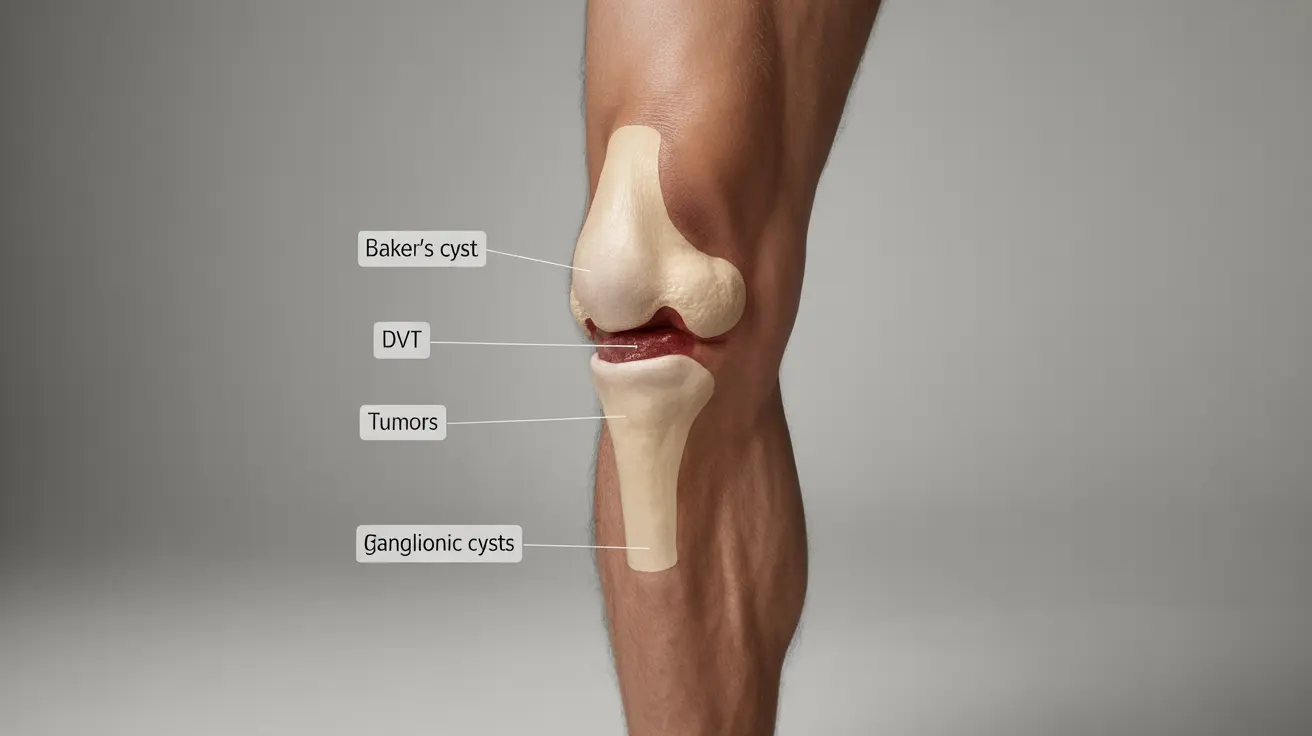
Finding a lump behind your knee can be concerning, especially when you're unsure of its cause. While Baker's cysts are common, several other conditions can create swelling or masses in this area. Understanding these different causes and knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
This comprehensive guide explores various conditions that can cause lumps behind the knee, helping you understand when to be concerned and what treatment options are available.
Common Causes of Posterior Knee Lumps
Several conditions can cause lumps behind the knee, each with distinct characteristics:
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Blood clots forming in the deep veins can cause swelling and tenderness behind the knee. This condition requires immediate medical attention as it can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Tumors
Both benign and malignant tumors can develop behind the knee, including:
- Lipomas (fatty tissue growths)
- Soft tissue sarcomas
- Synovial cell tumors
Ganglionic Cysts
These fluid-filled lumps develop from joint or tendon tissue and can appear suddenly behind the knee.
Inflammatory Conditions
Various forms of arthritis and inflammatory conditions can cause swelling behind the knee, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Bursitis
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to determine the exact cause of a knee lump:
Physical Examination
Doctors will assess the lump's size, consistency, mobility, and whether it causes pain or affects movement.
Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- CT scan
- X-rays
Warning Signs and Emergency Symptoms
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe pain
- Rapid swelling
- Redness and warmth
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever
- Limited knee mobility
Treatment Approaches
Treatment varies depending on the underlying cause:
Conservative Management
Many knee lumps respond to non-invasive treatments:
- Rest and elevation
- Ice therapy
- Compression
- Anti-inflammatory medications
Medical Interventions
More serious conditions may require:
- Prescription medications
- Fluid aspiration
- Surgical removal
- Physical therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common causes of a lump behind the knee if it's not a Baker's cyst?
Common causes include deep vein thrombosis (DVT), ganglionic cysts, lipomas, inflammatory conditions like arthritis, and various types of benign or malignant tumors. Each condition has distinct characteristics and requires different treatment approaches.
How can doctors tell the difference between a Baker's cyst and other serious conditions like blood clots or tumors behind the knee?
Doctors use a combination of physical examination and imaging studies such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans to differentiate between conditions. They also consider factors like the lump's consistency, mobility, associated symptoms, and your medical history.
What symptoms should make me seek urgent medical care for a lump behind my knee?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, rapid swelling, redness and warmth, difficulty breathing, fever, or significantly limited knee mobility. These symptoms could indicate serious conditions requiring prompt treatment.
What treatment options are available for lumps behind the knee that are not Baker's cysts?
Treatment options range from conservative approaches like rest, ice, compression, and anti-inflammatory medications to more intensive interventions such as fluid aspiration, surgical removal, or specific treatments targeting the underlying cause.
Can a lump behind the knee cause complications if left untreated, and how can these be prevented?
Yes, untreated knee lumps can lead to complications depending on their cause. DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, while untreated tumors may grow or spread. Prevention involves prompt medical evaluation, following prescribed treatments, and regular monitoring of any changes in the lump's size or associated symptoms.