Have you ever experienced a clicking or popping sound when opening your mouth? This phenomenon, known as jaw cracking, is a common occurrence that can range from harmless to potentially concerning. Understanding the causes, treatments, and warning signs of jaw cracking can help you maintain optimal oral health and know when to seek professional help.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various aspects of jaw cracking, including its potential causes, management strategies, and associated conditions. Whether you're dealing with occasional jaw popping or more persistent symptoms, this article will provide valuable insights to help you navigate this often perplexing issue.
Common Causes of Jaw Cracking
Jaw cracking or popping sounds can occur due to several reasons, ranging from benign to more serious conditions. Understanding these causes is the first step in addressing the issue:
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMD)
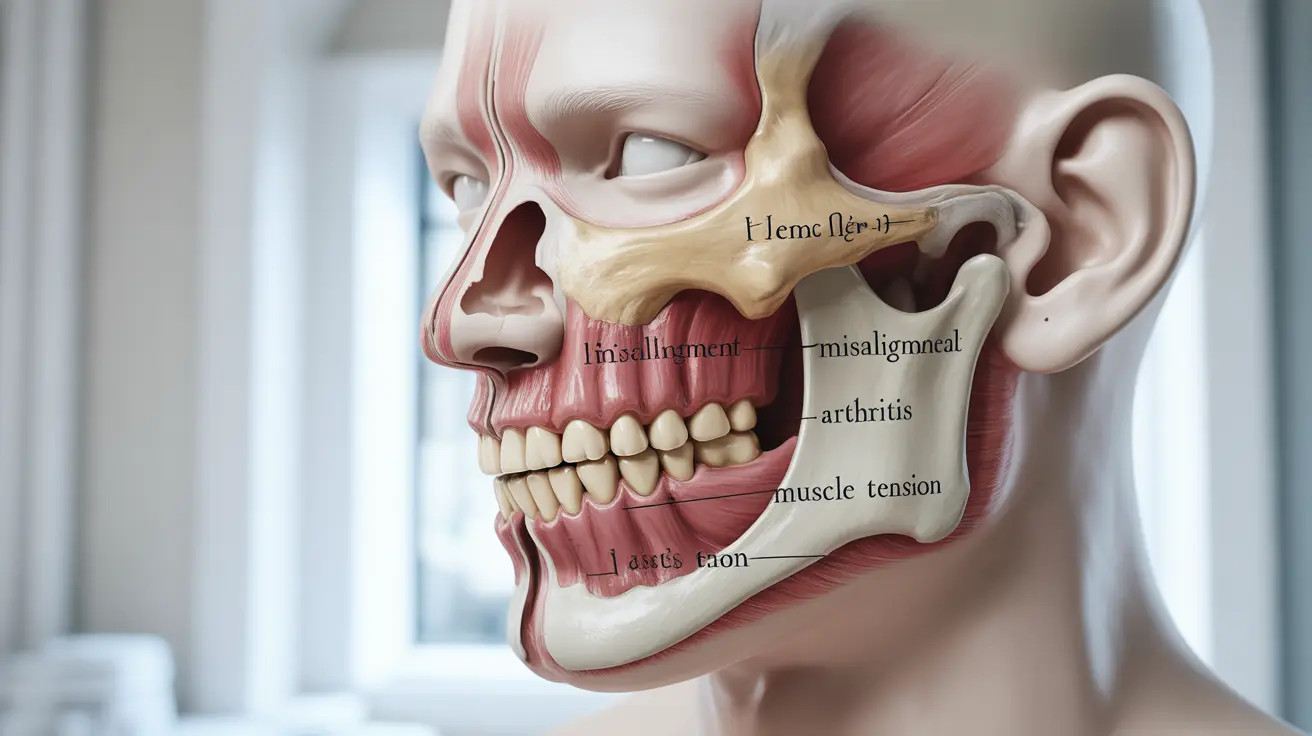
One of the most common causes of jaw cracking is temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD). This condition affects the joint that connects your jawbone to your skull, known as the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). TMD can result from various factors, including:
- Misalignment of the jaw
- Teeth grinding (bruxism)
- Arthritis in the joint
- Stress-induced muscle tension
When TMD is present, the jaw may make clicking or popping sounds as it moves, often accompanied by pain or discomfort.
