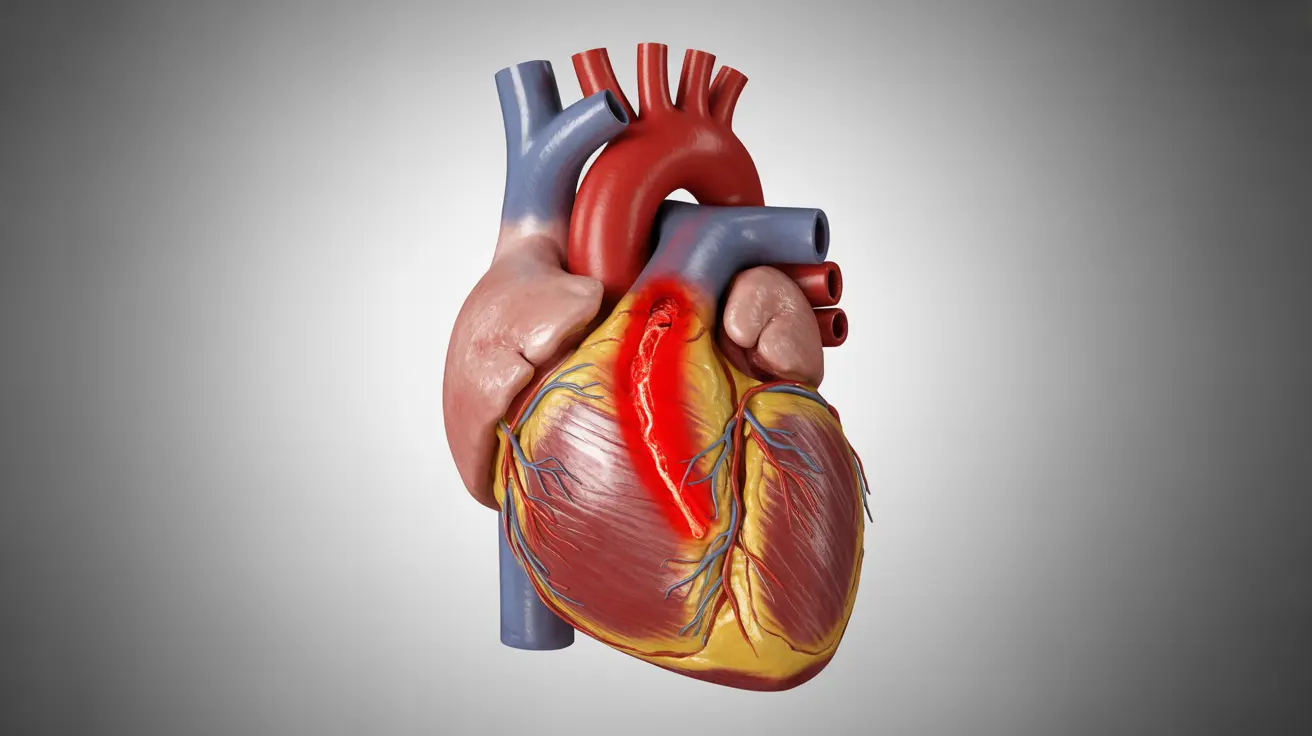
A blockage in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery, often called the "widowmaker" artery, represents one of the most serious cardiac emergencies. Understanding the symptoms of LAD artery blockage could mean the difference between life and death, as this condition requires immediate medical attention.
This comprehensive guide will help you recognize the warning signs of LAD artery blockage, understand when to seek emergency care, and learn about available treatments and prevention strategies.
Understanding LAD Artery Blockage
The left anterior descending artery supplies blood to approximately 50% of the heart muscle. When this crucial vessel becomes blocked, it can lead to a severe type of heart attack that can be particularly deadly if not treated promptly. Understanding the nature of this condition is crucial for recognizing its importance and potential impact.
Key Warning Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of LAD artery blockage can be sudden and severe, though some people may experience warning signs in the days or weeks before a complete blockage occurs.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Severe chest pain or pressure (angina)
- Pain radiating to the left arm, neck, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Profuse sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Extreme fatigue
Gender Differences in Symptoms
Women often experience LAD artery blockage symptoms differently than men, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Women are more likely to experience:
- Unusual fatigue
- Neck or jaw pain
- Upper back pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath without chest pain
Emergency Response and Treatment
When an LAD artery blockage occurs, immediate medical intervention is crucial. Treatment options typically include:
Immediate Interventions:
- Emergency coronary angioplasty
- Stent placement
- Coronary bypass surgery
- Clot-busting medications
The success of treatment largely depends on how quickly medical care is received, with the best outcomes occurring when treatment is administered within 90 minutes of symptom onset.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Several lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of developing LAD artery blockage:
- Maintaining a heart-healthy diet
- Regular physical activity
- Quitting smoking
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
- Controlling diabetes
- Regular medical check-ups
- Stress management
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of a LAD artery blockage and when should I seek emergency care?
The main symptoms include severe chest pain, shortness of breath, pain radiating to the arm or jaw, and profuse sweating. Seek immediate emergency care if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they last more than a few minutes or worsen with physical activity.
How is a widowmaker heart attack different from other types of heart attacks?
A widowmaker heart attack occurs when the LAD artery is completely blocked, affecting blood flow to a large portion of the heart muscle. This type is particularly dangerous because it impacts such a significant area of the heart, potentially causing more extensive damage than other types of heart attacks.
What treatments are available for a completely blocked LAD artery, and how quickly do they need to be given?
Treatment options include emergency angioplasty, stent placement, or bypass surgery. These interventions need to be performed as quickly as possible, ideally within 90 minutes of arrival at the hospital, to minimize heart muscle damage and improve survival chances.
Are the symptoms of a LAD artery blockage different for women, and what signs should women watch for?
Yes, women often experience different symptoms than men. Women should watch for unusual fatigue, neck or jaw pain, upper back pain, nausea, and shortness of breath. These symptoms may occur without the classic chest pain that men typically experience.
What lifestyle changes or habits can help lower the risk of a LAD artery blockage?
Key lifestyle changes include maintaining a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, managing stress, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular medical check-ups. These changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing arterial blockages.