Many people wonder about the relationship between asthma and the immune system, particularly whether asthma should be classified as an autoimmune disease. While both conditions involve immune system responses, understanding the distinct characteristics of asthma's immune mechanism is crucial for proper treatment and management.
This comprehensive guide explores the complex relationship between asthma and immune system function, clarifying the key differences between asthma and autoimmune conditions while examining how these health challenges interact.
The Nature of Asthma's Immune Response
Asthma is primarily characterized as a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, involving a complex immune response that differs significantly from autoimmune diseases. In asthma, the immune system reacts strongly to environmental triggers, such as allergens, irritants, or viral infections, but it doesn't typically attack healthy tissue as seen in autoimmune conditions.
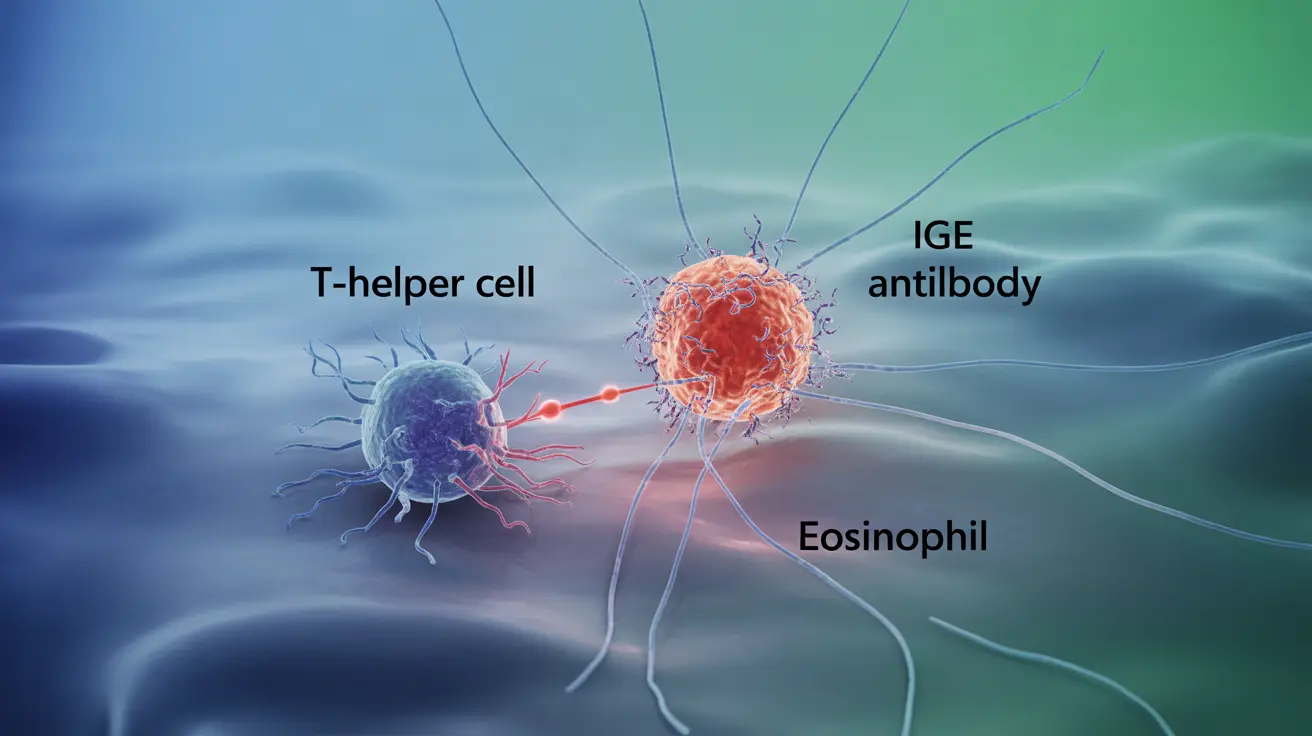
The immune response in asthma involves several key components:
- T-helper cells
- Inflammatory mediators
- IgE antibodies
- Eosinophils and other immune cells
How Asthma Differs from Autoimmune Diseases
Unlike autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy body tissues, asthma involves an overreaction to external triggers. This distinction is crucial for understanding both conditions:
Asthma's Immune Response
In asthma, the immune system responds to environmental triggers by:
- Releasing inflammatory chemicals
- Causing bronchial tube constriction
- Increasing mucus production
- Triggering airway inflammation
Autoimmune Disease Response
In contrast, autoimmune diseases involve:
- Direct attacks on healthy body tissues
- Chronic systemic inflammation
- Production of specific autoantibodies
- Multiple organ system involvement
The Connection Between Asthma and Autoimmune Conditions
While asthma isn't classified as an autoimmune disease, research suggests interesting connections between these conditions. Some individuals with asthma may have an increased risk of developing certain autoimmune disorders, though the exact relationship is still being studied.
Impact of Immune System Health on Asthma
The overall health of your immune system plays a crucial role in asthma management and severity. Factors that can influence this relationship include:
- Viral infections
- Stress levels
- Nutritional status
- Environmental exposures
- Sleep quality
Frequently Asked Questions
Is asthma considered an autoimmune disease or an immune system dysfunction?
Asthma is considered an immune system dysfunction rather than an autoimmune disease. It involves an overreaction to environmental triggers rather than an attack on healthy body tissues, which characterizes autoimmune conditions.
How does asthma's immune response differ from that of autoimmune diseases?
In asthma, the immune system responds excessively to external triggers like allergens or irritants. Autoimmune diseases, however, involve the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy body tissues. This fundamental difference affects how each condition is treated and managed.
Can autoimmune processes contribute to certain types of asthma symptoms?
While autoimmune processes don't directly cause asthma, some research suggests that inflammatory mechanisms similar to those in autoimmune conditions may contribute to severe or difficult-to-treat asthma in certain individuals.
Does having asthma increase the risk of developing autoimmune diseases?
Some studies indicate that people with asthma may have a slightly increased risk of developing certain autoimmune conditions, though the relationship is complex and requires further research to fully understand.
How do immune system weaknesses or infections affect asthma severity and management?
Immune system weaknesses and infections can significantly impact asthma severity and control. Viral infections, in particular, can trigger asthma exacerbations and make symptoms more difficult to manage, highlighting the importance of maintaining overall immune health.