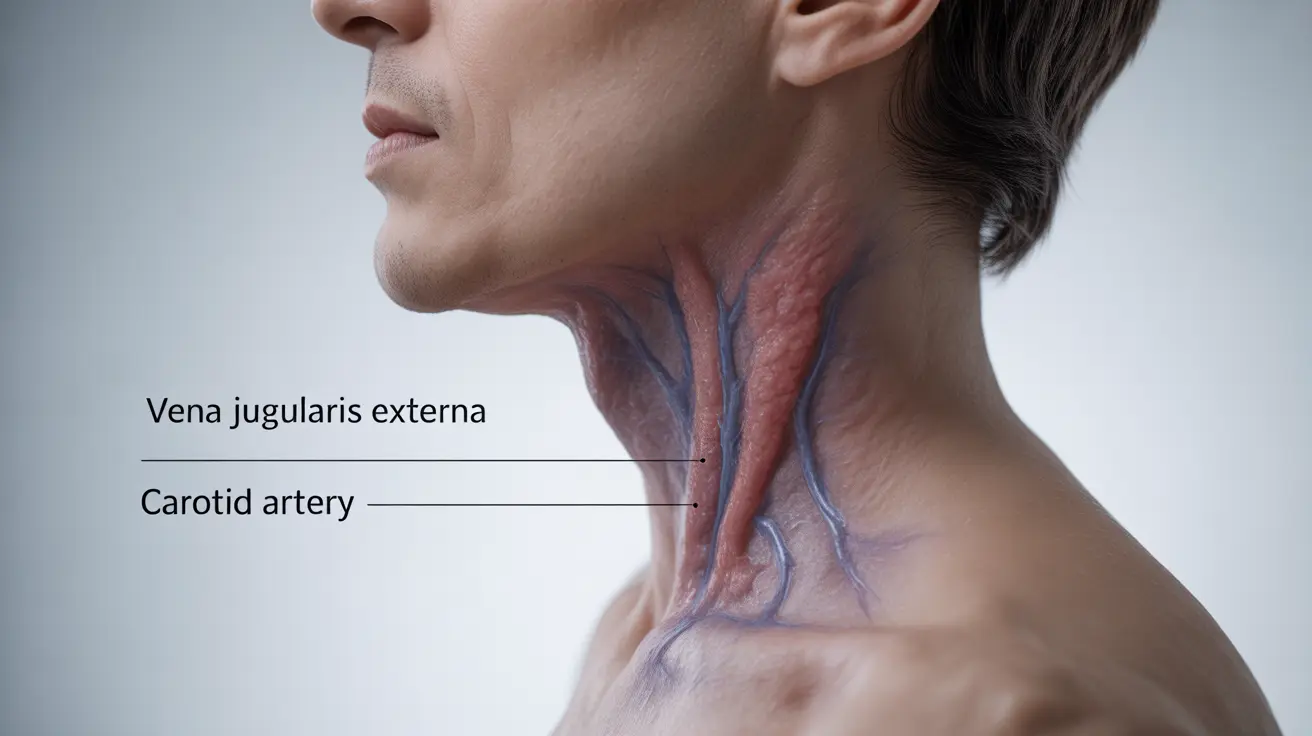
Jugular vein distention (JVD) is a significant medical sign that healthcare providers use to evaluate heart function and overall cardiovascular health. When the jugular veins in your neck become visibly enlarged or distended, it often signals underlying cardiovascular issues that require medical attention. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and proper medical intervention.
This comprehensive guide explores the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for jugular vein distention, helping you recognize when to seek medical care and what to expect during evaluation and treatment.
What Is Jugular Vein Distention?
Jugular vein distention occurs when the jugular veins in the neck become visibly enlarged due to increased pressure in the right side of the heart or superior vena cava. These veins normally transport blood from the head back to the heart, and their appearance can provide valuable information about heart function and blood pressure.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several cardiovascular conditions can lead to jugular vein distention:
- Congestive heart failure
- Right-sided heart failure
- Cardiac tamponade
- Superior vena cava syndrome
- Severe lung disease
- Tricuspid valve disease
Understanding these underlying causes is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning. Many of these conditions require immediate medical attention to prevent serious complications.
Signs and Symptoms
While jugular vein distention itself is a clinical sign, it often appears alongside other symptoms that may indicate serious cardiovascular issues:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Difficulty breathing when lying flat
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to evaluate jugular vein distention:
Physical Examination
During a physical exam, doctors typically observe the neck while the patient is positioned at a 45-degree angle. The height and character of the jugular venous pulsation provide important diagnostic information.
Additional Testing
To determine the underlying cause, doctors may order:
- Echocardiogram
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Cardiac catheterization
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for jugular vein distention focuses on addressing the underlying condition and may include:
Medical Management
- Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
- Heart medications to improve cardiac function
- Blood pressure management
- Anticoagulation therapy when necessary
Lifestyle Modifications
Supporting medical treatment with lifestyle changes can improve outcomes:
- Reducing salt intake
- Regular monitoring of fluid intake
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular physical activity as advised by healthcare providers
- Smoking cessation
Frequently Asked Questions
- What causes jugular vein distention and what underlying health conditions should I be concerned about?
Jugular vein distention is commonly caused by heart failure, lung disease, or obstruction of blood flow to the heart. The most concerning conditions include congestive heart failure, cardiac tamponade, and superior vena cava syndrome, all of which require immediate medical attention.
- How can jugular vein distention be diagnosed during a medical exam?
Doctors diagnose JVD through physical examination with the patient positioned at a 45-degree angle. They observe the height and character of neck vein distention and may use additional diagnostic tests like echocardiograms or chest X-rays to confirm underlying causes.
- What symptoms often appear along with jugular vein distention that might indicate heart failure?
Common accompanying symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and difficulty breathing when lying flat. These symptoms together may indicate heart failure and require immediate medical evaluation.
- How is jugular vein distention treated and managed to improve heart health?
Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause through medications like diuretics and heart medications, along with careful monitoring of fluid status. Management may also include regular cardiac check-ups and adjustments to medication dosages as needed.
- Can lifestyle changes or medications help prevent jugular vein distention from worsening?
Yes, lifestyle modifications such as reducing salt intake, maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise as prescribed, and medication compliance can help prevent worsening of JVD. Regular medical follow-up is essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.