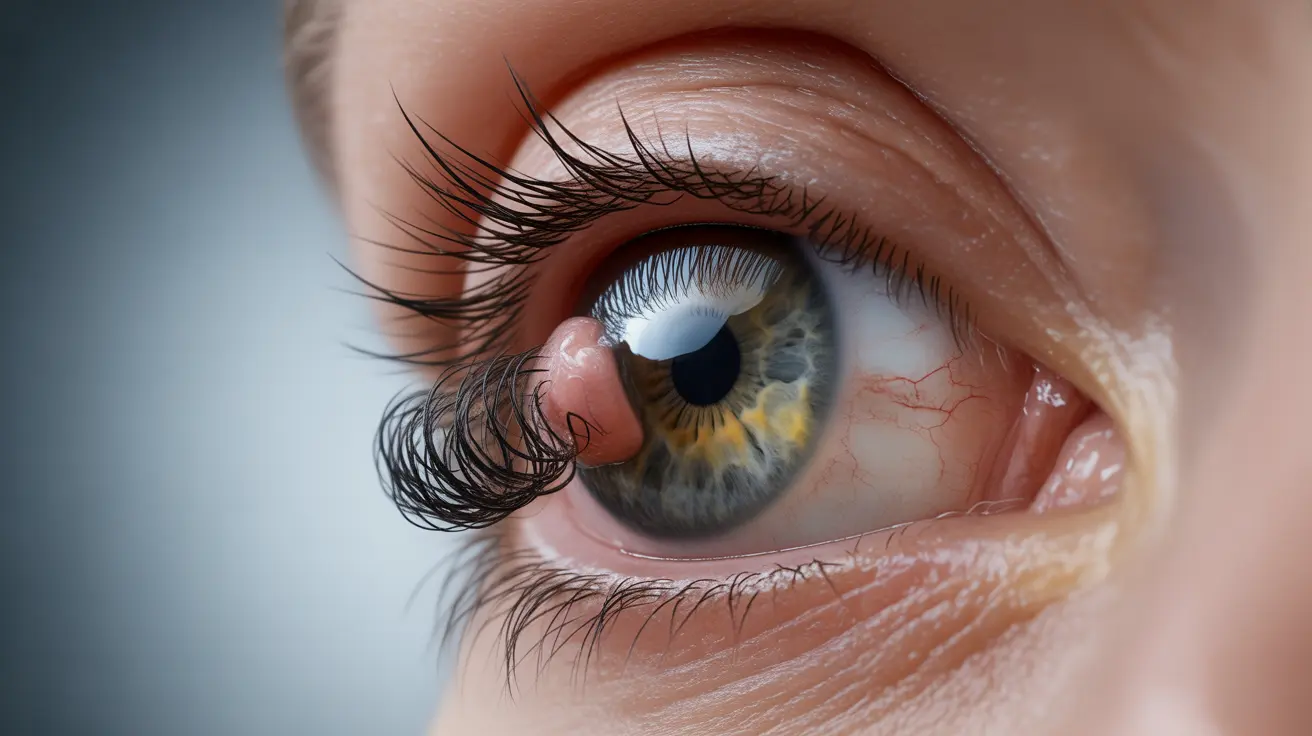
An ingrown eyelash occurs when an eyelash grows abnormally, turning inward toward the eye instead of outward. This common condition can cause significant discomfort and potentially affect eye health if not properly addressed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining optimal eye health and preventing complications.
What Is an Ingrown Eyelash?
An ingrown eyelash, also known as trichiasis, develops when an eyelash grows in an irregular direction, often curling back toward the eye surface. This condition can affect anyone, though certain factors may increase your risk of developing this uncomfortable eye condition.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of ingrown eyelashes:
- Trauma to the eyelid
- Previous eye surgeries
- Inflammatory conditions
- Genetic predisposition
- Age-related changes in eyelid structure
- Scarring from infections or injuries
Recognizing the Symptoms
Identifying an ingrown eyelash early can help prevent complications and ensure prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp or scratching sensation in the eye
- Redness and irritation
- Excessive tearing
- Light sensitivity
- Foreign body sensation
- Eye inflammation
Treatment Options and Solutions
Professional Medical Treatments
Several professional treatment options are available for managing ingrown eyelashes:
- Epilation (manual removal by a healthcare provider)
- Electrolysis for permanent hair removal
- Cryotherapy
- Laser treatment
- Surgical correction in severe cases
At-Home Care Methods
While professional treatment is often necessary, some self-care measures can help manage discomfort:
- Gentle warm compresses
- Keeping the eye area clean
- Avoiding eye rubbing
- Using prescribed eye drops or ointments
- Regular eyelid hygiene
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing ingrown eyelashes:
- Maintaining good eye hygiene
- Treating underlying conditions promptly
- Avoiding harsh eye makeup products
- Regular check-ups with an eye care professional
- Protecting eyes from trauma
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes an ingrown eyelash and how can I identify its symptoms? An ingrown eyelash is typically caused by trauma, inflammatory conditions, or genetic factors. Key symptoms include a sharp sensation in the eye, redness, excessive tearing, and visible misdirection of the eyelash growth.
How is an ingrown eyelash treated and what are the options for permanent removal? Treatment options range from temporary solutions like manual removal to permanent options such as electrolysis or laser treatment. A healthcare provider can recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the severity and underlying cause.
Can an ingrown eyelash damage my eye or affect my vision if left untreated? Yes, untreated ingrown eyelashes can potentially scratch the cornea, leading to infections, scarring, and vision problems. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent these complications.
Are there home remedies that can relieve discomfort from an ingrown eyelash? While home remedies like warm compresses and gentle cleaning can provide temporary relief, they should not replace professional medical treatment. These measures can help manage symptoms while awaiting professional care.
How can underlying conditions like blepharitis or eyelid inflammation contribute to ingrown eyelashes? Conditions like blepharitis and eyelid inflammation can alter the normal growth pattern of eyelashes and cause scarring, increasing the risk of ingrown eyelashes. Managing these underlying conditions is crucial for preventing recurring problems.
Remember, while ingrown eyelashes are generally treatable, it's important to seek professional medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if you experience persistent symptoms or discomfort.