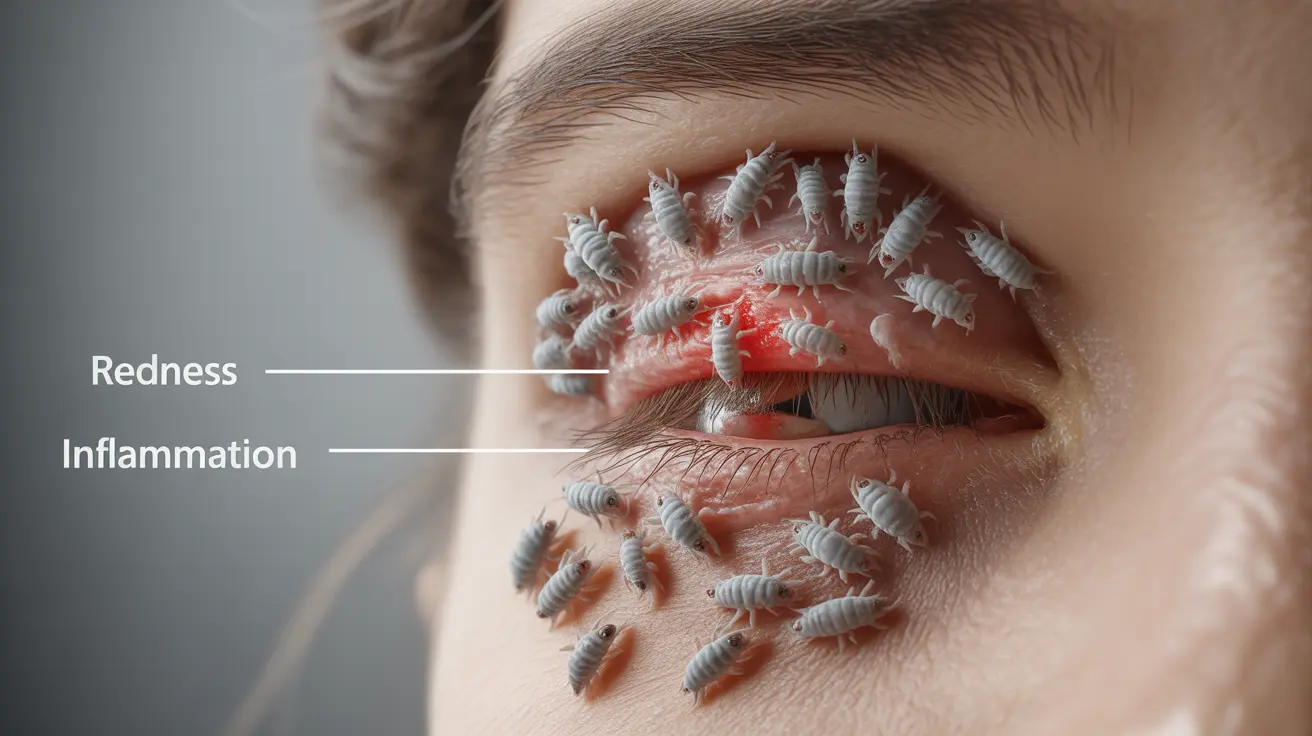
Scabies mites affecting the human eye area present a concerning medical condition that requires prompt attention and proper treatment. While these microscopic parasites typically affect the skin, they can occasionally impact the delicate tissues around and on the eyes, leading to significant discomfort and potential complications if left untreated.
Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for eye-related scabies is crucial for both affected individuals and healthcare providers. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about managing and preventing these troublesome mite infestations.
Understanding Eye Scabies and Its Causes
Eye scabies occurs when Sarcoptes scabiei mites infest the sensitive areas around or on the eyes. These microscopic parasites burrow into the skin, causing intense irritation and various uncomfortable symptoms. While relatively rare compared to general body scabies, eye involvement requires special attention due to the delicate nature of ocular tissues.
Identifying Symptoms of Eye Scabies
Recognition of eye scabies symptoms is crucial for early intervention and successful treatment. Common signs include:
- Intense itching around the eyes, especially at night
- Redness and inflammation of the eyelids
- Crusty or scaly skin around the eye area
- Burning sensation
- Watery eyes
- Small raised bumps or blisters near the eyes
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Healthcare providers diagnose eye scabies through careful examination of symptoms and microscopic identification of mites or their eggs. The process typically involves:
- Detailed visual examination of affected areas
- Skin scraping analysis
- Assessment of symptom patterns
- Evaluation of potential spread to other body areas
Treatment Approaches for Eye Scabies
Medical Treatments
Treatment for eye scabies requires a carefully coordinated approach due to the sensitive nature of the eye area. Common medical interventions include:
- Prescription antiparasitic medications
- Specialized eye-safe topical treatments
- Oral medications when necessary
- Regular follow-up examinations
Additional Care Measures
Supporting treatments and care practices often include:
- Gentle cleansing of the affected area
- Cool compresses to reduce inflammation
- Antihistamines for itch relief
- Protection of the eyes during treatment
Prevention and Control
Preventing the spread of scabies mites requires diligent attention to personal hygiene and environmental control measures:
- Regular washing of bedding and clothing in hot water
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals
- Proper hand hygiene
- Regular cleaning of personal items
- Immediate treatment of all household members if one person is infected
Managing Complications
Potential complications from eye scabies can include:
- Secondary bacterial infections
- Scarring around the eye area
- Chronic inflammation
- Vision problems if left untreated
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of scabies infestation, and how is it diagnosed?
Scabies infestation symptoms include intense itching (especially at night), rash, small burrows in the skin, and red bumps. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and microscopic analysis of skin scrapings to identify mites or their eggs.
How is scabies treated, and what are the most effective treatments?
The most effective treatments for scabies include prescription medications like permethrin cream or oral ivermectin. Treatment must be accompanied by thorough cleaning of clothing and bedding, and all household members should be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfestation.
Can scabies mites affect the eyes, and what are the symptoms if they do?
Yes, scabies mites can affect the eye area, causing symptoms such as intense itching, redness, inflammation of the eyelids, and crusting around the eyes. This requires immediate medical attention due to the sensitive nature of the eye area.
How can I prevent scabies from spreading to others in my household?
Prevent scabies spread by avoiding skin-to-skin contact with infected persons, washing all clothing and bedding in hot water, vacuum living areas thoroughly, and ensuring all household members receive treatment simultaneously if an infection is detected.
What are the common complications of scabies, and how are they managed?
Common complications include secondary bacterial infections, intense itching leading to skin damage, and potential scarring. These are managed through appropriate antibiotic treatment when necessary, proper skin care, and following complete treatment protocols to prevent reinfestation.