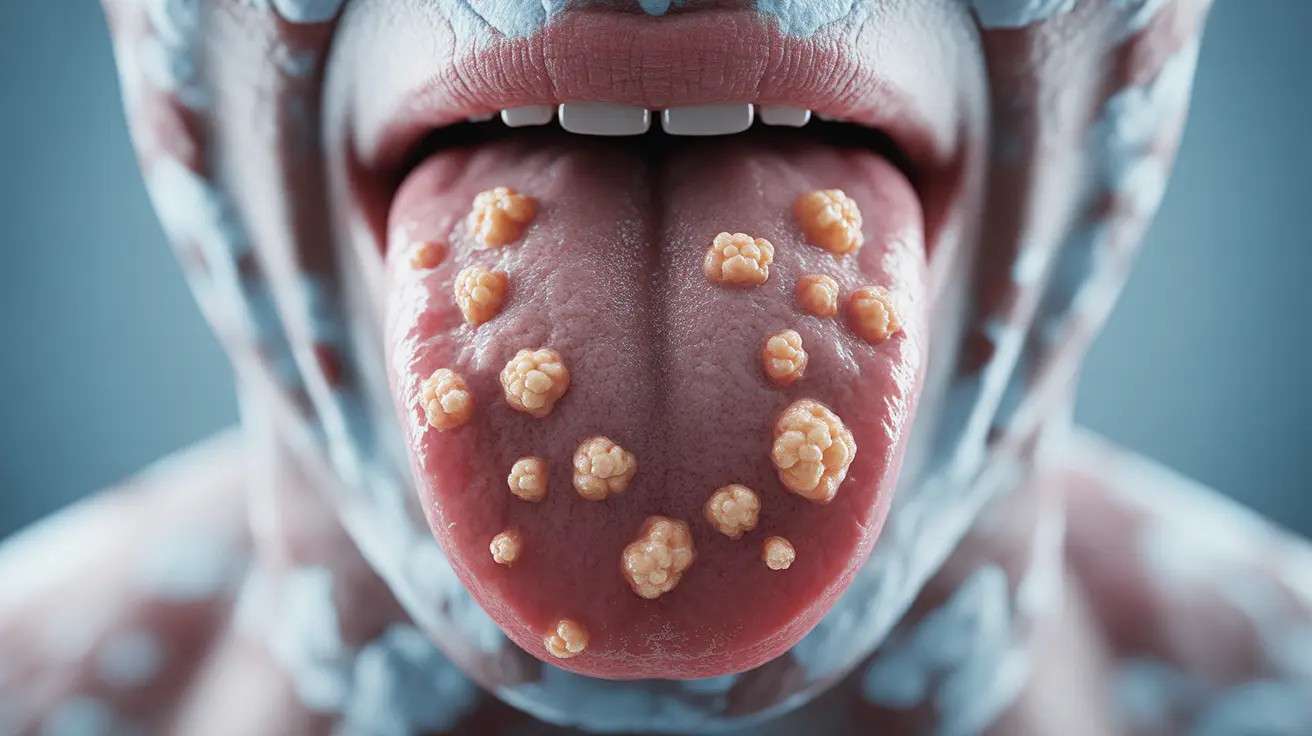
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infections can affect various parts of the body, including the mouth and throat. When HPV affects the oral cavity, it may cause bumps or warts to develop on the tongue, particularly on its posterior portion. Understanding these oral manifestations is crucial for early detection and proper medical care.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about HPV-related bumps on the back of the tongue, including their causes, appearance, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding HPV and Oral Transmission
HPV is a common viral infection that can spread through various forms of intimate contact, including oral activities. The virus can enter the mouth through direct contact with infected areas or through exposure to viral particles. While most people's immune systems clear the virus naturally, some cases may lead to the development of visible bumps or lesions.
Identifying HPV Bumps on the Tongue
HPV-related bumps on the tongue typically have distinct characteristics that help differentiate them from other oral conditions:
- Small, raised growths
- Flesh-colored or slightly whitish appearance
- Clustered or scattered distribution
- Generally painless
- May have a cauliflower-like texture
These bumps most commonly appear on the back portion of the tongue, though they can develop elsewhere in the mouth. While usually benign, any persistent oral growths should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose HPV-related tongue bumps:
- Visual examination
- Tissue biopsy when necessary
- HPV testing
- Oral cancer screening as a precautionary measure
Early diagnosis is essential, as some HPV strains can increase the risk of oral cancer. Professional evaluation helps determine the specific type of HPV present and guides appropriate treatment.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for HPV bumps on the tongue vary depending on their size, location, and severity:
Medical Interventions
- Topical medications
- Surgical removal
- Laser therapy
- Cryotherapy (freezing)
Supportive Care
- Regular monitoring
- Immune system support
- Oral hygiene maintenance
- Lifestyle modifications
Prevention and Oral Health Protection
Several strategies can help reduce the risk of developing HPV-related tongue bumps:
- Practice safe intimate contact
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene
- Get vaccinated against HPV
- Regular dental check-ups
- Avoid tobacco products
- Strengthen immune system through healthy lifestyle choices
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes HPV bumps on the back of the tongue and how is the virus transmitted?
HPV bumps on the tongue are caused by human papillomavirus infection, primarily transmitted through intimate contact with an infected person. The virus can spread through oral activities and direct contact with infected areas. Transmission can occur even when no visible symptoms are present.
What do HPV warts on the tongue look and feel like, and what symptoms should I watch for?
HPV warts on the tongue typically appear as small, raised growths with a flesh-colored or whitish appearance. They often have a cauliflower-like texture and are usually painless. Watch for persistent bumps, changes in texture, or unusual growths on your tongue.
How are HPV bumps on the tongue diagnosed and when should I see a doctor?
Diagnosis involves visual examination by a healthcare provider, possibly accompanied by tissue biopsy and HPV testing. See a doctor if you notice persistent bumps, changes in tongue appearance, or unusual growths that don't resolve within a few weeks.
What treatment options are available for HPV bumps on the back of the tongue?
Treatment options include topical medications, surgical removal, laser therapy, and cryotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, and severity of the bumps. Some cases may resolve naturally with immune system support.
How can I prevent getting HPV bumps in my mouth and protect my oral health?
Prevention strategies include HPV vaccination, practicing safe intimate contact, maintaining good oral hygiene, having regular dental check-ups, and supporting immune health through healthy lifestyle choices. Avoiding tobacco products and limiting alcohol consumption can also help protect oral health.