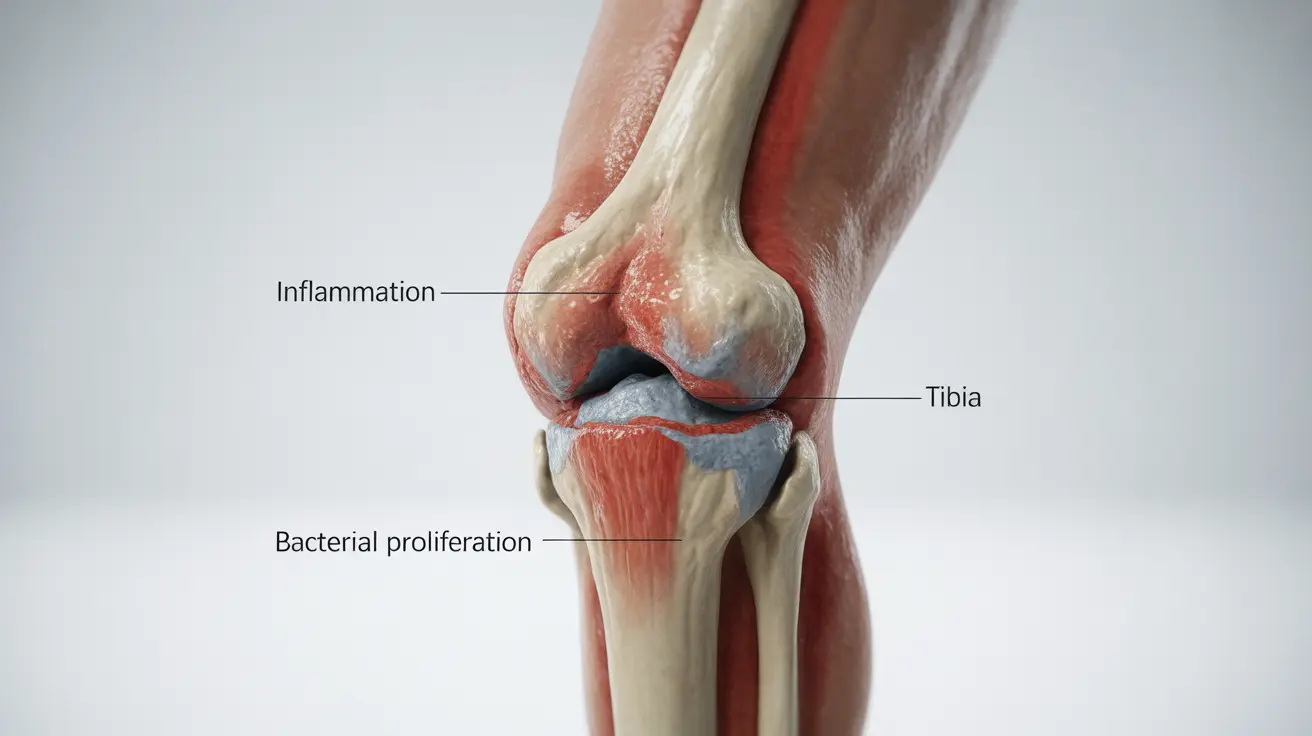
A knee infection, also known as septic arthritis of the knee, is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. When bacteria or other microorganisms invade the knee joint, they can cause severe inflammation, pain, and potential long-term damage if left untreated. Understanding the signs, treatments, and preventive measures is crucial for maintaining joint health and avoiding complications.
Whether resulting from injury, surgery, or spreading infection elsewhere in the body, knee infections can affect people of all ages and activity levels. Early recognition and proper medical care are essential for successful treatment and preventing permanent joint damage.
Signs and Symptoms of Knee Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a knee infection early can lead to better outcomes. Common signs include:
- Severe knee pain that worsens with movement
- Significant swelling around the joint
- Redness and warmth in the affected area
- Fever and chills
- Limited range of motion
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg
If you experience any combination of these symptoms, especially following surgery or injury, seek immediate medical attention. Delayed treatment can lead to serious complications.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes knee infections and who is most at risk can help with prevention and early intervention. Several factors can increase your risk:
- Recent knee surgery or joint replacement
- Open wounds or injuries near the knee
- Weakened immune system
- Chronic conditions like diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis
- Previous joint infections
- Intravenous drug use
The most common way bacteria enter the knee joint is through direct injury, surgery, or through the bloodstream from another infection in the body.
Diagnosis and Testing
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose knee infections accurately:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to check for infection markers
- Joint fluid analysis (arthrocentesis)
- Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, or CT scans)
- Culture tests to identify specific bacteria
These diagnostic tools help determine the type of infection and guide appropriate treatment choices.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for knee infections typically involves a comprehensive approach:
Immediate Interventions
- Antibiotic therapy (often intravenous)
- Joint drainage
- Rest and immobilization
- Pain management
Surgical Options
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, particularly for:
- Removing infected tissue
- Draining accumulated fluid
- Repairing damaged joint structures
- Addressing underlying joint problems
Prevention Strategies
While not all knee infections can be prevented, several measures can reduce risk:
- Proper wound care and hygiene
- Following post-surgical instructions carefully
- Managing chronic health conditions
- Maintaining a strong immune system
- Prompt treatment of any infections elsewhere in the body
- Regular check-ups if you have artificial joints
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of a knee infection and when should I see a doctor?
The main symptoms include severe knee pain, swelling, redness, warmth, fever, and limited mobility. See a doctor immediately if you experience these symptoms, especially if they develop rapidly or follow surgery or injury.
How is a knee infection treated, and will I need surgery?
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, joint drainage, and rest. Surgery may be necessary in severe cases or if conservative treatment fails. The specific approach depends on the infection's severity and cause.
What causes a knee infection, and what are the biggest risk factors?
Knee infections are typically caused by bacteria entering the joint through injury, surgery, or via the bloodstream. Major risk factors include recent knee surgery, compromised immune system, chronic health conditions, and previous joint infections.
Can a knee infection be prevented, especially after surgery or with chronic health conditions?
While not all infections can be prevented, following proper wound care, maintaining good hygiene, following medical instructions after surgery, and managing chronic conditions can significantly reduce risk.
How is a knee infection diagnosed, and what tests should I expect?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, blood tests, joint fluid analysis, and imaging studies like X-rays or MRI. Your doctor may also order culture tests to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.