Iatrogenic Cushing syndrome is a serious medical condition that occurs as a side effect of prolonged glucocorticoid medication use. Unlike naturally occurring Cushing syndrome, which results from the body's overproduction of cortisol, the iatrogenic form develops specifically from medical treatment. Understanding this condition is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients using corticosteroid medications.
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and management of iatrogenic Cushing syndrome, helping you recognize early warning signs and understand available treatment options.
What Causes Iatrogenic Cushing Syndrome?
Iatrogenic Cushing syndrome primarily develops from extended exposure to glucocorticoid medications, which are commonly prescribed to treat various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. These medications include:
- Prednisone
- Dexamethasone
- Hydrocortisone
- Betamethasone
- Triamcinolone
The condition can develop through various administration routes, including oral medications, injectable steroids, inhaled corticosteroids, and even topical preparations in some cases. The risk increases with higher doses and longer duration of use.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of iatrogenic Cushing syndrome typically develop gradually and can affect multiple body systems. Common signs include:
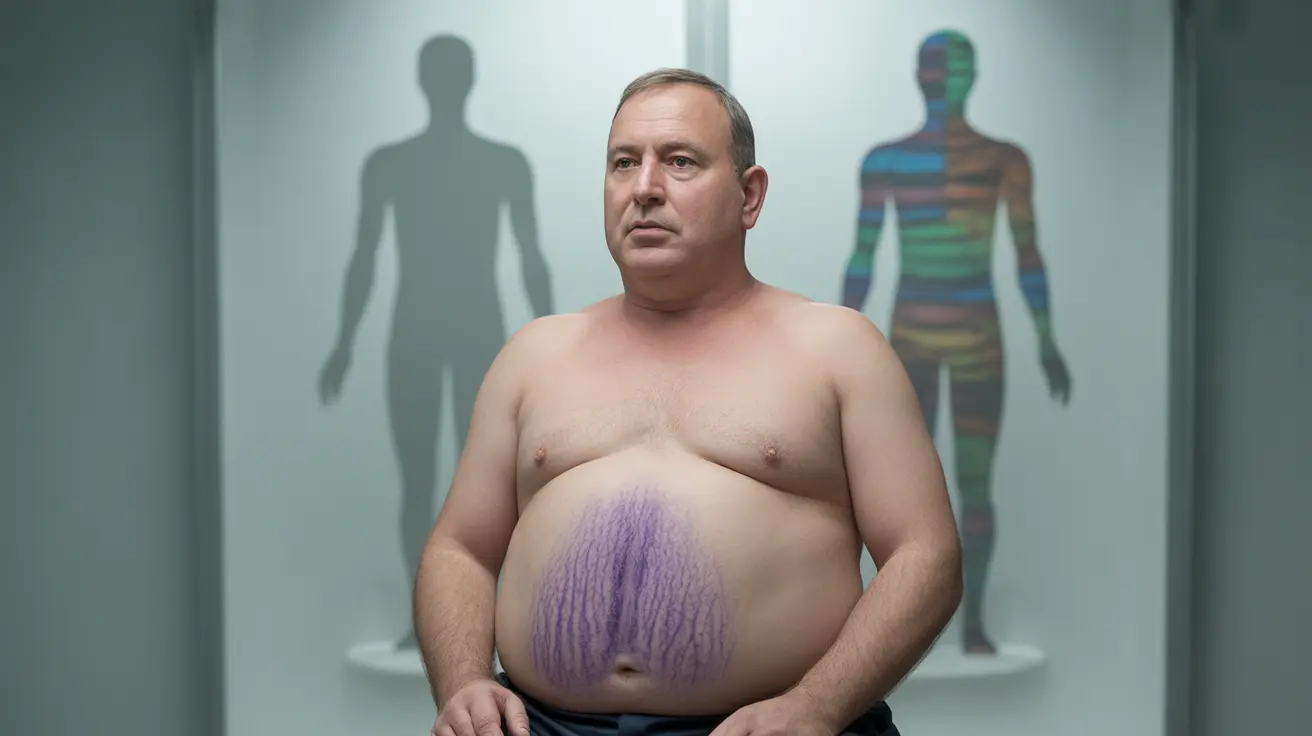
- Weight gain, particularly in the face and trunk
- Development of a "buffalo hump" (fat deposit between the shoulders)
- Rounded "moon face"
- Purple stretch marks
- Thin, fragile skin that bruises easily
- Muscle weakness
- Mood changes and irritability
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Elevated blood pressure
Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for proper management and prevention of long-term complications.
Treatment Approaches and Recovery
The primary treatment for iatrogenic Cushing syndrome involves carefully managing the underlying glucocorticoid therapy. This typically requires:
Medication Management
Healthcare providers must balance treating the original condition while minimizing Cushing syndrome symptoms. This might involve:
- Gradual dose reduction when possible
- Switching to alternative medications
- Using different administration routes
- Implementing alternate-day dosing schedules
Supporting Treatments
Additional measures may include:
- Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar
- Bone density screenings
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation
- Regular exercise within personal limitations
- Dietary modifications to manage weight gain
Prevention Strategies
Preventing iatrogenic Cushing syndrome requires careful medication management and monitoring. Key preventive measures include:
- Using the lowest effective dose of glucocorticoids
- Regular medical check-ups during treatment
- Monitoring for early signs and symptoms
- Following prescribed dosing schedules exactly
- Never stopping medication abruptly without medical supervision
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes iatrogenic Cushing syndrome and which medications are involved? Iatrogenic Cushing syndrome is caused by prolonged exposure to glucocorticoid medications, including prednisone, dexamethasone, and other corticosteroids used to treat various medical conditions. These medications can be administered orally, through injection, or even topically in some cases.
What are the common symptoms of iatrogenic Cushing syndrome to recognize early? Early symptoms include weight gain (especially in the face and trunk), rounded "moon face," buffalo hump formation, purple stretch marks, thin skin, easy bruising, muscle weakness, mood changes, and elevated blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
How is iatrogenic Cushing syndrome treated and can it be reversed? Yes, iatrogenic Cushing syndrome can be reversed by carefully adjusting the glucocorticoid medication dosage under medical supervision. Treatment involves gradually reducing the medication dose while managing the underlying condition that required steroid treatment initially.
How can iatrogenic Cushing syndrome be prevented when using glucocorticoid medications? Prevention strategies include using the lowest effective dose possible, regular medical monitoring, following prescribed dosing schedules exactly, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers about any developing symptoms.
What are the risks of stopping glucocorticoid treatment too quickly in iatrogenic Cushing syndrome? Abruptly stopping glucocorticoid treatment can lead to adrenal crisis, a potentially life-threatening condition. Other risks include return of the underlying condition being treated, withdrawal symptoms, and adrenal insufficiency. Any dose reduction must be gradual and supervised by a healthcare provider.