Diabetes is a complex metabolic condition that significantly impacts the endocrine system, a network of glands that produce and regulate hormones throughout the body. Understanding diabetes as an endocrine disorder helps explain its widespread effects on overall health and provides insights into its management and treatment approaches.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the relationship between diabetes and the endocrine system, examining how this condition affects hormone production, regulation, and metabolic processes throughout the body.
The Endocrine System and Diabetes Connection
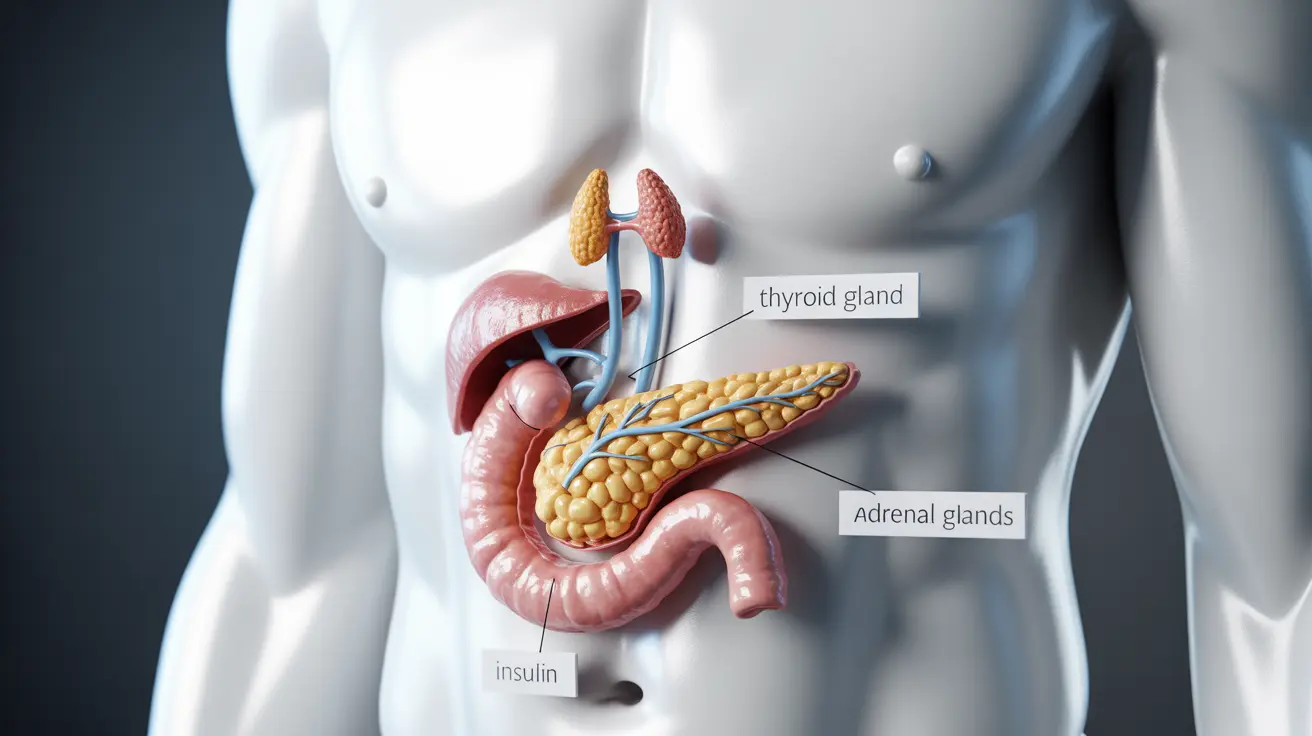
Diabetes is classified as an endocrine disorder because it directly involves the pancreas, a crucial endocrine gland responsible for producing insulin and other important hormones. When the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin or when the body becomes resistant to insulin's effects, diabetes develops, disrupting the delicate balance of hormone regulation.
The endocrine system's role in diabetes extends beyond just insulin production, affecting multiple hormone pathways and metabolic processes throughout the body.
Types of Diabetes and Their Endocrine Impact
Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune response creates a severe endocrine dysfunction, as the body can no longer produce the insulin necessary for glucose metabolism.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes involves both insulin resistance and decreased insulin production. This form of diabetes significantly impacts the endocrine system through various hormone pathways, affecting not only blood glucose regulation but also fat metabolism and other metabolic processes.
Broader Effects on the Endocrine System
Diabetes can influence multiple endocrine glands and their functions:
- Thyroid gland function
- Adrenal hormone production
- Growth hormone regulation
- Reproductive hormone balance
These interconnected effects demonstrate why diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach to endocrine health.
Managing Diabetes as an Endocrine Disorder
Effective diabetes management involves understanding and addressing its impact on the entire endocrine system. Treatment approaches typically include:
- Blood glucose monitoring and control
- Hormone replacement therapy when necessary
- Regular endocrine system function assessment
- Lifestyle modifications to support overall hormonal health
- Medications that target specific endocrine pathways
Frequently Asked Questions
Is diabetes classified as an endocrine disorder and why?
Yes, diabetes is classified as an endocrine disorder because it primarily involves dysfunction in the pancreas, an endocrine gland. The condition directly affects hormone production and regulation, particularly insulin, which is crucial for blood glucose control.
How does diabetes affect the endocrine system, especially insulin production and hormone balance?
Diabetes impacts the endocrine system by disrupting insulin production and/or effectiveness, which in turn affects other hormone systems. This creates a cascade effect throughout the body's endocrine network, influencing metabolism, growth, and various other hormonal processes.
What are the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes in relation to endocrine dysfunction?
Type 1 diabetes involves complete failure of insulin production due to autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells. Type 2 diabetes involves both insulin resistance and reduced insulin production, affecting the endocrine system through multiple pathways.
Can diabetes lead to problems with other endocrine glands like the thyroid or pituitary?
Yes, diabetes can affect other endocrine glands. People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing thyroid disorders, and the condition can impact pituitary function, adrenal hormone production, and other endocrine processes.
How does managing diabetes impact overall hormone regulation and metabolism?
Managing diabetes effectively helps maintain balance in the entire endocrine system. Proper blood glucose control, along with lifestyle modifications and appropriate medications, supports overall hormone regulation and metabolic health.