When liver disease affects the body's vital organs, it can significantly impact blood sugar regulation, leading to a dangerous condition called hypoglycemia. Understanding the connection between liver disease and low blood sugar is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike, as it helps in better management and prevention of potentially serious complications.
The liver plays a central role in maintaining stable blood glucose levels, and when liver function is compromised, this delicate balance can be disrupted. This article explores the relationship between liver disease and hypoglycemia, including its causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
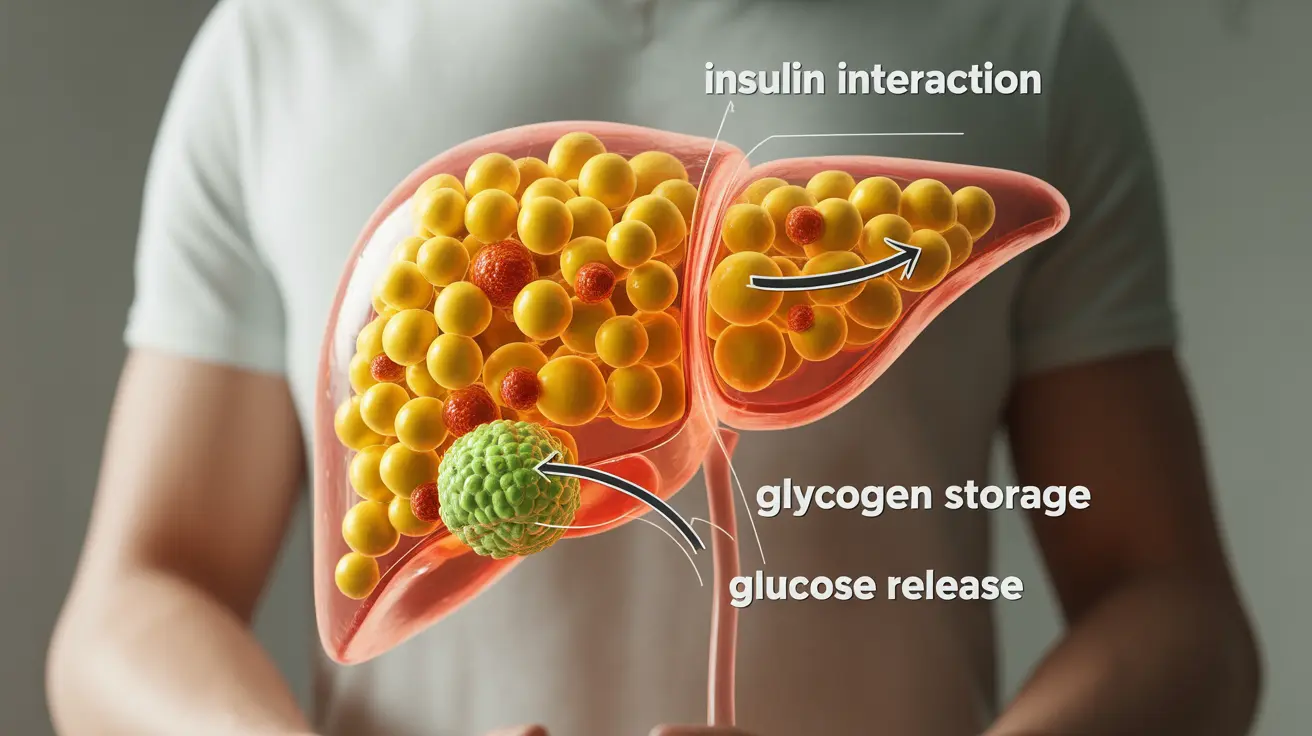
How Liver Disease Affects Blood Sugar Regulation
The liver serves as the body's primary glucose storage facility and regulator. When liver disease occurs, several crucial functions become impaired:
- Glucose storage and release
- Hormone processing
- Insulin metabolism
- Glycogen conversion
These disruptions can lead to unexpected drops in blood sugar levels, particularly in patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis. The liver's reduced ability to store and release glucose when needed makes blood sugar control particularly challenging.
Recognizing Hypoglycemia Symptoms in Liver Disease
People with liver disease may experience distinct hypoglycemic symptoms that require immediate attention:
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating
- Excessive sweating
- Shakiness and tremors
- Heart palpitations
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Anxiety or irritability
These symptoms may be more severe in patients with advanced liver disease, and recognition of early warning signs is crucial for proper management.
Managing Blood Sugar with Liver Disease
Dietary Considerations
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels:
- Regular, small meals throughout the day
- Complex carbohydrates for sustained energy
- Adequate protein intake as recommended by healthcare providers
- Evening snacks to prevent overnight hypoglycemia
Medication Management
Patients with both liver disease and diabetes require careful medication management:
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels
- Adjustment of diabetes medications when necessary
- Consultation with healthcare providers for personalized treatment plans
Prevention Strategies
Several preventive measures can help reduce the risk of hypoglycemic episodes:
- Carrying quick-acting glucose sources
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- Maintaining consistent meal times
- Avoiding alcohol consumption
- Regular communication with healthcare providers
Frequently Asked Questions
How does liver cirrhosis cause hypoglycemia and affect blood sugar regulation?
Liver cirrhosis impairs the organ's ability to store and release glucose. When the liver is damaged, it cannot effectively maintain blood sugar balance through glycogen storage and conversion, leading to unexpected drops in blood glucose levels.
What are the common symptoms of hypoglycemia in people with liver disease?
Common symptoms include confusion, sweating, tremors, fatigue, anxiety, and blurred vision. These symptoms may be more pronounced in liver disease patients due to their body's compromised ability to regulate blood sugar.
How can patients with cirrhosis and diabetes manage the risk of low blood sugar?
Management involves regular blood sugar monitoring, careful medication adjustment, consistent meal timing, and working closely with healthcare providers to develop an appropriate treatment plan that accounts for both conditions.
Why does acute liver failure increase the risk of hypoglycemia?
Acute liver failure severely compromises the liver's ability to maintain glucose homeostasis, process hormones, and store glycogen, leading to an increased risk of dangerous blood sugar drops.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent hypoglycemia in people with liver disease?
Key lifestyle changes include eating regular, small meals throughout the day, avoiding alcohol, carrying glucose sources for emergencies, maintaining consistent meal times, and regular blood sugar monitoring.