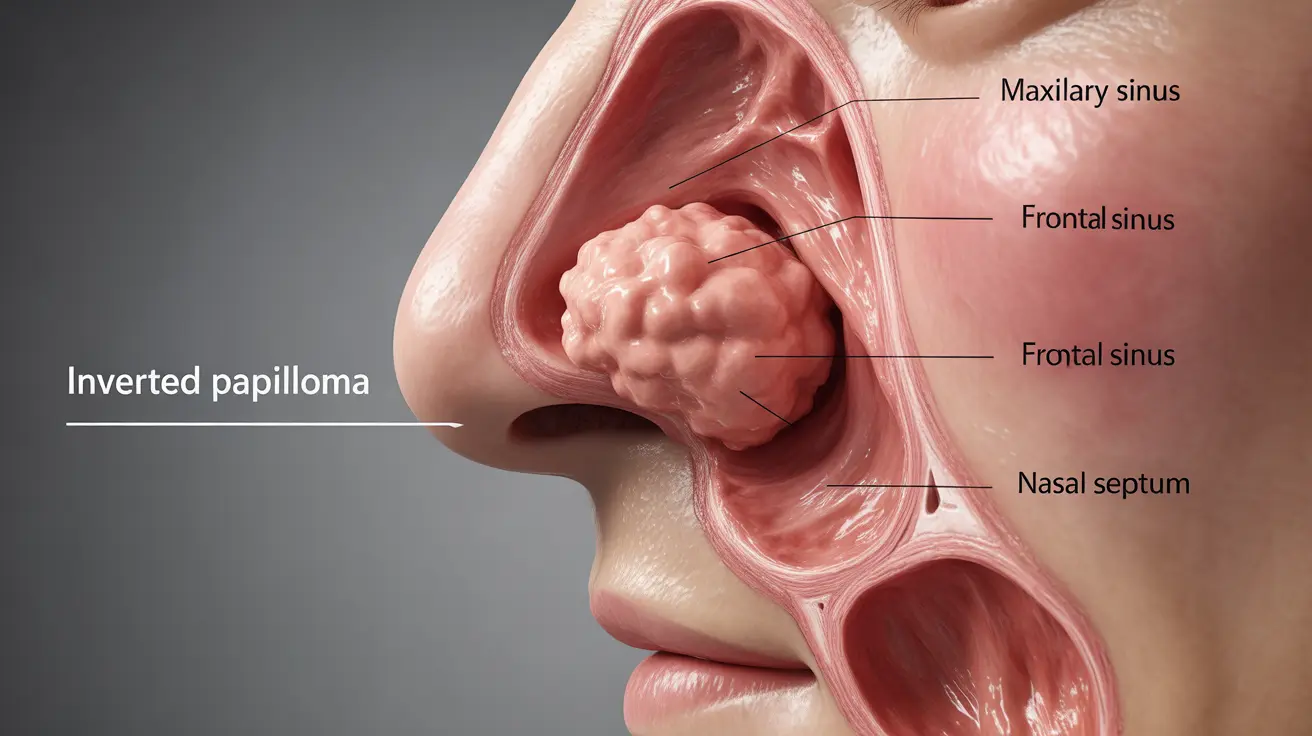
An inverted papilloma is a rare but significant type of benign tumor that typically develops in the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. While these growths are generally non-cancerous, they require careful medical attention due to their tendency to grow locally and potentially cause complications. Understanding the nature of this condition, its symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for anyone affected by or concerned about inverted papilloma.
This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of inverted papilloma, including its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment approaches, and long-term management strategies. We'll also address important concerns about recurrence and prevention methods.
Signs and Symptoms of Inverted Papilloma
Inverted papilloma typically presents with several characteristic symptoms that may develop gradually over time. The most common signs include:
- Persistent nasal obstruction (usually on one side)
- Recurring nosebleeds
- Changes in sense of smell
- Facial pressure or pain
- Clear or mucoid nasal drainage
- Chronic sinusitis symptoms
These symptoms can significantly impact quality of life and should prompt medical evaluation, especially if they persist or worsen over time.
Diagnostic Process and Cancer Screening
Accurate diagnosis of inverted papilloma involves multiple steps and specialized medical procedures. Healthcare providers typically employ:
- Nasal endoscopy for direct visualization
- CT scans to determine the extent of the growth
- MRI imaging in some cases
- Biopsy for definitive diagnosis and cancer screening
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial because approximately 5-15% of inverted papillomas can be associated with malignant changes. Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential parts of the management strategy.
Treatment Approaches and Surgical Options
The primary treatment for inverted papilloma is surgical removal. Modern surgical techniques include:
Endoscopic Surgery
This minimally invasive approach is now the gold standard for most cases. It allows surgeons to remove the tumor through the nostrils, avoiding external incisions and reducing recovery time.
Traditional Open Surgery
In some cases, particularly for larger tumors or those in difficult-to-reach locations, traditional open surgery may be necessary. This approach provides better access to certain areas but involves a longer recovery period.
Post-Treatment Monitoring and Recurrence Prevention
Following treatment, patients require regular follow-up care to monitor for potential recurrence. This typically includes:
- Regular endoscopic examinations
- Periodic imaging studies
- Long-term follow-up appointments
- Prompt evaluation of any new symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions
**What are the common signs and symptoms of an inverted papilloma in the nose or sinuses?** The most common symptoms include unilateral nasal obstruction, nosebleeds, changes in smell sensation, facial pressure, and nasal drainage. These symptoms often develop gradually and may be initially mistaken for chronic sinusitis.
**How do doctors diagnose inverted papilloma and confirm if it is cancerous?** Doctors use a combination of nasal endoscopy, imaging studies (CT and MRI), and tissue biopsy for diagnosis. The biopsy is crucial for confirming the diagnosis and ruling out malignancy.
**What are the treatment options for inverted papilloma and how effective is surgery?** Surgery is the primary treatment option, with endoscopic approaches being most common. When performed by experienced surgeons, the success rate is high, though the specific approach depends on the tumor's location and extent.
**Can inverted papilloma come back after surgery, and how is recurrence monitored?** Yes, inverted papillomas can recur after surgery, with recurrence rates varying from 5-30%. Regular follow-up with endoscopic examinations and imaging studies is essential for early detection of any recurrence.
**What causes inverted papilloma and are there ways to reduce the risk of developing it?** The exact cause remains unclear, though some research suggests links to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. While there are no proven prevention methods, maintaining good nasal hygiene and avoiding known irritants may be beneficial.
Understanding and managing inverted papilloma requires a comprehensive approach involving expert medical care, appropriate surgical intervention, and vigilant follow-up. While the condition can be challenging to treat, modern medical approaches offer excellent outcomes for most patients when diagnosed and treated promptly.