Jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic surgery, is a specialized surgical procedure that corrects irregularities of the jawbones and realigns the jaws and teeth. This transformative procedure can significantly improve a patient's ability to speak, breathe, and eat while enhancing facial appearance and overall quality of life.
Whether you're considering jaw surgery for functional improvements or have been recommended this procedure by your healthcare provider, understanding the process, recovery, and expected outcomes is crucial for making an informed decision about your treatment.
Types of Jaw Surgery
Different jaw surgery procedures address specific skeletal and dental irregularities:
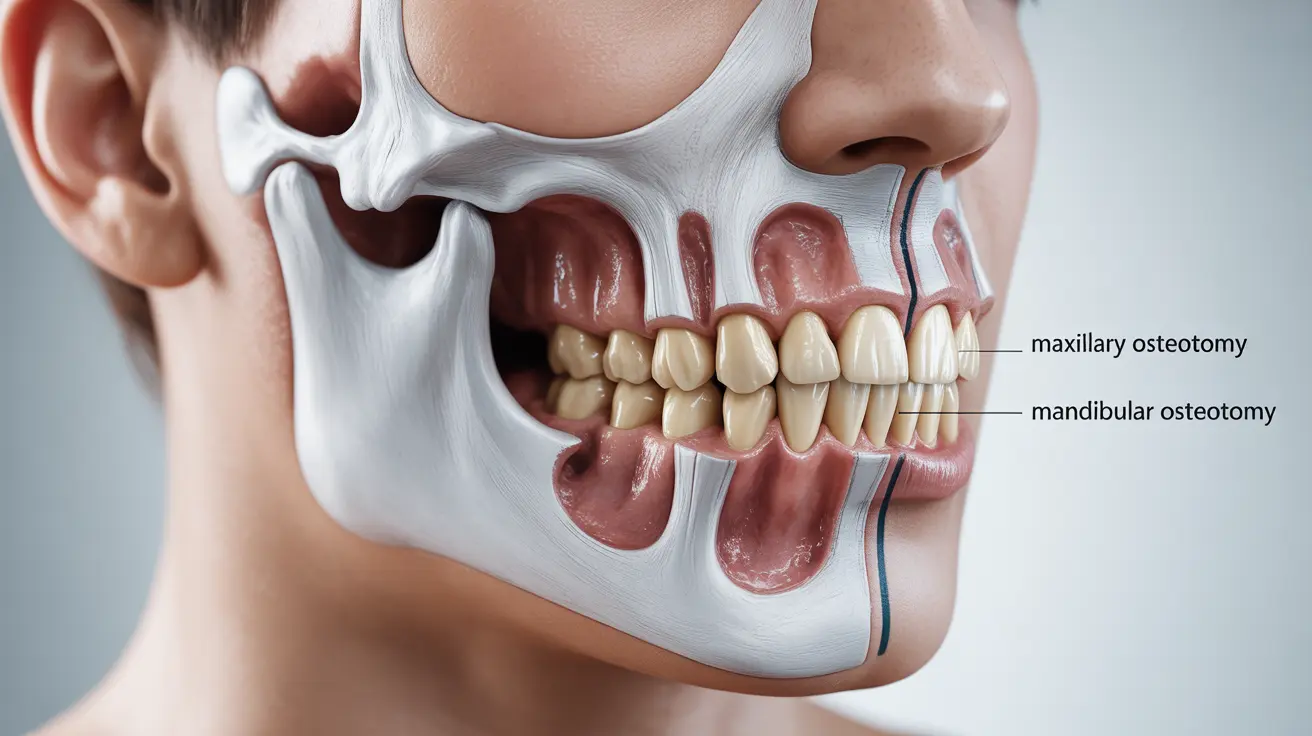
Maxillary Osteotomy (Upper Jaw)
This procedure corrects an overbite, underbite, or open bite by repositioning the upper jaw. Surgeons make incisions above the teeth to move the entire upper jaw and secure it with plates and screws.
Mandibular Osteotomy (Lower Jaw)
This surgery addresses an underbite or overbite by adjusting the lower jaw position. The surgeon creates incisions behind the molars to modify the jawbone and secure it in its new position.
Genioplasty (Chin Surgery)
This procedure reshapes and repositions the chin for better facial balance and jaw alignment. It can be performed alone or in combination with other jaw surgeries.
Conditions Treated by Jaw Surgery
Jaw surgery can effectively address various conditions, including:
- Severe overbite or underbite
- Difficulty chewing or biting food
- Chronic jaw pain or TMJ disorders
- Sleep apnea
- Facial asymmetry
- Speech problems
- Breathing difficulties
Preparing for Jaw Surgery
Proper preparation is essential for successful jaw surgery outcomes. Your surgical team will typically require:
- Comprehensive dental and medical evaluations
- Orthodontic treatment before surgery
- 3D imaging and surgical planning
- Discussion of anesthesia options
- Detailed review of post-operative care instructions
Recovery and Healing Process
Recovery from jaw surgery requires patience and careful attention to post-operative instructions. The typical timeline includes:
Immediate Post-Surgery (1-2 weeks)
Expect significant swelling, discomfort, and limited jaw movement. Liquid diet and careful oral hygiene are essential during this period.
Early Recovery (2-6 weeks)
Swelling gradually subsides, and patients can usually return to work or school. Soft food diet continues, and jaw exercises may begin.
Long-term Recovery (3-6 months)
Complete healing occurs, and patients can resume normal diet and activities. Final results become apparent as swelling fully resolves.
Risks and Complications
While jaw surgery is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Infection
- Nerve injury
- Bleeding
- Relapse of jaw position
- Numbness or altered sensation
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- TMJ problems
Frequently Asked Questions
What is jaw surgery and what conditions can it treat?
Jaw surgery (orthognathic surgery) is a procedure that corrects jaw alignment and positioning. It treats conditions including severe overbite/underbite, TMJ disorders, sleep apnea, facial asymmetry, and difficulties with chewing, speaking, or breathing.
How long does recovery from jaw surgery typically take and what should I expect during the healing process?
Full recovery typically takes 3-6 months. Initially, patients experience swelling and discomfort for 1-2 weeks, followed by gradual improvement. The first six weeks require a liquid/soft food diet, with normal activities usually resuming after 2-6 weeks.
What types of jaw surgery are available and how do they differ?
The main types include maxillary osteotomy (upper jaw), mandibular osteotomy (lower jaw), and genioplasty (chin). Each procedure targets specific areas and alignment issues, with some patients requiring combinations of these surgeries.
What are the common risks and complications associated with jaw surgery?
Common risks include infection, nerve injury, bleeding, relapse of jaw position, numbness, and temporary difficulty speaking or swallowing. While complications are possible, they are generally manageable with proper medical care.
How should I prepare for jaw surgery and what kind of post-operative care will I need?
Preparation includes dental evaluations, orthodontic treatment, 3D imaging, and comprehensive medical assessments. Post-operative care involves following a liquid/soft food diet, maintaining careful oral hygiene, attending follow-up appointments, and following specific recovery protocols provided by your surgical team.