Keratomalacia is a serious eye condition characterized by the softening and ulceration of the cornea, primarily caused by severe vitamin A deficiency. This potentially devastating condition can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated, making early detection and proper treatment crucial for preserving eye health.
While relatively rare in developed countries, keratomalacia remains a significant health concern in regions where malnutrition and vitamin A deficiency are prevalent. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for both healthcare providers and those at risk.
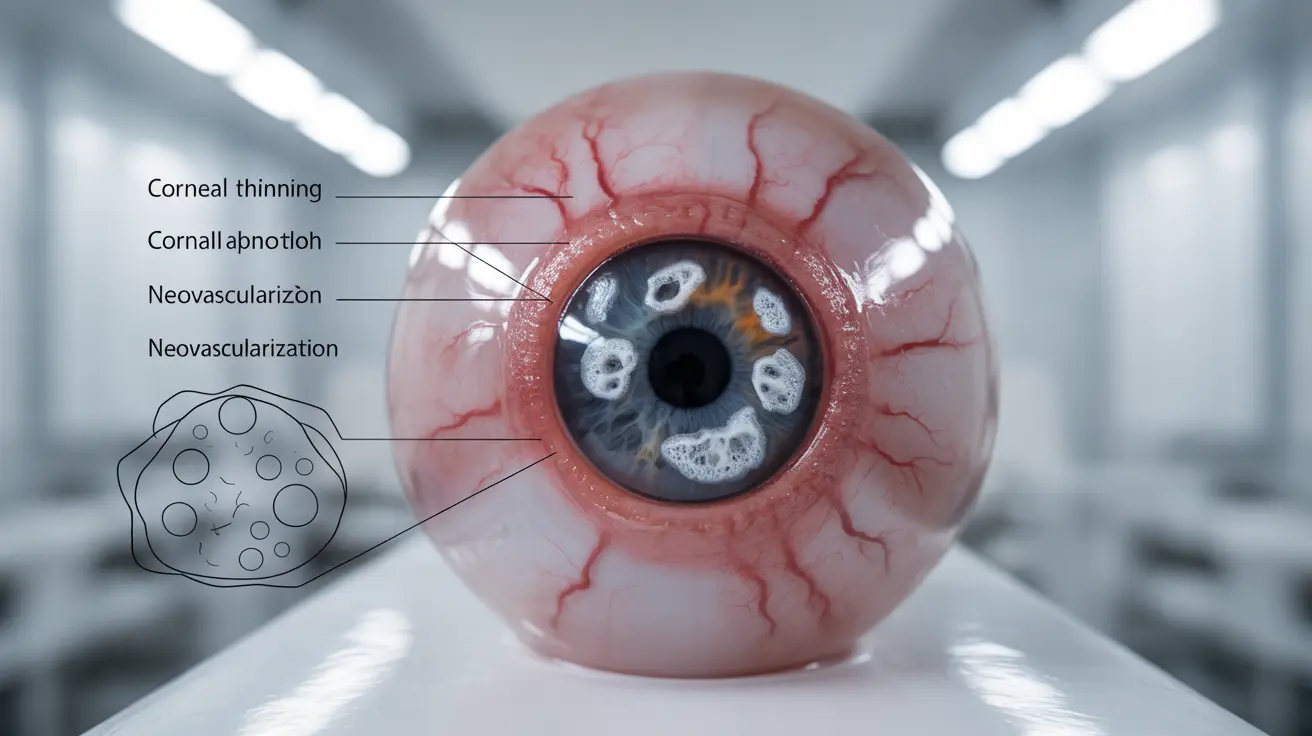
Understanding the Progression of Keratomalacia
Keratomalacia typically develops as part of a broader condition known as xerophthalmia, which encompasses various eye problems related to vitamin A deficiency. The condition progresses through several stages, beginning with night blindness and potentially culminating in severe corneal damage.
Early Warning Signs
The initial symptoms of keratomalacia often include:
- Difficulty seeing in low light conditions (night blindness)
- Persistent dry eyes
- Foamy patches on the whites of the eyes
- Increased sensitivity to light
- Redness and irritation
Advanced Symptoms
As the condition progresses, more severe symptoms may develop:
- Corneal ulceration
- Softening of the corneal tissue
- Clouding of the cornea
- Permanent scarring
- Potential perforation of the cornea
Diagnostic Process and Medical Assessment
Diagnosing keratomalacia requires a comprehensive eye examination and medical history review. Eye care professionals typically employ several diagnostic tools and techniques to confirm the condition and assess its severity.
Common Diagnostic Methods
Doctors may use the following approaches to diagnose keratomalacia:
- Detailed eye examination using a slit lamp
- Blood tests to measure vitamin A levels
- Assessment of overall nutritional status
- Evaluation of tear production
- Photography documentation of corneal changes
Treatment Approaches and Vision Recovery
The treatment of keratomalacia focuses on addressing both the immediate eye condition and its underlying cause. Quick intervention is essential to prevent permanent vision loss and promote healing.
Primary Treatment Strategies
Treatment typically involves:
- Immediate vitamin A supplementation
- Nutritional counseling and dietary modifications
- Antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection
- Protective eye patches when necessary
- Regular monitoring of corneal healing
Prevention Through Proper Nutrition
Preventing keratomalacia primarily involves maintaining adequate vitamin A levels through proper nutrition and supplementation when necessary. A balanced diet rich in vitamin A sources is essential for long-term eye health.
Key Dietary Sources of Vitamin A
Important food sources include:
- Orange and yellow vegetables (carrots, sweet potatoes)
- Dark leafy greens
- Liver and fish oils
- Eggs and dairy products
- Fortified cereals and foods
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of keratomalacia caused by vitamin A deficiency?
The main symptoms include night blindness, dry eyes, corneal softening, ulceration, and potential perforation. Early signs often start with difficulty seeing in low light conditions and progress to more severe corneal damage if left untreated.
How is keratomalacia diagnosed and what tests do doctors use?
Doctors diagnose keratomalacia through comprehensive eye examinations using a slit lamp, blood tests to check vitamin A levels, and assessment of tear production. They also evaluate overall nutritional status and document corneal changes.
What are the most effective treatments for keratomalacia and can vision loss be reversed?
The most effective treatments include immediate vitamin A supplementation, nutritional intervention, and antibiotic eye drops when needed. Vision loss can often be prevented or minimized if treatment begins early, though severe cases may result in permanent damage.
How can keratomalacia be prevented through diet and supplementation?
Prevention involves maintaining adequate vitamin A intake through a balanced diet rich in orange and yellow vegetables, dark leafy greens, liver, fish oils, and fortified foods. Supplementation may be recommended for at-risk individuals under medical supervision.
What is the relationship between xerophthalmia and keratomalacia in eye health?
Xerophthalmia is the broader condition of eye changes caused by vitamin A deficiency, while keratomalacia represents its most severe form. Keratomalacia typically develops as an advanced stage of xerophthalmia when left untreated.