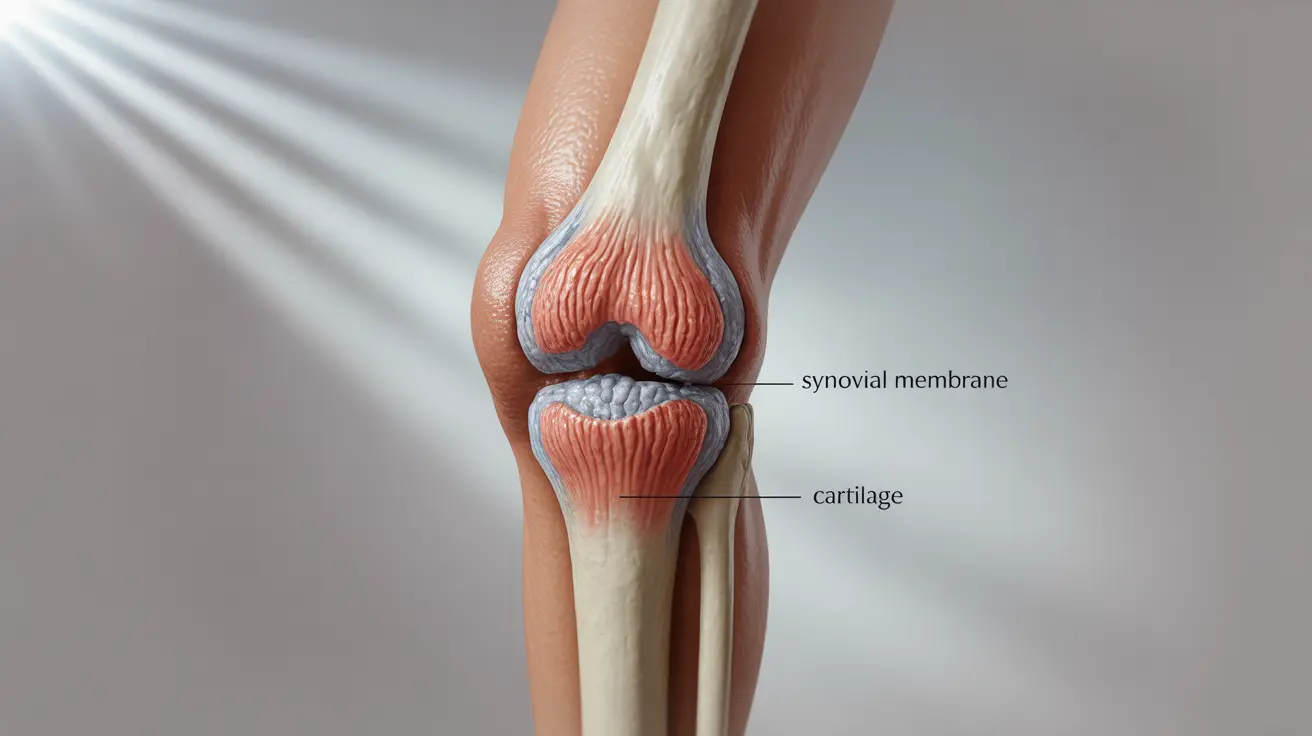
Joint swelling can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, making even simple tasks challenging. Whether it appears suddenly or develops gradually, understanding the underlying causes and available treatments is crucial for managing this common condition effectively.
This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of joint swelling, from identifying its root causes to finding appropriate treatment options and implementing lifestyle changes that can help manage symptoms.
Common Causes of Joint Swelling
Joint swelling can occur due to various conditions, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches:
Inflammatory Arthritis
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis can cause chronic joint inflammation, typically affecting multiple joints symmetrically. These autoimmune conditions often result in morning stiffness lasting more than an hour.
Osteoarthritis
This degenerative joint disease typically develops with age or following injury. Swelling usually affects weight-bearing joints and may worsen with activity but improve with rest.
Injury or Trauma
Acute injuries, such as sprains, strains, or fractures, can cause immediate swelling accompanied by pain and limited mobility. Sports injuries and accidents are common triggers.
Infection
Septic arthritis, caused by bacterial infection within the joint, requires immediate medical attention. It usually affects a single joint and comes with fever and severe pain.
Warning Signs and When to Seek Medical Care
While some joint swelling may resolve with home care, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe pain that limits normal movement
- Sudden, unexplained swelling in multiple joints
- Joint swelling accompanied by fever
- Redness and warmth around the affected joint
- Inability to bear weight on the affected limb
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Healthcare providers use various methods to determine the cause of joint swelling:
Physical Examination
Doctors assess joint appearance, range of motion, and surrounding tissue condition. They also review medical history and symptom patterns.
Imaging Tests
X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasound help visualize joint damage, inflammation, or fluid accumulation. These tests can reveal structural problems and guide treatment decisions.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests can identify markers of inflammation, infection, or autoimmune conditions. Joint fluid analysis may be performed to determine the presence of crystals, bacteria, or inflammatory cells.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of joint swelling:
Medical Interventions
- Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs)
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for inflammatory arthritis
- Corticosteroid injections
- Antibiotics for infection-related swelling
Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises and techniques can help maintain joint function, strengthen supporting muscles, and improve range of motion. Physical therapists may also recommend specific activities and modifications for daily tasks.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Several self-care strategies can help manage joint swelling:
- RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling
- Using assistive devices when needed
- Following an anti-inflammatory diet
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of joint swelling and how can I tell which one I have?
The most common causes include osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, injury, and infection. The pattern of swelling (single vs. multiple joints), timing (sudden vs. gradual onset), and accompanying symptoms can help identify the cause. However, accurate diagnosis requires professional medical evaluation.
What symptoms should prompt me to see a doctor for joint swelling?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, sudden swelling in multiple joints, fever, significant joint warmth and redness, or inability to use the affected joint. These symptoms may indicate serious conditions requiring prompt treatment.
How is joint swelling diagnosed and what tests are usually recommended?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, ultrasound), and laboratory tests including blood work and joint fluid analysis. The specific tests ordered depend on suspected causes and symptom presentation.
What treatment options are available to reduce joint swelling and manage pain?
Treatment options include medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, DMARDs), physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, and in some cases, surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Can lifestyle changes or home remedies help prevent or reduce joint swelling?
Yes, lifestyle modifications can significantly impact joint health. Regular exercise, maintaining healthy weight, proper posture, using the RICE method when needed, and following an anti-inflammatory diet can help prevent and manage joint swelling. However, these should complement, not replace, medical treatment when necessary.