The latissimus dorsi, often called the "lats," is one of the body's most powerful and versatile muscles. This large, flat muscle plays a crucial role in various upper body movements and everyday activities. Understanding its function is essential for both fitness enthusiasts and those dealing with back-related concerns.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the latissimus dorsi's vital functions, location, and importance in maintaining proper upper body strength and mobility.
Anatomy and Location of the Latissimus Dorsi
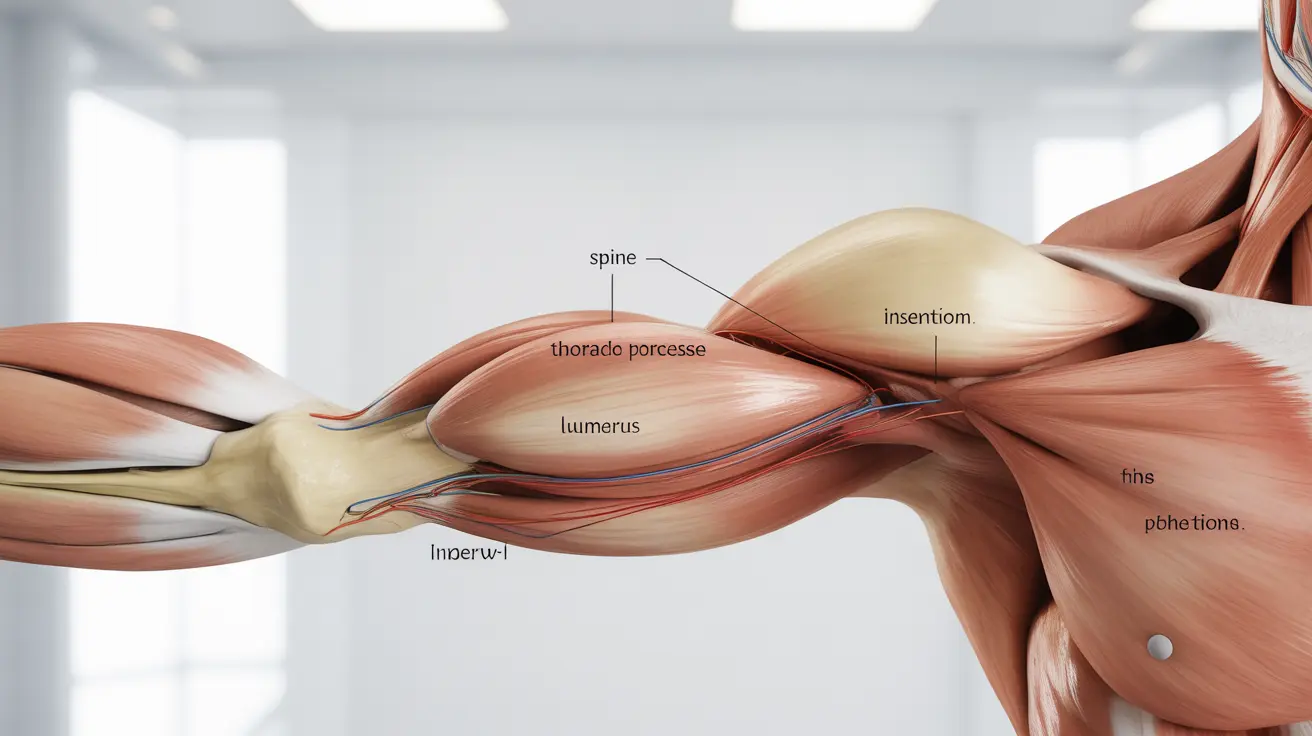
The latissimus dorsi is a broad, triangle-shaped muscle that spans across the lower and middle back. It originates from the spine (thoracic vertebrae T7-T12), lower ribs, and posterior iliac crest of the hip bone. The muscle fibers converge into a thick tendon that attaches to the upper arm bone (humerus).
This unique anatomical arrangement allows the muscle to connect the spine, pelvis, and arm, creating a powerful foundation for upper body movements and core stability.
Primary Functions and Movement Patterns
Arm and Shoulder Movements
The latissimus dorsi primarily controls several key arm movements:
- Extension (pulling the arm backward)
- Adduction (pulling the arm toward the body's midline)
- Internal rotation of the shoulder
- Depression of the shoulder blade
Role in Daily Activities
This powerful muscle assists in numerous everyday activities:
- Pulling movements (opening heavy doors, rowing)
- Climbing and pulling up movements
- Reaching behind the back
- Supporting proper posture
- Stabilizing the spine during lifting
Respiratory Function and Core Support
Beyond movement, the latissimus dorsi plays a vital role in breathing mechanics. During forceful exhalation, such as coughing or sneezing, the muscle contracts to compress the ribcage. It also helps maintain core stability during challenging physical activities.
Common Injuries and Prevention
The latissimus dorsi can be injured through overuse or sudden strain. Common issues include:
- Muscle strains from excessive pulling movements
- Tendon inflammation
- Poor posture-related tension
- Overtraining injuries
Warning Signs of Injury
Watch for these symptoms that may indicate a latissimus dorsi injury:
- Sharp pain during arm movements
- Difficulty reaching overhead
- Muscle stiffness or spasms
- Reduced range of motion
- Pain during deep breathing
Strengthening Exercises and Recovery
Proper training can help maintain healthy latissimus dorsi function:
- Lat pulldowns
- Cable rows
- Pull-ups (modified or assisted if needed)
- Swimming strokes
- Resistance band exercises
For injury recovery, always start with gentle stretches and gradually progress to strengthening exercises under professional guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the latissimus dorsi muscle do, and how does it affect arm and shoulder movements?
The latissimus dorsi controls arm extension, adduction, and internal rotation of the shoulder. It enables pulling movements, helps maintain posture, and assists in activities requiring arm strength and control.
Where is the latissimus dorsi muscle located in the back, and what connects it to the arm?
The muscle spans the lower and middle back, originating from the spine, lower ribs, and hip bone. It connects to the upper arm bone (humerus) through a thick tendon, forming a crucial link between the torso and arms.
Can a latissimus dorsi injury cause shoulder or neck pain, and what are the common symptoms?
Yes, latissimus dorsi injuries can cause shoulder and neck pain. Common symptoms include sharp pain during movement, reduced range of motion, muscle stiffness, and difficulty with overhead activities.
How can I strengthen my latissimus dorsi, and what exercises are most effective for recovery after an injury?
Effective exercises include lat pulldowns, rows, and modified pull-ups. For injury recovery, start with gentle stretches and progressively advance to strengthening exercises under professional supervision.
Does the latissimus dorsi muscle help with breathing, and how does it assist during activities like coughing or climbing?
Yes, the latissimus dorsi assists in forceful exhalation during activities like coughing and sneezing by compressing the ribcage. During climbing, it helps stabilize the core and enables powerful pulling movements.