Normal Joint Sounds
It's important to note that not all jaw cracking sounds are cause for concern. Some people may experience occasional popping or clicking without any pain or functional issues. These sounds can be a result of:
- Gas bubbles in the joint fluid
- Minor misalignments that don't cause discomfort
- Natural variations in joint structure
Muscle Tension and Overuse
Excessive jaw muscle tension, often caused by stress or habitual clenching, can lead to jaw cracking. This tension can affect the smooth movement of the jaw, resulting in audible sounds during opening and closing.
Managing and Treating Jaw Cracking
If you're experiencing persistent jaw cracking, especially if accompanied by pain or limited jaw movement, there are several management and treatment options available:
Conservative Treatments
For many cases of jaw cracking, especially those related to TMD, conservative treatments can be effective:
- Applying hot or cold packs to the jaw area
- Practicing gentle jaw exercises and stretches
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers
- Avoiding hard or chewy foods that strain the jaw
Professional Interventions
For more severe or persistent cases, professional treatments may be necessary:
- Custom-fitted night guards to prevent teeth grinding
- Physical therapy to improve jaw mobility and strength
- Orthodontic treatments to correct bite issues
- In rare cases, surgical intervention for severe TMJ problems
Underlying Conditions and Associated Symptoms
While jaw cracking is often benign, it can sometimes be a sign of underlying conditions such as arthritis. When jaw cracking is associated with a more serious issue, you may notice additional symptoms:
- Persistent pain in the jaw, face, or neck
- Difficulty opening or closing the mouth fully
- Swelling around the jaw area
- Headaches or earaches
- Changes in how your upper and lower teeth fit together
If you experience these symptoms along with jaw cracking, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Jaw Cracking
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can help prevent or reduce jaw cracking:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or deep breathing
- Avoid excessive gum chewing or nail biting
- Maintain good posture to reduce tension in the neck and jaw
- Be mindful of jaw clenching during the day and try to relax your facial muscles
- Use proper ergonomics when working at a desk or using electronic devices
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional jaw cracking without pain is usually not a cause for concern, certain symptoms warrant professional evaluation:
- Persistent pain or tenderness in the jaw
- Difficulty opening or closing your mouth fully
- Jaw cracking accompanied by headaches or ear pain
- Changes in your bite or the way your teeth fit together
- Any sudden change in the frequency or intensity of jaw cracking
If you experience these symptoms, consult a dentist or oral surgeon for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common causes of jaw cracking or popping sounds?
Common causes of jaw cracking include temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD), normal joint sounds due to gas bubbles or minor misalignments, muscle tension, and overuse of the jaw. In some cases, it can also be related to arthritis or structural issues in the jaw joint.
- How can I manage or treat temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD) to alleviate symptoms like jaw stiffness and pain?
TMD can be managed through a combination of conservative treatments and lifestyle changes. These may include applying hot or cold packs, practicing jaw exercises, using over-the-counter pain relievers, avoiding hard foods, and using a custom-fitted night guard. In more severe cases, physical therapy or orthodontic treatments may be recommended.
- Can jaw cracking be a sign of an underlying condition like arthritis, and if so, what are the typical symptoms?
Yes, jaw cracking can sometimes indicate underlying conditions like arthritis. Typical symptoms may include persistent pain in the jaw, face, or neck, difficulty opening or closing the mouth fully, swelling around the jaw area, headaches, and changes in bite alignment. If you experience these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare professional.
- What are some lifestyle changes or habits I can avoid to prevent jaw popping and clicking?
To prevent jaw popping and clicking, try to reduce stress through relaxation techniques, avoid excessive gum chewing or nail biting, maintain good posture, be mindful of jaw clenching, and use proper ergonomics when working. Additionally, practicing gentle jaw exercises and avoiding hard or chewy foods can help reduce strain on the jaw joint.
- How can I differentiate between normal jaw sounds and symptoms that require medical attention?
Normal jaw sounds are typically occasional and not accompanied by pain or limited jaw movement. Symptoms that require medical attention include persistent pain or tenderness in the jaw, difficulty opening or closing your mouth fully, jaw cracking accompanied by headaches or ear pain, changes in your bite, or any sudden change in the frequency or intensity of jaw cracking. If you're unsure, it's best to consult a healthcare professional for an evaluation.