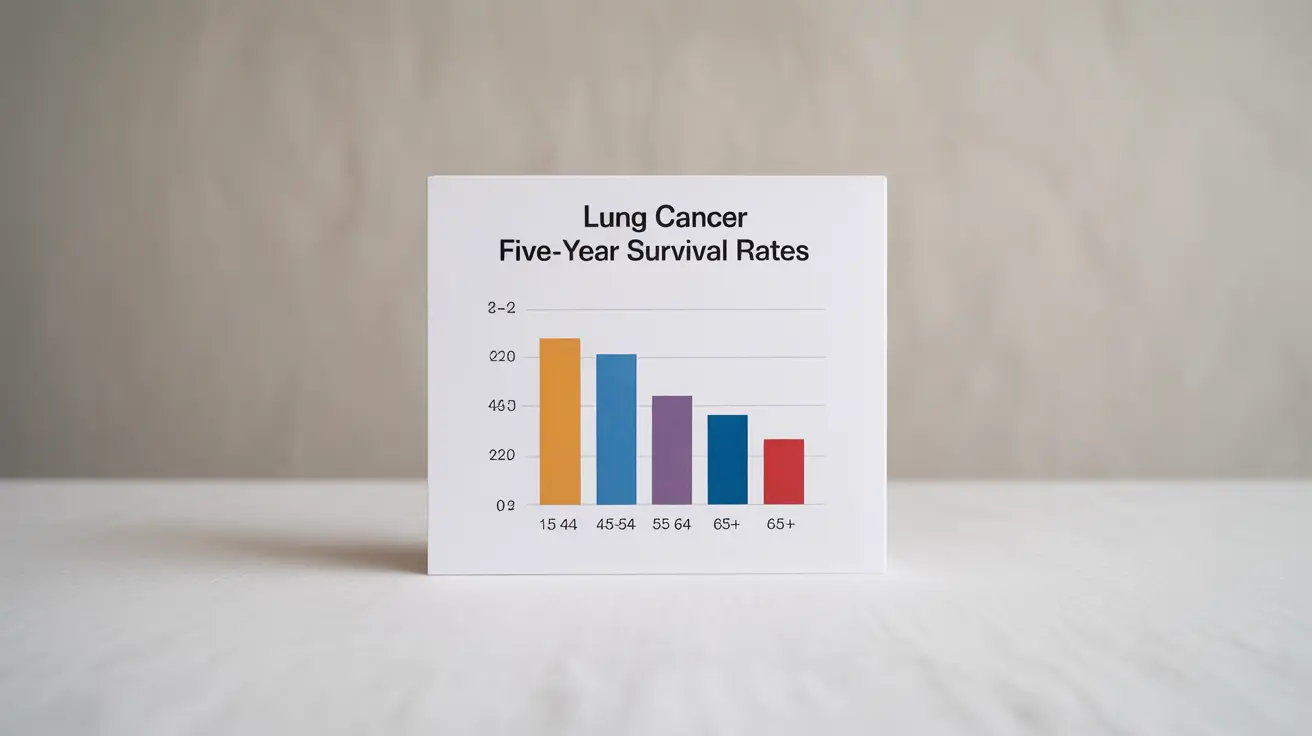
When diagnosed with lung cancer, understanding survival rates across different age groups can help patients and their families better prepare for treatment decisions and set realistic expectations. These statistics, while important, represent averages based on historical data and don't predict individual outcomes.
Age plays a significant role in lung cancer survival rates, influencing both treatment options and overall prognosis. Let's explore how age impacts survival rates and what factors contribute to these differences.
Age-Related Survival Rate Patterns
Research shows that lung cancer survival rates typically vary significantly across age groups. Younger patients generally have higher survival rates compared to older adults, though individual outcomes can vary considerably based on multiple factors.
Survival Rates in Different Age Groups
The five-year survival rates for lung cancer patients show distinct patterns across age brackets:
- Ages 15-44: Generally higher survival rates
- Ages 45-54: Moderately good survival rates
- Ages 55-64: Slightly lower survival rates
- Ages 65 and older: Generally lower survival rates
Factors Affecting Survival Rates in Older Adults
Several key factors contribute to lower survival rates in older lung cancer patients:
- Decreased organ function and recovery capacity
- Higher likelihood of multiple health conditions
- Reduced tolerance for aggressive treatments
- Delayed diagnosis due to symptom overlap with other conditions
- Complex medication interactions
Treatment Considerations Across Age Groups
Treatment approaches often vary based on age and overall health status. Younger patients may receive more aggressive treatment options, while older adults might require modified approaches:
Treatment Options for Younger Patients
Younger patients often receive:
- Combined therapy approaches
- More aggressive surgical interventions
- Higher doses of chemotherapy
- Innovative treatment protocols
- Clinical trial opportunities
Treatment Modifications for Older Adults
Older patients may receive:
- Modified treatment intensities
- Targeted therapy options
- Carefully balanced medication plans
- Supportive care focus
- Quality of life considerations
Advanced Stage Lung Cancer and Age
Stage 4 lung cancer presents unique challenges across different age groups. While survival rates are generally lower for advanced-stage disease, age continues to play a significant role in treatment outcomes and survival statistics.
Impact of Overall Health on Survival
General health status significantly influences lung cancer survival rates, particularly in older adults. Key factors include:
- Presence of other medical conditions
- Overall physical fitness
- Nutritional status
- Immune system function
- Social support systems
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the five-year lung cancer survival rates for different age groups?
Survival rates vary significantly by age group, with younger patients (15-44) generally showing higher survival rates compared to older age groups. Rates typically decrease progressively with age, particularly after 65.
Why do lung cancer survival rates decrease as people get older?
Survival rates decrease with age due to factors including reduced physical resilience, presence of multiple health conditions, decreased tolerance for aggressive treatments, and more complex medical management needs.
How does age affect treatment options and outcomes for lung cancer patients?
Age influences treatment selection and outcomes through factors like physical stamina, organ function, medication tolerance, and recovery capacity. Younger patients often receive more aggressive treatments, while older patients may require modified approaches.
What are the survival rates for advanced stage (stage 4) lung cancer by age?
Stage 4 lung cancer survival rates are generally lower across all age groups but tend to be relatively better in younger patients due to their ability to tolerate more aggressive treatments and better overall health status.
How do overall health and other medical conditions influence lung cancer survival in older adults?
Overall health and existing medical conditions significantly impact survival rates in older adults. Factors like cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and the presence of other chronic conditions can affect treatment options and outcomes.