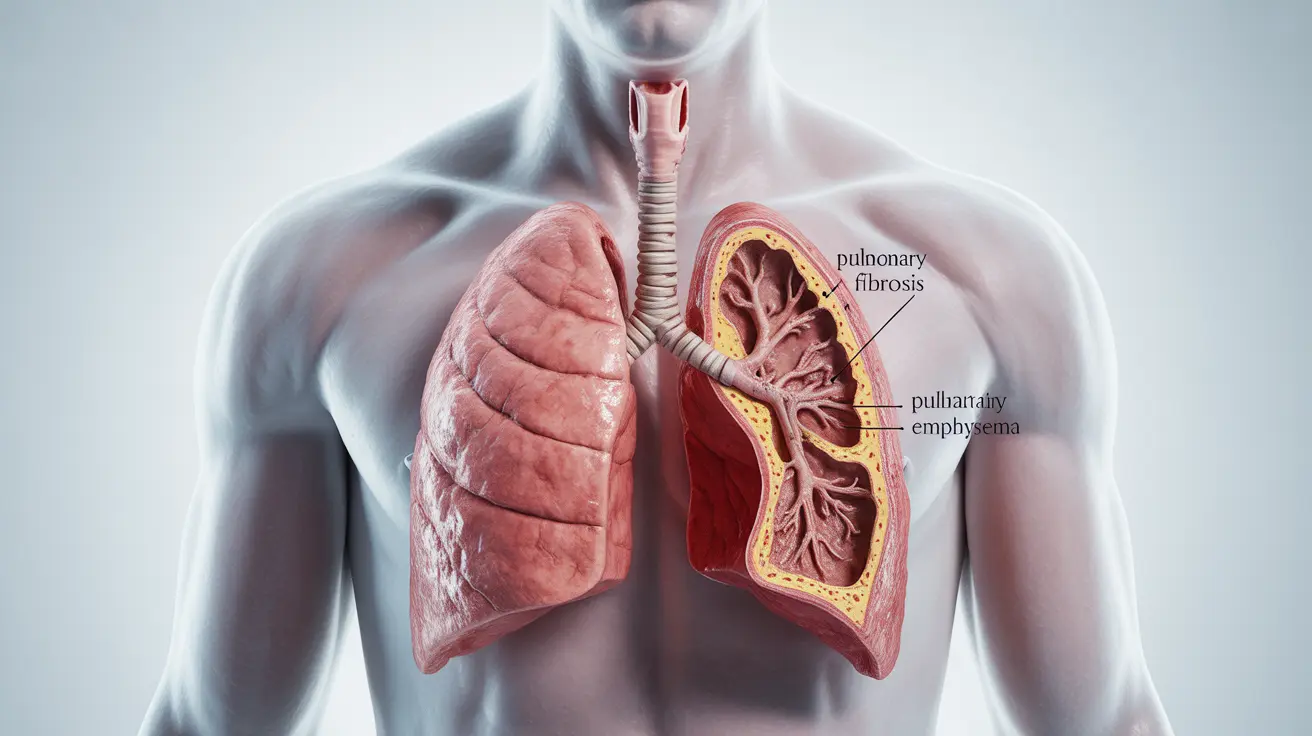
Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) is a serious lung condition that presents unique challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. Understanding the life expectancy and management options for this complex condition is crucial for those affected and their families.
This comprehensive guide explores the factors that influence life expectancy, essential symptoms, treatment approaches, and ways to manage this challenging combination of lung diseases.
Understanding CPFE and Life Expectancy
Life expectancy with emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis varies significantly among individuals, typically ranging from 2.1 to 8.5 years after diagnosis. Several factors influence survival rates, including:
- Age at diagnosis
- Overall health status
- Presence of complications
- Response to treatment
- Smoking history
- Severity of lung function impairment
Early diagnosis and proper management can help improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected by CPFE.
Key Symptoms and Diagnostic Process
Recognizing CPFE symptoms early is crucial for proper management. Common symptoms include:
- Progressive shortness of breath
- Chronic cough
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Fatigue
- Chest discomfort
Diagnosis typically involves multiple tests and procedures:
- High-resolution CT scans
- Pulmonary function tests
- Blood oxygen level measurements
- Exercise capacity tests
- Lung tissue biopsies (in some cases)
Treatment Approaches and Management Strategies
While there is no cure for CPFE, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression:
Medical Interventions
- Bronchodilators
- Anti-fibrotic medications
- Corticosteroids in specific cases
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lifestyle Modifications
Important lifestyle changes can help manage the condition:
- Immediate smoking cessation
- Regular exercise within limitations
- Proper nutrition
- Stress management
- Avoiding respiratory irritants
Impact of Smoking on CPFE
Smoking plays a significant role in both the development and progression of CPFE. It is the primary risk factor for this condition, and continued smoking after diagnosis can dramatically reduce life expectancy and quality of life.
Potential Complications
Several complications can impact life expectancy in CPFE patients:
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Right heart failure
- Acute exacerbations
- Respiratory infections
- Lung cancer risk
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average life expectancy for someone diagnosed with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE)? The average life expectancy after CPFE diagnosis typically ranges from 2.1 to 8.5 years, though individual cases vary significantly based on multiple factors including age, overall health, and response to treatment.
What are the main symptoms to look out for in CPFE, and how is it diagnosed? Key symptoms include progressive breathlessness, chronic cough, and reduced exercise tolerance. Diagnosis involves high-resolution CT scans, pulmonary function tests, and sometimes lung biopsies to confirm the presence of both conditions.
What treatment options are available to manage emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis when they occur together? Treatment options include bronchodilators, anti-fibrotic medications, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications. The approach is typically individualized based on specific symptoms and disease severity.
How does smoking affect the risk and progression of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema? Smoking is the primary risk factor for CPFE and significantly accelerates disease progression. Immediate smoking cessation is crucial for improving outcomes and life expectancy.
What complications can shorten life expectancy in patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema? Major complications that can impact life expectancy include pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure, acute exacerbations, respiratory infections, and increased risk of lung cancer.
Managing CPFE requires a comprehensive approach and close cooperation with healthcare providers. While the condition presents significant challenges, proper treatment and lifestyle modifications can help improve quality of life and potentially extend survival.