Hypertriglyceridemia is a condition characterized by elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood. Understanding its symptoms and implications is crucial for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize the signs and understand the importance of proper medical care for this condition.
What is Hypertriglyceridemia?
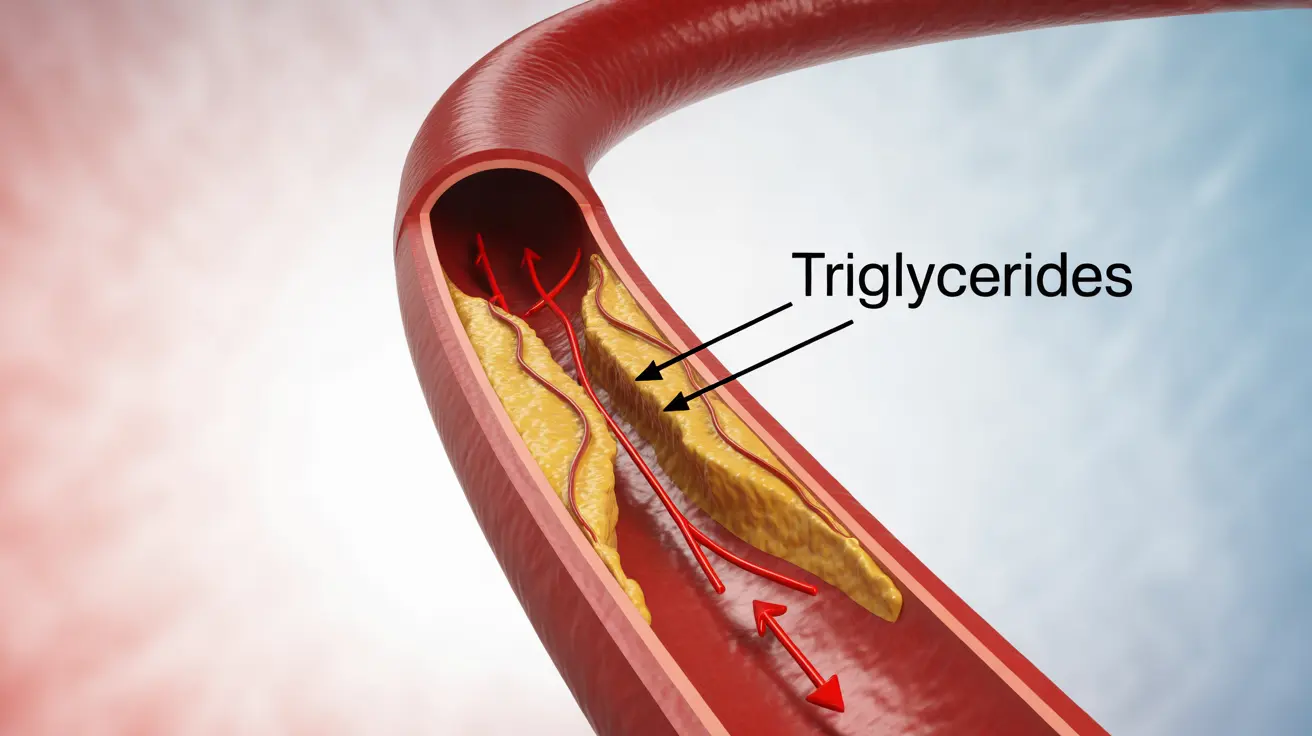
Hypertriglyceridemia occurs when triglyceride levels in the blood exceed normal ranges. While some people inherit this condition (familial hypertriglyceridemia), others may develop it due to lifestyle factors or other medical conditions. Understanding the condition's nature is essential for proper management and prevention of complications.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Many individuals with hypertriglyceridemia may not experience noticeable symptoms, especially in mild cases. However, when triglyceride levels become significantly elevated, several symptoms may appear:
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Fatty deposits under the skin (xanthomas)
- Chronic fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Memory problems
- Shortness of breath
Health Risks and Complications
High triglyceride levels can lead to several serious health complications if left unmanaged:
Pancreatitis Risk
Severely elevated triglycerides can trigger acute pancreatitis, a painful and potentially dangerous inflammation of the pancreas. This condition requires immediate medical attention and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Cardiovascular Complications
Individuals with hypertriglyceridemia face an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The condition can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, potentially leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Diagnosis and Testing
Proper diagnosis of hypertriglyceridemia involves several key steps:
- Comprehensive blood lipid panel
- Physical examination
- Family history assessment
- Evaluation of other risk factors
- Fasting triglyceride level tests
Management Strategies
Managing hypertriglyceridemia often requires a multi-faceted approach:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Following a low-fat diet
- Avoiding refined carbohydrates
Medical Management
Treatment may include prescription medications, particularly when lifestyle changes alone aren't sufficient to control triglyceride levels. Regular monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans are essential for optimal results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of familial hypertriglyceridemia and when do they usually appear?
Common symptoms typically appear in adulthood and may include abdominal pain, fatty deposits under the skin, and fatigue. However, many people may be asymptomatic until triglyceride levels become severely elevated.
How can familial hypertriglyceridemia increase the risk of pancreatitis or heart disease?
Very high triglyceride levels can directly trigger inflammation of the pancreas, leading to pancreatitis. Additionally, elevated triglycerides contribute to the buildup of arterial plaque, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
What role does family history play in diagnosing and managing familial hypertriglyceridemia?
Family history is crucial in diagnosis as the condition often runs in families. A positive family history helps doctors identify at-risk individuals and implement early prevention strategies.
How is familial hypertriglyceridemia diagnosed through blood tests and physical exams?
Diagnosis typically involves fasting blood tests to measure triglyceride levels, comprehensive lipid panels, and physical examinations to check for visible signs like xanthomas. Additional testing may be needed to rule out other conditions.
What lifestyle changes can help manage high triglyceride levels caused by familial hypertriglyceridemia?
Effective lifestyle management includes maintaining a low-fat, low-sugar diet, regular exercise, weight management, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding refined carbohydrates. These changes should be implemented alongside any prescribed medical treatments.