Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease that affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain unaware of its warning signs until the condition progresses. Understanding leishmaniasis symptoms is crucial for early detection and proper treatment, as this disease can present in various forms ranging from skin lesions to life-threatening organ involvement.
This tropical disease, transmitted through infected sandfly bites, manifests differently depending on the type of parasite and the body system affected. Recognizing the early signs can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes and prevent serious complications.
Understanding the Different Forms of Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis presents in three primary forms, each with distinct symptoms and severity levels. The cutaneous form affects the skin, creating visible lesions that develop over weeks or months. Visceral leishmaniasis impacts internal organs including the spleen, liver, and bone marrow, making it the most serious variant. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis affects both skin and mucous membranes, particularly in the nose and mouth area.
Each form requires different approaches to diagnosis and treatment, making symptom recognition essential for healthcare providers and patients alike. The progression and appearance of symptoms can vary significantly based on individual immune response, parasite species, and overall health status.
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Skin Manifestations and Development
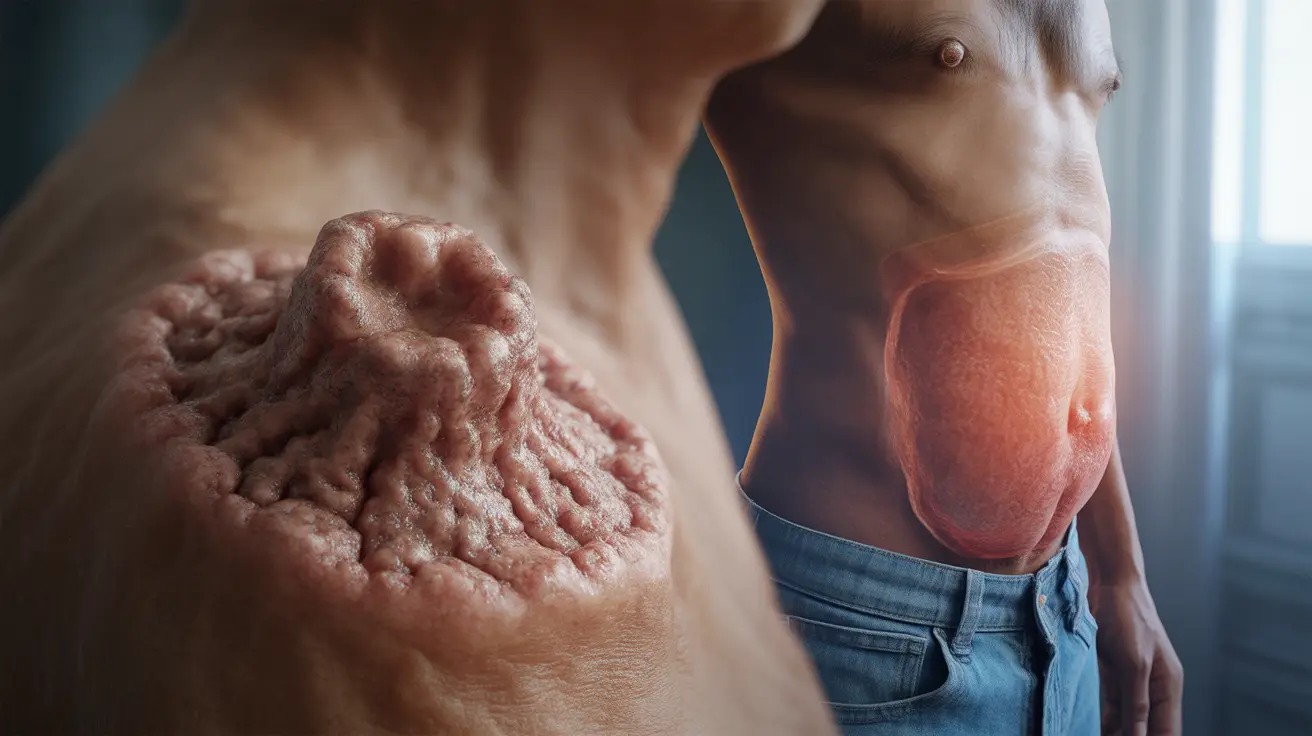
Cutaneous leishmaniasis typically begins as small, red bumps at the site of the sandfly bite. These initial lesions may appear weeks or even months after exposure, as the parasite has a lengthy incubation period. The bumps gradually enlarge and develop into painless ulcers with raised borders and depressed centers.
The characteristic appearance includes a volcano-like crater with well-defined edges. These sores may measure anywhere from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. While typically painless, some patients experience mild discomfort or itching around the affected area.
Over time, these lesions may develop a crusty appearance or become covered with scales. Multiple lesions can occur if a person receives several infected bites. The sores tend to heal slowly over months or years, often leaving permanent scars even after successful treatment.
