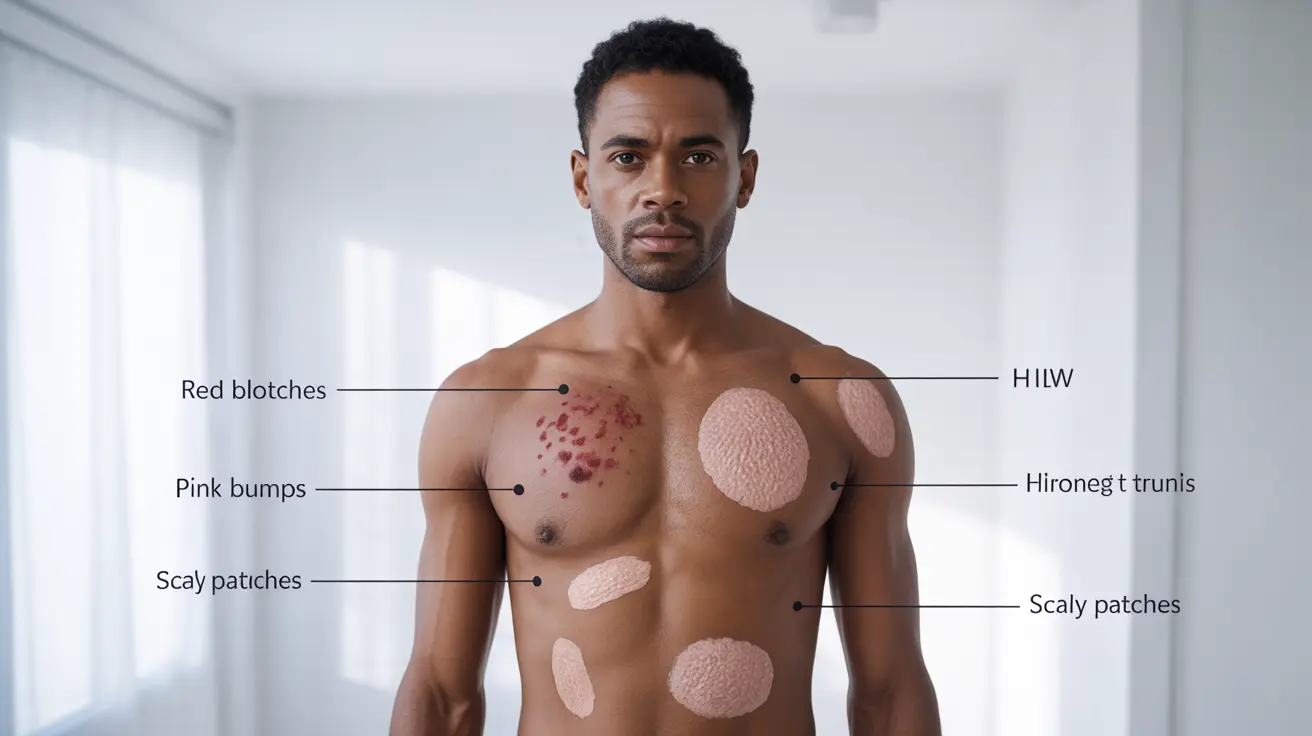
Skin changes are frequently observed in HIV-positive men and can manifest in various ways:
- Red or purple blotches
- Small pink or brown bumps
- Flaky or scaly patches
- Severe itching
- Unusual bruising
Identifying HIV Rash Patterns
HIV-related rashes typically appear on the:
- Upper chest and face
- Hands and feet
- Trunk area
- Inside of the mouth
These rashes may be flat or raised, and their appearance can range from mild to severe. The texture and color can vary depending on skin tone and the stage of infection.
Genital Symptoms and Signs
Men may experience specific genital symptoms during HIV infection, including:
- Sores or ulcers on the penis or scrotum
- Unusual discharge
- Pain or burning during urination
- Swelling in the groin area
- Persistent itching
When to Seek Medical Care
It's essential to seek immediate medical attention if you:
- Have had potential exposure to HIV
- Experience persistent flu-like symptoms
- Notice unusual skin changes or rashes
- Develop unexplained genital symptoms
Early testing and diagnosis are crucial for optimal treatment outcomes and preventing transmission to others.
Treatment for HIV-Related Skin Conditions
HIV-related skin conditions can be managed through various treatments:
- Topical corticosteroids for inflammation
- Antihistamines for itching
- Antifungal medications for fungal infections
- Specific treatments for particular skin conditions
- Adjustments to HIV medications if they're causing skin reactions
Frequently Asked Questions
What do early HIV symptoms look like in men and how soon do they appear after exposure?
Early HIV symptoms in men typically appear 2-4 weeks after exposure and include fever, night sweats, fatigue, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms often resemble the flu and may last for several days to weeks.
How can I recognize an HIV-related rash in males and what does it typically look like?
HIV-related rashes in males usually appear as red or purple blotches, small pink or brown bumps, or scaly patches. They commonly occur on the upper chest, face, hands, feet, and trunk area. The rash may be flat or raised and can vary in appearance depending on skin tone.
What are common genital symptoms of HIV in men, such as sores or ulcers?
Common genital symptoms include sores or ulcers on the penis or scrotum, unusual discharge, pain during urination, groin swelling, and persistent itching. These symptoms may appear during different stages of HIV infection.
When should a man with possible HIV symptoms see a doctor and get tested?
Men should seek immediate medical attention if they've had potential HIV exposure, experience persistent flu-like symptoms, notice unusual skin changes or rashes, or develop unexplained genital symptoms. Early testing is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How is HIV-related skin rash treated and can it be caused by HIV medications?
HIV-related skin rashes can be treated with topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and specific medications depending on the cause. Some HIV medications can cause skin rashes as a side effect. If this occurs, your healthcare provider may adjust your treatment regimen while maintaining effective HIV control.