Natural Growth Patterns and Development
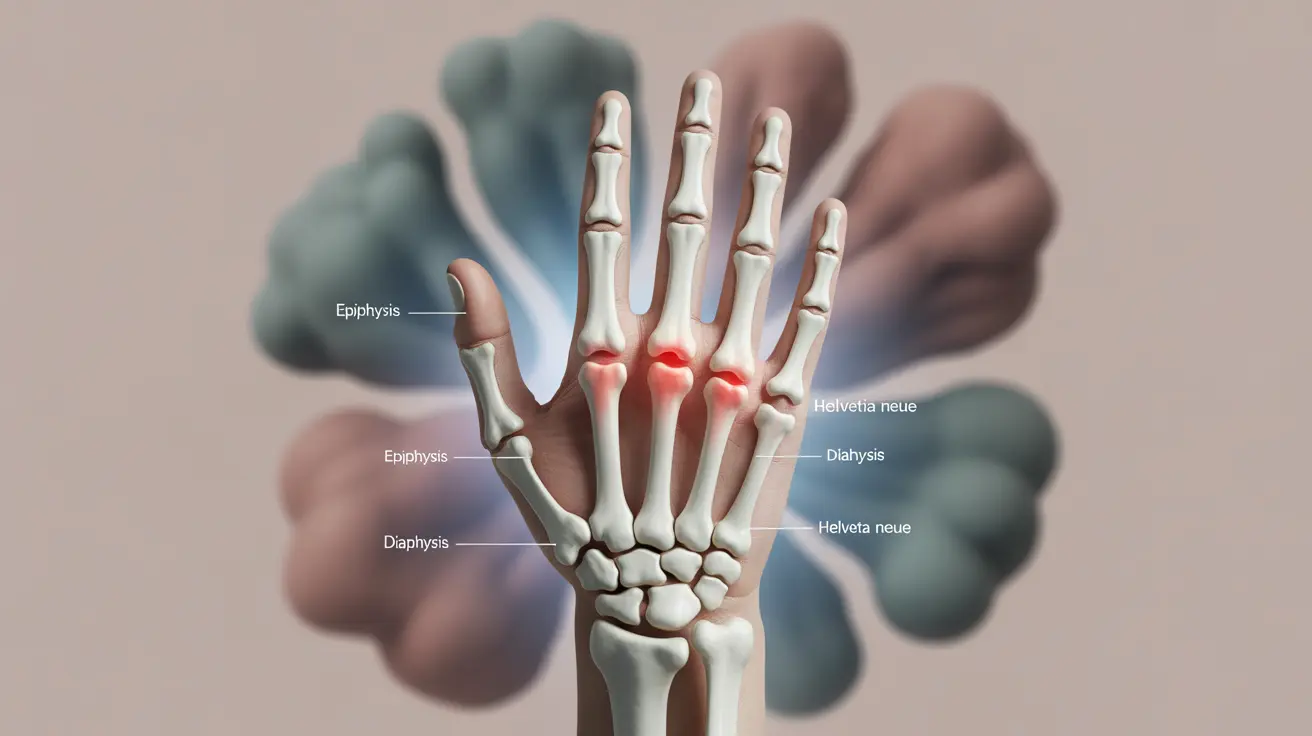
Height growth is primarily determined by genetics, nutrition, and hormones. During puberty, growth plates (epiphyseal plates) at the ends of long bones are active, allowing for continued height increase. This process naturally slows and eventually stops when these growth plates close.
For most people, major growth periods occur during:
- Early childhood (ages 0-4)
- Pre-puberty growth spurt (ages 8-13 for girls, 10-15 for boys)
- Puberty-related growth (until late teens or early 20s)
When Growth Becomes a Concern
While rapid growth is typically normal during adolescence, certain conditions may cause excessive growth that requires medical attention:
Medical Conditions That Affect Growth
- Gigantism
- Marfan syndrome
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Growth hormone disorders
If you're concerned about unusual growth patterns, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for proper evaluation and guidance.
Medical Interventions and Growth Management
In specific cases, medical professionals may recommend treatments to manage extreme growth. These interventions are prescribed only when medically necessary and after careful evaluation:
Hormone-Related Treatments
Hormone therapy, particularly estrogen treatment in specific cases for females, may be considered to influence growth plate closure. However, these treatments are only prescribed under strict medical supervision and in particular circumstances.
Important Considerations
Any medical intervention to affect growth must be:
- Prescribed by qualified healthcare professionals
- Medically necessary and justified
- Carefully monitored for side effects
- Started at the appropriate developmental stage
Natural Height Development Timeline
Understanding when growth typically stops can help manage expectations:
- Girls usually stop growing 1-2 years after their first menstrual period
- Boys typically continue growing until age 16-17
- Some individuals may experience minor changes until their early 20s
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a safe and effective way to stop growing taller naturally or with medical treatments?
There is no safe way to stop natural growth through non-medical means. Medical interventions are only recommended in specific cases where excessive growth poses health risks, and these must be prescribed and monitored by healthcare professionals.
What causes rapid or excessive growth in children, and when should I see a doctor?
Rapid growth can be caused by hormonal conditions, genetic factors, or normal growth spurts. Consult a doctor if growth seems unusually rapid, is accompanied by pain, or causes significant concern.
Are hormone treatments or estrogen therapy effective in limiting height growth?
In specific medical cases, hormone treatments can influence growth plate closure. However, these treatments are only appropriate in certain situations and must be prescribed by medical professionals after careful evaluation.
What are the risks or side effects of trying to stop growth or using hormone-related treatments?
Hormone treatments can have significant side effects, including impacts on bone density, fertility, and overall development. Any attempts to artificially stop growth without medical supervision can be dangerous and potentially harmful.
At what age do most people stop growing taller, and can growth continue into the 20s?
Most girls stop growing by age 14-15, while boys typically stop around 16-17. Minor changes in height can occur into the early 20s, but significant growth usually ends when growth plates close during late teens.