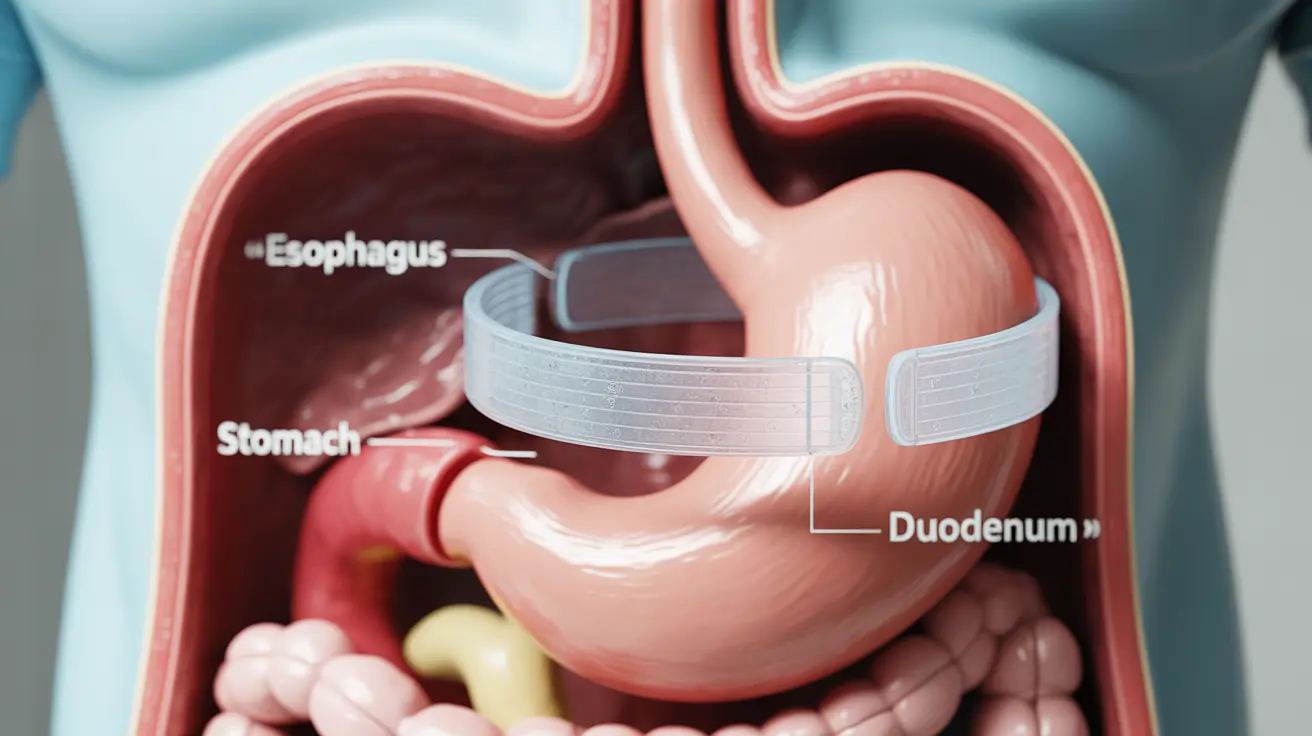
Lap band surgery, also known as adjustable gastric banding, represents a significant advancement in weight loss procedures. This minimally invasive bariatric surgery option helps individuals achieve sustainable weight loss through a adjustable silicone band placed around the upper portion of the stomach. Understanding this procedure's benefits, requirements, and considerations is crucial for those contemplating surgical weight loss solutions.
While once highly popular, lap band surgery has evolved over the years, with medical professionals and patients now having access to various bariatric surgery options. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about lap band surgery, from its mechanism of action to long-term maintenance requirements.
How Lap Band Surgery Works
During lap band surgery, surgeons laparoscopically place an adjustable silicone band around the upper part of the stomach. This creates a small pouch above the band, effectively limiting food intake and helping patients feel full with smaller portions. The band connects to a small port placed under the skin, allowing for adjustments to optimize weight loss results.
The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes to complete and usually requires only a short hospital stay. Unlike other bariatric procedures, lap band surgery doesn't involve cutting or stapling the stomach, making it both reversible and adjustable.
Candidacy and Eligibility Requirements
Not everyone qualifies for lap band surgery. Healthcare providers carefully evaluate potential candidates based on several crucial factors:
- Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or 35+ with obesity-related health conditions
- History of unsuccessful attempts at medically supervised weight loss
- Commitment to long-term lifestyle changes
- No alcohol or drug dependency
- Understanding of the procedure and its requirements
- Generally good health to undergo surgery
The Surgery Process and Recovery
The lap band procedure involves several key steps:
- Pre-surgery evaluation and preparation
- Laparoscopic placement of the band
- Creation of the subcutaneous port for future adjustments
- Initial recovery period of 4-6 weeks
Most patients return home within 24 hours after surgery and can resume normal activities within a week. However, a liquid diet is necessary for the first few weeks, followed by a gradual transition to soft and then solid foods.
Band Adjustments and Maintenance
Regular band adjustments are crucial for optimal weight loss results. These adjustments, known as "fills," involve adding or removing saline solution through the access port to modify the band's tightness. The frequency of adjustments varies by individual but typically occurs more often in the first year after surgery.
Patients should expect:
- Monthly adjustments during the first year
- Regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare team
- Ongoing dietary and lifestyle counseling
- Periodic evaluation of weight loss progress
Potential Risks and Complications
While lap band surgery is generally safe, potential complications can include:
- Band slippage or erosion
- Port-related issues
- Infection
- Nausea or vomiting
- Difficulty swallowing
- Poor weight loss results
Alternative Weight Loss Procedures
Several alternatives to lap band surgery have gained prominence in recent years:
- Gastric sleeve surgery
- Gastric bypass
- Duodenal switch
- Non-surgical weight loss programs
- Medication-assisted weight management
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is lap band surgery and how does it help with weight loss?
Lap band surgery involves placing an adjustable silicone band around the upper stomach to create a small pouch, restricting food intake and promoting earlier satiety. This helps patients consume fewer calories while still feeling satisfied, leading to gradual, sustainable weight loss.
- Who is a good candidate for lap band surgery and what are the eligibility requirements?
Good candidates typically have a BMI of 40+ or 35+ with obesity-related health conditions, have tried other weight loss methods without success, and are committed to making long-term lifestyle changes. They must also be in generally good health and free from alcohol or drug dependencies.
- What are the common complications and risks associated with lap band surgery?
Common complications include band slippage, erosion, port-related issues, infection, difficulty swallowing, and potential inadequate weight loss. Some patients may require additional surgeries to address complications or remove the band.
- How is the lap band adjusted after surgery and how often are adjustments needed?
The lap band is adjusted through a port placed under the skin by adding or removing saline solution. Adjustments are typically more frequent in the first year, occurring monthly, then become less frequent based on individual progress and needs.
- What are the alternatives to lap band surgery and why has its popularity decreased?
Alternatives include gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, and duodenal switch surgeries. Lap band surgery's popularity has decreased due to higher rates of revision surgery, slower weight loss compared to other procedures, and the emergence of more effective bariatric surgery options.