Visceral Leishmaniasis: Internal System Warning Signs
Visceral leishmaniasis presents with systemic symptoms that can be life-threatening if left untreated. The most common early signs include persistent fever that comes and goes over several weeks or months. Patients often experience significant weight loss and fatigue that interferes with daily activities.
As the disease progresses, the spleen and liver become enlarged, creating abdominal swelling and discomfort. This enlargement can be detected through physical examination and imaging studies. Patients may notice their abdomen protruding or feeling unusually full after small meals.
Additional symptoms include pale skin due to anemia, easy bruising from low platelet counts, and increased susceptibility to other infections. Some individuals develop darkening of the skin, particularly on the hands, feet, and face, which gives the disease its alternative name "kala-azar" meaning "black fever."
Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis: Nasal and Oral Symptoms
Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis often begins with skin lesions similar to the cutaneous form but subsequently spreads to mucous membranes. The nose is frequently the first mucous membrane affected, with symptoms including persistent nasal congestion, nosebleeds, and changes in nasal appearance.
Patients may notice their nose becoming swollen or developing an unusual shape as the infection progresses. Mouth involvement can lead to painful sores on the lips, gums, or inside the cheeks. These oral lesions may interfere with eating, drinking, or speaking comfortably.
The progression from cutaneous to mucocutaneous form can occur months or years after the initial skin infection. This delayed progression makes it essential to monitor any persistent nasal or oral symptoms in individuals with a history of leishmaniasis or travel to endemic areas.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical evaluation is necessary for anyone experiencing persistent fever, unexplained weight loss, or abdominal swelling, especially with a history of travel to areas where leishmaniasis is common. These symptoms may indicate visceral leishmaniasis, which requires prompt treatment to prevent serious complications.
Skin lesions that don't heal within a few weeks or continue to grow should also prompt medical consultation. While cutaneous leishmaniasis is less immediately dangerous than the visceral form, early treatment can prevent scarring and reduce healing time.
Any combination of nasal symptoms, mouth sores, and previous skin lesions warrants urgent medical attention, as this may indicate mucocutaneous leishmaniasis requiring specialized treatment to prevent permanent disfigurement.
Treatment Approaches for Different Forms
Treatment varies significantly based on the type of leishmaniasis and severity of symptoms. Cutaneous leishmaniasis may sometimes heal without treatment, but medication can speed recovery and reduce scarring. Common treatments include topical medications for localized infections or systemic drugs for multiple or large lesions.
Visceral leishmaniasis requires immediate systemic treatment with specific anti-parasitic medications. The choice of drug depends on the parasite species, geographic location, and patient factors such as age and overall health. Treatment typically involves hospitalization and close monitoring for complications.
Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis demands aggressive systemic therapy to prevent permanent tissue damage. Treatment duration is often longer than for other forms, and patients require careful follow-up to ensure complete parasite elimination and prevent relapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of leishmaniasis?
The most common symptoms vary by type. Cutaneous leishmaniasis typically causes painless skin sores that develop slowly over weeks to months. Visceral leishmaniasis presents with fever, weight loss, fatigue, and enlarged spleen and liver. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis combines skin lesions with nasal congestion, nosebleeds, and mouth sores.
How do cutaneous leishmaniasis skin sores look and develop over time?
Cutaneous leishmaniasis sores begin as small red bumps that gradually enlarge into painless ulcers with raised borders and depressed centers, resembling a volcano crater. They may develop crusty surfaces or scales and can range from millimeters to several centimeters in size. These lesions heal slowly over months or years, often leaving permanent scars.
What are the signs of visceral leishmaniasis and when should I seek medical help?
Signs of visceral leishmaniasis include persistent intermittent fever, significant weight loss, fatigue, enlarged abdomen due to spleen and liver enlargement, pale skin, and easy bruising. Seek immediate medical help if you experience these symptoms, especially with a history of travel to endemic areas, as this form can be life-threatening without prompt treatment.
Can leishmaniasis cause nosebleeds and mouth sores, and what does that mean?
Yes, nosebleeds and mouth sores are characteristic of mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, which affects both skin and mucous membranes. These symptoms indicate the infection has spread beyond the initial skin lesion to involve nasal and oral tissues. This progression requires urgent medical attention and aggressive treatment to prevent permanent disfigurement.
How is leishmaniasis treated, and what are the options for different forms of the disease?
Treatment depends on the form and severity. Cutaneous leishmaniasis may be treated with topical medications for localized infections or oral/injectable drugs for multiple lesions. Visceral leishmaniasis requires immediate systemic treatment with anti-parasitic medications and hospitalization. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis needs aggressive systemic therapy with longer treatment duration and careful monitoring to prevent relapse.