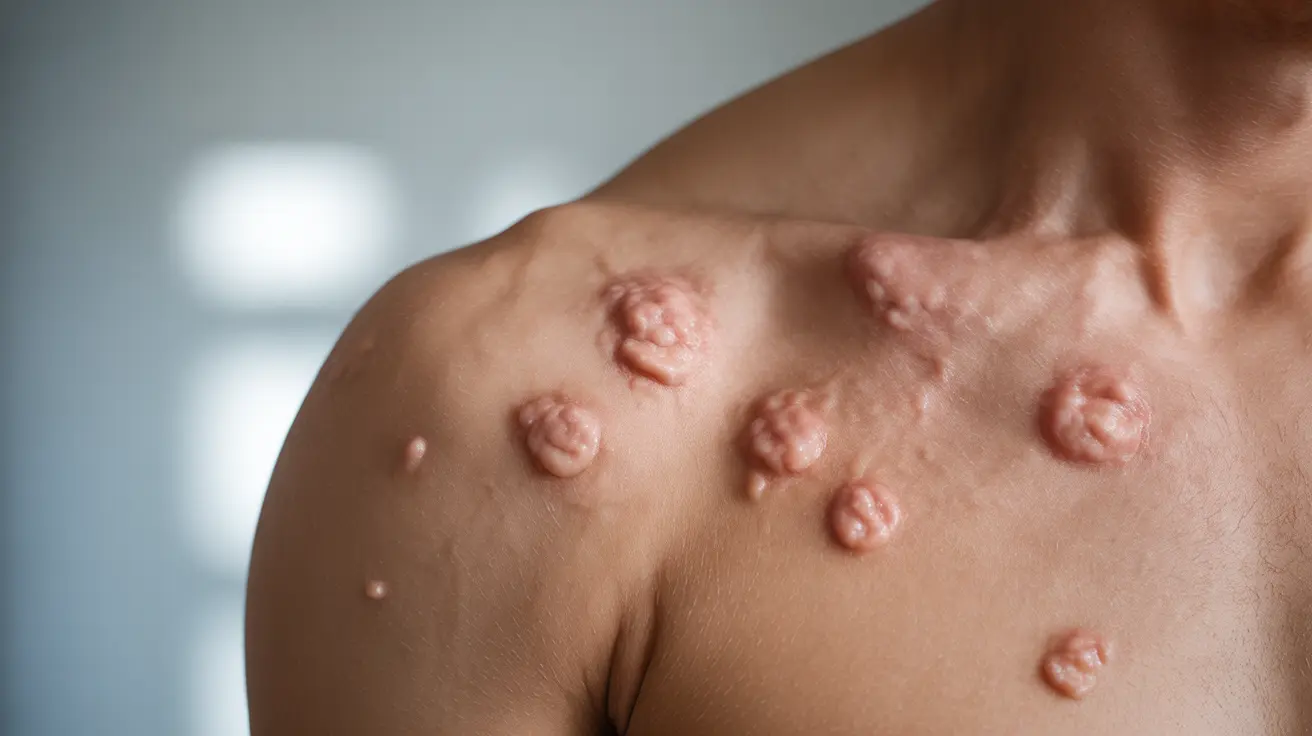
Developing hives on the chest can be an uncomfortable and concerning experience. These raised, itchy welts can appear suddenly and may cause significant discomfort in the chest and breast area. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and appropriate treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
While chest hives are often harmless and temporary, they can sometimes indicate an underlying allergic reaction or medical condition that requires attention. This comprehensive guide will help you understand what causes chest hives, how to identify them, and when you should consult a healthcare provider.
Understanding Chest Hives
Hives, medically known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body, including the chest area. These welts typically appear as pink or red patches with clearly defined edges and may change shape or move around over time.
When hives occur on the chest, they can be particularly noticeable and uncomfortable due to clothing friction and the sensitivity of the area. Individual hives usually fade within 24 hours, though new ones may continue to appear.
Common Causes of Chest Hives
Several factors can trigger hives to appear on the chest area:
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or environmental allergens
- Contact with irritating materials or fabrics
- Stress or emotional triggers
- Temperature changes or physical pressure
- Underlying medical conditions
- Infections or illnesses
- Exercise or sweating
Identifying Chest Hives vs. Other Skin Conditions
Chest hives typically have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other skin conditions:
Key Features of Chest Hives
- Raised welts with defined borders
- Blanching (turning white) when pressed
- Appearing and disappearing rapidly
- Intense itching or burning sensation
- Changes in size and shape within hours
Treatment Options
Several effective treatments can help manage chest hives and provide relief:
Immediate Relief Measures
- Over-the-counter antihistamines
- Cool compresses
- Loose, breathable clothing
- Avoiding hot showers or baths
- Calamine lotion or anti-itch creams
Long-term Management
For recurring or chronic hives, your healthcare provider might recommend:
- Prescription antihistamines
- Oral corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Allergy testing to identify triggers
- Lifestyle modifications
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the likelihood of developing chest hives, consider these preventive measures:
- Identify and avoid known triggers
- Wear loose-fitting, natural fiber clothing
- Keep a symptom diary to track potential causes
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques
- Maintain good skin hygiene
- Use fragrance-free products
When to Seek Medical Care
While many cases of chest hives resolve on their own, certain situations warrant immediate medical attention:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Severe swelling, especially of the face or throat
- Hives persisting beyond six weeks
- Symptoms accompanied by fever or joint pain
- Recurring episodes without clear triggers
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes hives to appear specifically on the chest or breast area?
Hives on the chest can be triggered by various factors, including allergic reactions, tight clothing, heat, sweat, stress, or pressure on the skin. The chest area is particularly susceptible due to frequent contact with clothing and environmental irritants.
How can I tell if hives on my chest are due to an allergy or a more serious condition like breast cancer?
Hives typically appear as raised, itchy welts that change position and fade within 24 hours. Unlike breast cancer symptoms, hives are usually temporary and move around. However, if you have persistent skin changes or other concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
What are the most effective treatments to relieve itching and other symptoms of hives on the chest?
The most effective treatments include oral antihistamines, cool compresses, and avoiding triggers. For immediate relief, over-the-counter antihistamines and topical anti-itch creams can help manage symptoms. Severe cases may require prescription medications.
When should I seek medical help for hives on my chest that do not go away or keep coming back?
Seek medical attention if hives persist for more than six weeks, cause severe discomfort, or are accompanied by breathing difficulties, fever, or severe swelling. Chronic or recurring hives may require professional evaluation to identify underlying causes.
Are there common triggers or lifestyle changes that can help prevent hives from developing on the chest?
Yes, common preventive measures include wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing, avoiding known allergens, managing stress, maintaining good skin hygiene, and using fragrance-free products. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify and avoid specific triggers.