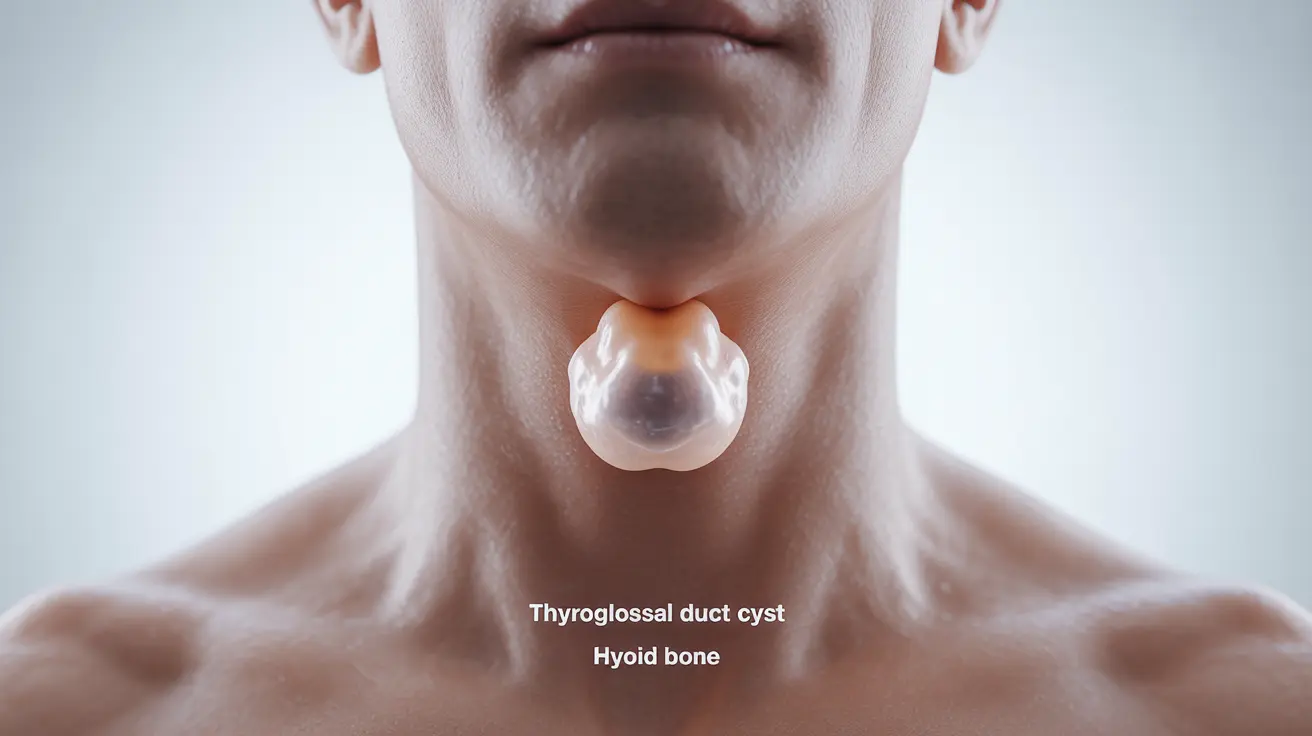
Finding a lump in your neck can be concerning, especially when it's located above the Adam's apple and under the chin. One common cause of such lumps is a thyroglossal duct cyst, a congenital condition that develops during embryonic development. Understanding this condition, its symptoms, and treatment options can help ease concerns and guide appropriate medical care.
While these cysts are present from birth, they may not become noticeable until childhood or even adulthood. They typically appear as smooth, soft masses in the middle of the neck that move when swallowing or sticking out the tongue.
What Is a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst?
A thyroglossal duct cyst forms along the path where the thyroid gland descended during fetal development. During embryonic development, the thyroid gland starts near the base of the tongue and moves down to its final position in the neck. The path it takes, called the thyroglossal duct, usually disappears after the thyroid reaches its destination. When this duct fails to close completely, fluid-filled cysts can develop.
Signs and Symptoms
The most notable sign of a thyroglossal duct cyst is a visible lump above the Adam's apple and under the chin. These cysts typically have specific characteristics:
- Painless unless infected
- Round and smooth to the touch
- Mobile, especially when swallowing or extending the tongue
- Located in the midline of the neck
- May gradually increase in size over time
Signs of Infection
When a thyroglossal duct cyst becomes infected, you may notice:
- Redness around the lump
- Tenderness or pain
- Warmth in the affected area
- Swelling
- Difficulty swallowing
- Potential drainage from the cyst
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose a thyroglossal duct cyst:
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI)
- Fine-needle aspiration in some cases
- Movement tests during swallowing and tongue protrusion
Treatment Options
Treatment approaches vary depending on the size of the cyst, presence of infection, and associated symptoms:
Conservative Management
For small, uninfected cysts that aren't causing problems, doctors may recommend monitoring the condition. However, most medical professionals advocate for removal, as these cysts rarely go away on their own and may become infected.
Infection Treatment
If the cyst becomes infected, treatment typically involves:
- Antibiotics to clear the infection
- Pain management
- Waiting for the infection to resolve before considering surgery
Surgical Treatment
The definitive treatment for a thyroglossal duct cyst is surgical removal through a procedure called the Sistrunk operation. This involves:
- Removing the cyst
- Excising the middle portion of the hyoid bone
- Removing the tract leading to the base of the tongue
- Creating a small incision in the neck
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a lump above the Adam's apple under the chin that moves when swallowing or sticking out the tongue?
A moving lump in this location is often a thyroglossal duct cyst, which develops from remnants of embryonic tissue that should have disappeared during fetal development. The movement during swallowing or tongue extension is a characteristic feature of these cysts.
What are the common symptoms of a thyroglossal duct cyst and how can I tell if it is infected?
Common symptoms include a painless, smooth lump in the middle of the neck that moves with swallowing. If infected, the cyst may become painful, red, and swollen, possibly accompanied by fever and difficulty swallowing.
How is a thyroglossal duct cyst diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors diagnose these cysts through physical examination, observing cyst movement during swallowing and tongue protrusion, and imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to confirm the diagnosis and plan treatment.
What treatment options are available for a thyroglossal duct cyst, and when is surgery needed?
While small, uninfected cysts may be monitored, the definitive treatment is surgical removal through the Sistrunk procedure. Surgery is typically recommended to prevent future infections and complications, even for asymptomatic cysts.
Can a lump like a thyroglossal duct cyst cause difficulty breathing or swallowing?
Yes, particularly large or infected thyroglossal duct cysts can cause difficulty breathing or swallowing. If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention as they may indicate a need for urgent treatment.