Understanding how doctors test for multiple sclerosis (MS) is crucial for anyone concerned about this neurological condition. The diagnosis process involves several sophisticated tests and specific criteria, as no single test can definitively confirm MS. This guide explores the various diagnostic methods healthcare providers use to identify multiple sclerosis accurately.
MRI Scanning: The Primary Diagnostic Tool
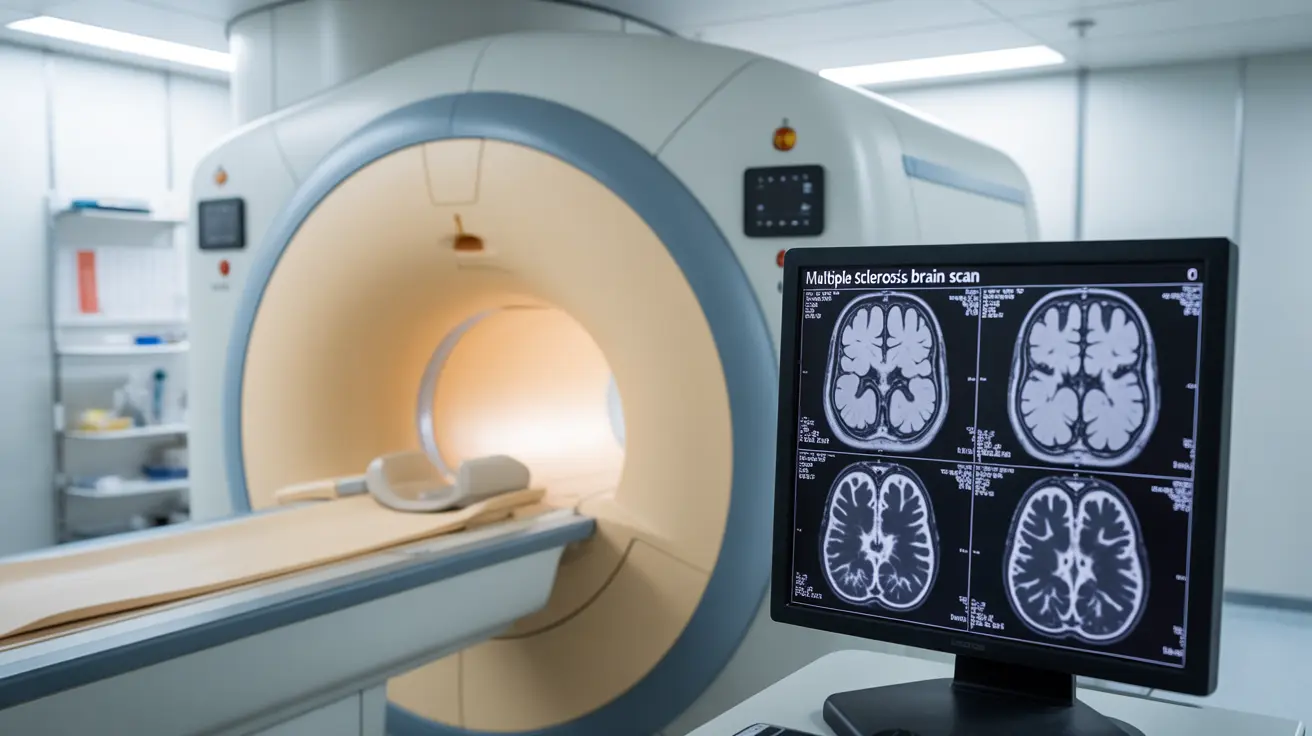
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) stands as the cornerstone of MS diagnosis. This advanced imaging technique provides detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord, revealing the characteristic lesions associated with MS. Modern MRI technology can show both active inflammation and older damage, helping doctors track disease progression and distinguish MS from other conditions.
During an MRI scan for MS diagnosis, doctors typically use contrast dye to highlight areas of active inflammation. The presence, location, and pattern of lesions help healthcare providers determine whether symptoms are consistent with MS and rule out other potential causes.
Lumbar Puncture: Analyzing Cerebrospinal Fluid
A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, provides valuable information about the immune system's activity within the central nervous system. During this procedure, doctors collect and analyze cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to look for specific markers associated with MS, including elevated levels of certain proteins and antibodies.
The presence of oligoclonal bands in the CSF can indicate the type of inflammation characteristic of MS, though this finding alone isn't sufficient for diagnosis. This test helps support the diagnosis when MRI results are inconclusive or additional confirmation is needed.
Blood Testing in MS Diagnosis
While blood tests cannot definitively diagnose MS, they play a crucial role in the diagnostic process. These tests help doctors rule out other conditions that can mimic MS symptoms, such as lupus, Lyme disease, or other autoimmune disorders. Blood work can also identify vitamin deficiencies or other medical conditions that might contribute to neurological symptoms.
Evoked Potential Tests
Evoked potential tests measure how quickly and accurately your nervous system responds to specific stimuli. These tests record the electrical signals produced by your nervous system in response to stimulation of specific sensory nerve pathways. Three main types of evoked potential tests are commonly used:
- Visual evoked potentials (VEP)
- Brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEP)
- Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEP)
The McDonald Criteria: Standardizing MS Diagnosis
The McDonald Criteria provide a standardized framework for MS diagnosis, incorporating various test results and clinical findings. These criteria help doctors determine if a patient meets the requirements for an MS diagnosis, focusing on demonstrating disease activity separated in time and space within the central nervous system.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do doctors use MRI scans to test for multiple sclerosis?
Doctors use MRI scans to detect and monitor lesions in the brain and spinal cord characteristic of MS. They often employ contrast dye to highlight areas of active inflammation and track changes over time, helping to establish the diagnosis and monitor disease progression.
What role does a lumbar puncture play in diagnosing multiple sclerosis?
A lumbar puncture helps diagnose MS by analyzing cerebrospinal fluid for specific markers of inflammation and immune system activity. The presence of oligoclonal bands and elevated protein levels can support an MS diagnosis, particularly when MRI results are inconclusive.
Why are blood tests done when testing for MS if they cannot confirm the disease?
Blood tests are performed to rule out other conditions that can mimic MS symptoms, such as other autoimmune diseases, infections, or vitamin deficiencies. While they cannot confirm MS, they are essential for ensuring an accurate diagnosis by excluding other potential causes.
How do evoked potential tests help in diagnosing multiple sclerosis?
Evoked potential tests measure the speed and accuracy of nerve signal transmission in response to specific stimuli. These tests can reveal slowed nerve conduction, which may indicate damage to the myelin sheath characteristic of MS, helping support the diagnosis.
What are the McDonald criteria and how do they guide the diagnosis of MS?
The McDonald criteria are standardized guidelines that help doctors diagnose MS by combining clinical findings with test results. These criteria require evidence of disease activity occurring at different times and in different areas of the central nervous system, ensuring a consistent approach to diagnosis across the medical community.