Nutella, the beloved chocolate-hazelnut spread that has become a breakfast staple in many households, has sparked ongoing debates about its nutritional value and health implications. As consumers become increasingly health-conscious, it's important to understand what this popular spread really contains and how it affects our wellbeing.
In this comprehensive analysis, we'll explore the nutritional profile of Nutella, examine its ingredients, and discuss whether it deserves a place in a balanced diet. We'll also look at healthier alternatives for those seeking better options.
Understanding Nutella's Nutritional Profile
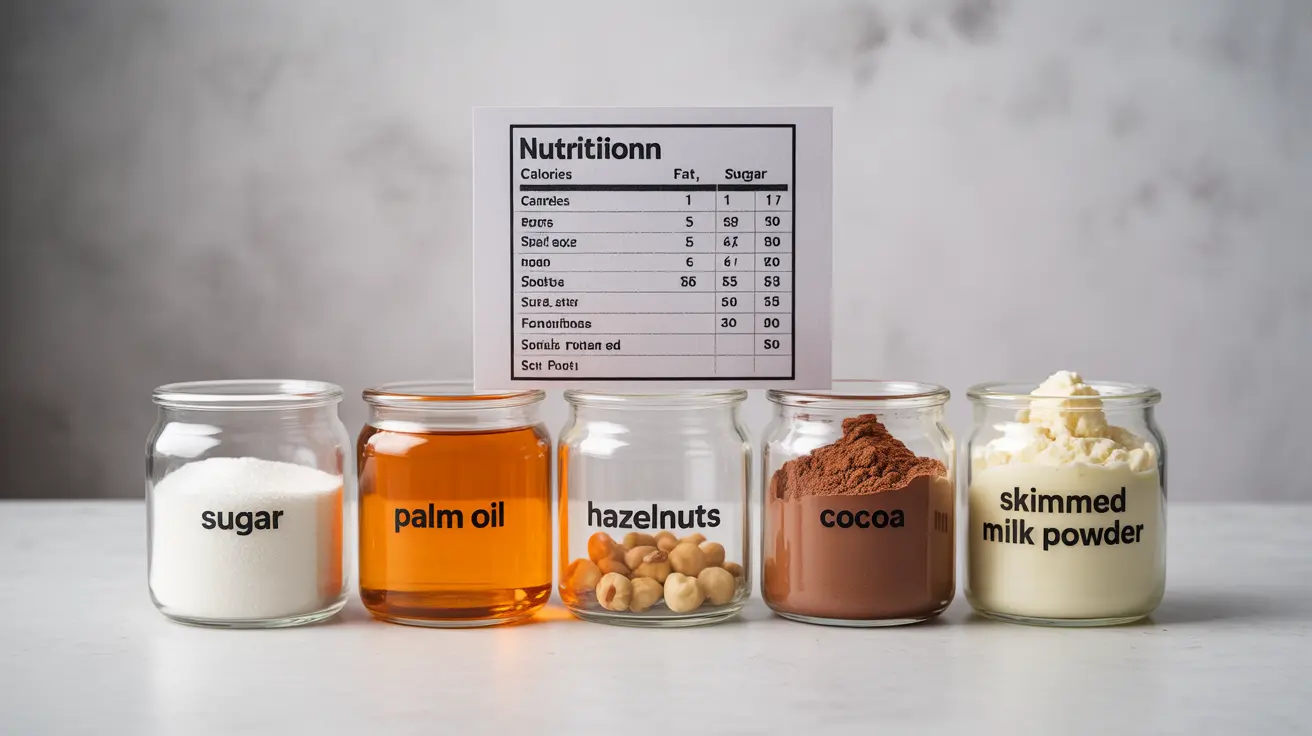
Nutella's primary ingredients include sugar, palm oil, hazelnuts, cocoa, and skimmed milk powder. While hazelnuts and cocoa do offer some nutritional benefits, the high sugar and saturated fat content raises significant concerns:
- Two tablespoons (37g) contain approximately:
- 200 calories
- 21 grams of sugar
- 12 grams of fat
- 2 grams of protein
- Less than 1 gram of fiber
Sugar Content and Health Implications
The most concerning aspect of Nutella is its high sugar content. Sugar is listed as the first ingredient, meaning it's the most abundant component by weight. This high sugar concentration can lead to several health issues:
- Blood sugar spikes
- Increased risk of tooth decay
- Potential weight gain
- Higher risk of type 2 diabetes
- Elevated inflammation markers
The Palm Oil Controversy
Nutella's use of palm oil has raised both health and environmental concerns. While palm oil helps create the spread's smooth texture and extends its shelf life, it comes with several drawbacks:
- High in saturated fats
- Potential environmental impact due to deforestation
- Sustainability concerns
- Processing methods may produce harmful compounds
Hazelnuts and Cocoa: The Beneficial Ingredients
Despite its nutritional drawbacks, Nutella does contain some beneficial ingredients:
- Hazelnuts provide:
- Healthy fats
- Vitamin E
- Fiber
- Protein
- Cocoa offers:
- Antioxidants
- Flavonoids
- Potential mood-boosting properties
Healthier Alternatives to Consider
For those looking to enjoy similar flavors with better nutritional profiles, consider these alternatives:
- Natural nut butters without added sugars
- Homemade chocolate-hazelnut spreads
- Pure hazelnut butter with a touch of cocoa
- Almond butter with cacao
- Sugar-free chocolate spreads
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Nutella a healthy option for breakfast or as a snack, and what are its nutritional drawbacks?
Nutella should not be considered a healthy breakfast or snack option due to its high sugar and saturated fat content. The primary nutritional drawbacks include excessive sugar (21g per serving), significant calories (200 per serving), and high saturated fat content from palm oil.
How does the high sugar content in Nutella affect overall health, especially for children?
The high sugar content in Nutella can significantly impact children's health by contributing to tooth decay, weight gain, and potential blood sugar regulation issues. It may also establish unhealthy eating patterns and preferences for overly sweet foods.
What are some healthier alternatives to Nutella that are lower in sugar and saturated fat?
Healthier alternatives include natural nut butters without added sugars, homemade chocolate-hazelnut spreads with controlled ingredients, or pure hazelnut butter mixed with unsweetened cocoa powder. These options provide similar flavors with better nutritional profiles.
Is it safe to consume Nutella regularly, or should it be treated as a treat due to its palm oil and sugar content?
Nutella should be treated as an occasional treat rather than a regular part of daily nutrition. Its high sugar and saturated fat content make it unsuitable for regular consumption, especially for those monitoring their sugar intake or cardiovascular health.
What are the potential environmental and health impacts of consuming Nutella due to its use of palm oil?
The use of palm oil in Nutella raises both health and environmental concerns. From a health perspective, palm oil is high in saturated fats, which may contribute to cardiovascular issues. Environmentally, palm oil production has been linked to deforestation, habitat destruction, and reduced biodiversity in tropical regions.