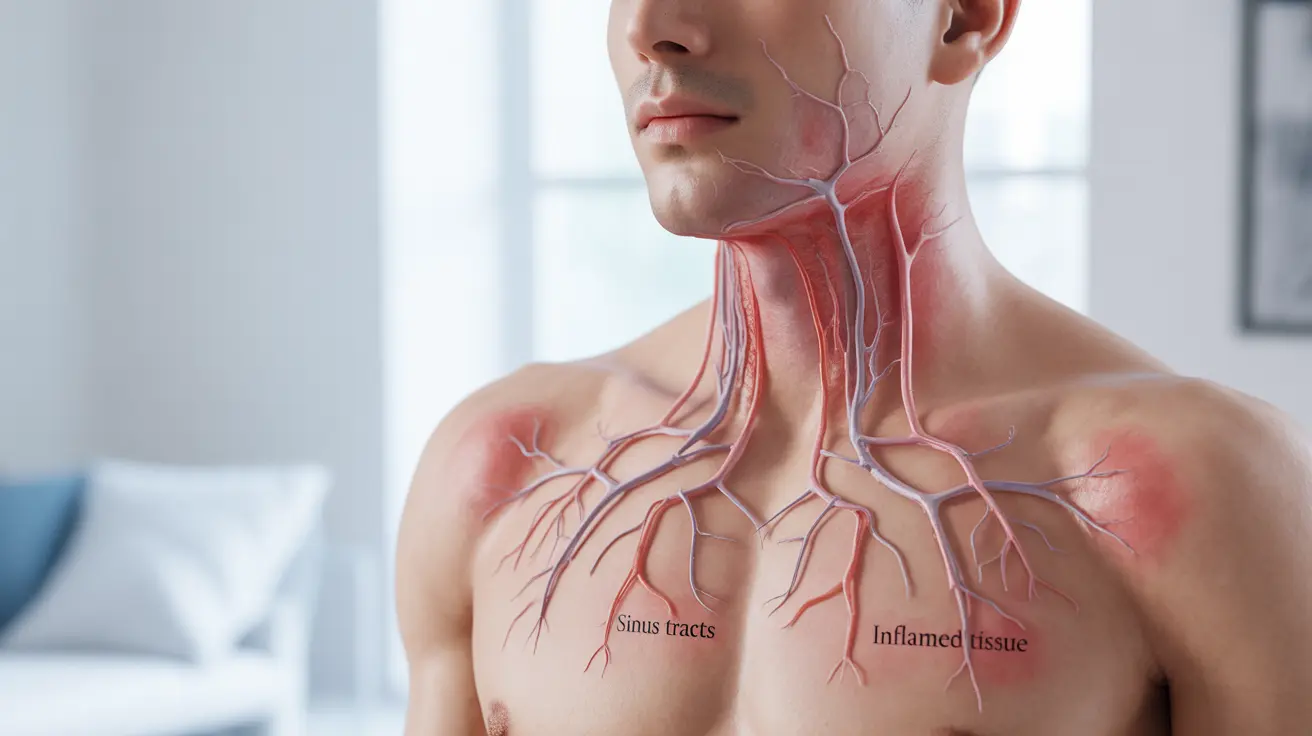
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) tunneling is a serious complication of this chronic inflammatory skin condition that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. These tunnel-like structures, also known as sinus tracts, develop beneath the skin when inflammation becomes severe and persistent. Understanding the nature of HS tunnels is crucial for proper management and treatment of this challenging condition.
For individuals living with HS, recognizing the signs of tunneling early can make a substantial difference in treatment outcomes and help prevent further complications. This article explores the essential aspects of HS tunneling, from its formation to treatment options and preventive measures.
What Causes HS Tunnels to Form?
HS tunnels develop when chronic inflammation leads to the connection of multiple abscesses under the skin. This process typically occurs through several stages:
- Initial inflammation of hair follicles
- Formation of painful nodules and abscesses
- Recurring inflammation creating permanent channels
- Connection of multiple infection sites beneath the skin
The persistent inflammation causes the body to create these pathways as it attempts to manage recurring infections and inflammation. Over time, these channels can become permanent structures within the affected tissue.
Identifying HS Tunneling
Recognizing the signs of HS tunneling early is crucial for effective treatment. Common indicators include:
- Deep, painful lumps that persist for weeks or months
- Multiple connected areas of inflammation
- Drainage from several openings in the skin
- Scarring and tissue changes in affected areas
- Chronic pain and discomfort
These symptoms typically appear in areas where skin folds meet, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
Treatment Approaches for HS Tunneling
Medical Management
Treatment often begins with conservative medical approaches, including:
- Oral and topical antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Biologic drugs for severe cases
- Regular wound care and management
Surgical Options
When medical management isn't sufficient, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Deroofing procedures for individual tunnels
- Wide excision surgery for extensive tunneling
- Laser treatment for certain cases
- Reconstructive surgery when needed
Prevention and Lifestyle Management
While HS tunnels can't always be prevented, several lifestyle modifications can help reduce their likelihood or severity:
- Maintaining good hygiene practices
- Wearing loose, breathable clothing
- Avoiding triggers like smoking and excess weight
- Managing stress levels effectively
- Following prescribed treatment plans consistently
Frequently Asked Questions
What are HS tunnels and what causes them to form under the skin?
HS tunnels are interconnected channels that form beneath the skin due to chronic inflammation and recurring abscesses in hidradenitis suppurativa. They develop when multiple inflammatory sites connect, creating permanent pathways in the affected tissue.
How can I tell if my hidradenitis suppurativa is developing HS tunnels, and what do they look and feel like?
HS tunnels typically present as deep, painful areas with multiple connected points of drainage. They may feel like firm, rope-like structures under the skin and often cause persistent pain and drainage from several openings.
What are the best treatment options for HS tunnels, and when is surgery needed?
Treatment options range from medical management with antibiotics and biologics to surgical interventions. Surgery becomes necessary when medical treatments fail to control symptoms or when tunnels become extensive and chronic.
Can HS tunnels heal on their own, or do they always require medical treatment?
HS tunnels rarely heal completely on their own and typically require medical intervention. While some mild cases might show improvement with conservative management, most cases need professional medical treatment to prevent progression and complications.
What lifestyle changes or preventive steps can help reduce the risk of developing HS tunnels or prevent them from getting worse?
Key preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene, wearing appropriate clothing, avoiding known triggers, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and following prescribed treatment plans consistently. Regular medical monitoring is also essential for preventing progression.