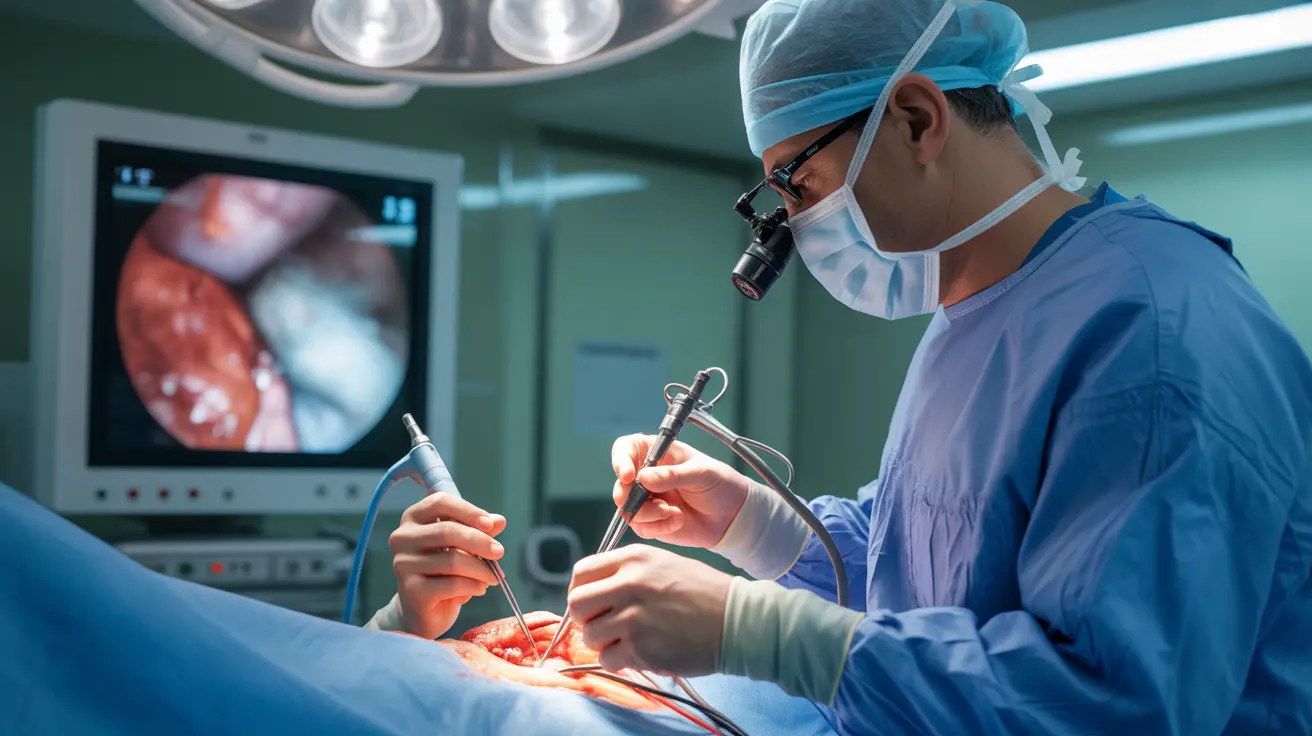
Laparoscopy is a revolutionary surgical technique that has transformed modern medicine by offering a minimally invasive approach to diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. This advanced procedure allows surgeons to operate through small incisions using specialized instruments and a camera, providing numerous benefits over traditional open surgery.
Whether you're scheduled for a laparoscopic procedure or simply wanting to learn more, this comprehensive guide will explain what laparoscopy is, its applications, and what to expect during and after the procedure.
What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, involves making several small incisions (usually 0.5-1.5 cm) in the abdomen or pelvis. Through these tiny openings, surgeons insert a thin, fiber-optic instrument called a laparoscope, which has a tiny camera and light source, along with other specialized surgical tools.
The camera transmits high-definition images to monitors in the operating room, allowing surgeons to view the internal organs and perform procedures with exceptional precision. This advanced visualization system eliminates the need for large surgical incisions traditionally required for open surgery.
Common Applications of Laparoscopic Surgery
Diagnostic Procedures
Laparoscopy is frequently used to investigate and diagnose various conditions, including:
- Unexplained pelvic or abdominal pain
- Fertility issues
- Suspected endometriosis
- Evaluation of masses or tumors
- Investigation of chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
Treatment Procedures
Many surgical procedures can now be performed laparoscopically, including:
- Gallbladder removal (laparoscopic cholecystectomy)
- Appendix removal (laparoscopic appendectomy)
- Hernia repair
- Gynecological procedures
- Weight loss surgery
- Some cancer-related procedures
The Laparoscopic Procedure Process
Pre-operative Preparation
Before the procedure, patients typically receive specific instructions regarding:
- Fasting requirements
- Medication adjustments
- Pre-operative testing
- Arrival time at the medical facility
During Surgery
The procedure begins with general anesthesia administration. The surgeon then creates small incisions and inflates the abdomen with carbon dioxide gas to create better visibility and working space. Through these incisions, the laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted to perform the necessary diagnostic or treatment procedure.
Advantages and Potential Risks
Benefits
Laparoscopic surgery offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery:
- Smaller incisions and minimal scarring
- Reduced post-operative pain
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster recovery time
- Lower risk of infection
- Quicker return to normal activities
Possible Risks
While generally safe, laparoscopic surgery carries some potential risks:
- Bleeding or infection at incision sites
- Internal organ damage
- Adverse reaction to anesthesia
- Blood clots
- Temporary shoulder pain from gas used during procedure
Recovery and Post-operative Care
Recovery from laparoscopic surgery is typically faster than traditional surgery, but proper care is essential. Most patients can return home the same day or within 24 hours after the procedure. Full recovery usually takes 1-2 weeks, depending on the specific procedure performed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is laparoscopy and how does it differ from traditional open surgery?
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses small incisions, specialized instruments, and a camera to perform procedures, unlike traditional open surgery which requires larger incisions. This approach results in less scarring, faster healing, and shorter recovery times.
What conditions or symptoms can laparoscopy help diagnose or treat?
Laparoscopy can diagnose and treat various conditions including endometriosis, gallbladder disease, hernias, appendicitis, and unexplained pelvic or abdominal pain. It's also commonly used for gynecological procedures and some cancer-related surgeries.
How is a laparoscopic surgery performed and what should I expect during the procedure?
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Small incisions are made to insert a camera and surgical instruments. The abdomen is inflated with gas to create working space. The entire procedure is viewed on monitors, allowing precise surgical manipulation.
What are the benefits and risks of laparoscopic surgery compared to open surgery?
Benefits include smaller incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays. Risks, though generally minimal, include potential bleeding, infection, organ damage, and reactions to anesthesia. Overall, risks are typically lower than with traditional open surgery.
How long is the recovery time after laparoscopy and what care is needed post-surgery?
Recovery typically takes 1-2 weeks, though this varies by procedure. Post-operative care includes keeping incisions clean, following pain management instructions, gradually increasing activity levels, and attending follow-up appointments. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days to weeks.