Open heart surgery is a major medical procedure that can significantly impact lung function during the recovery period. Understanding the potential lung complications and how to manage them is crucial for patients and their caregivers to ensure optimal recovery and prevent respiratory issues.
While temporary breathing difficulties are common after cardiac surgery, being informed about possible lung problems and their management can help patients take proactive steps toward better recovery outcomes. This guide explores the most common respiratory challenges following open heart surgery and provides essential information for managing these complications.
Common Lung Complications After Open Heart Surgery
Several respiratory issues can develop following cardiac surgery, affecting patients' breathing and recovery process:
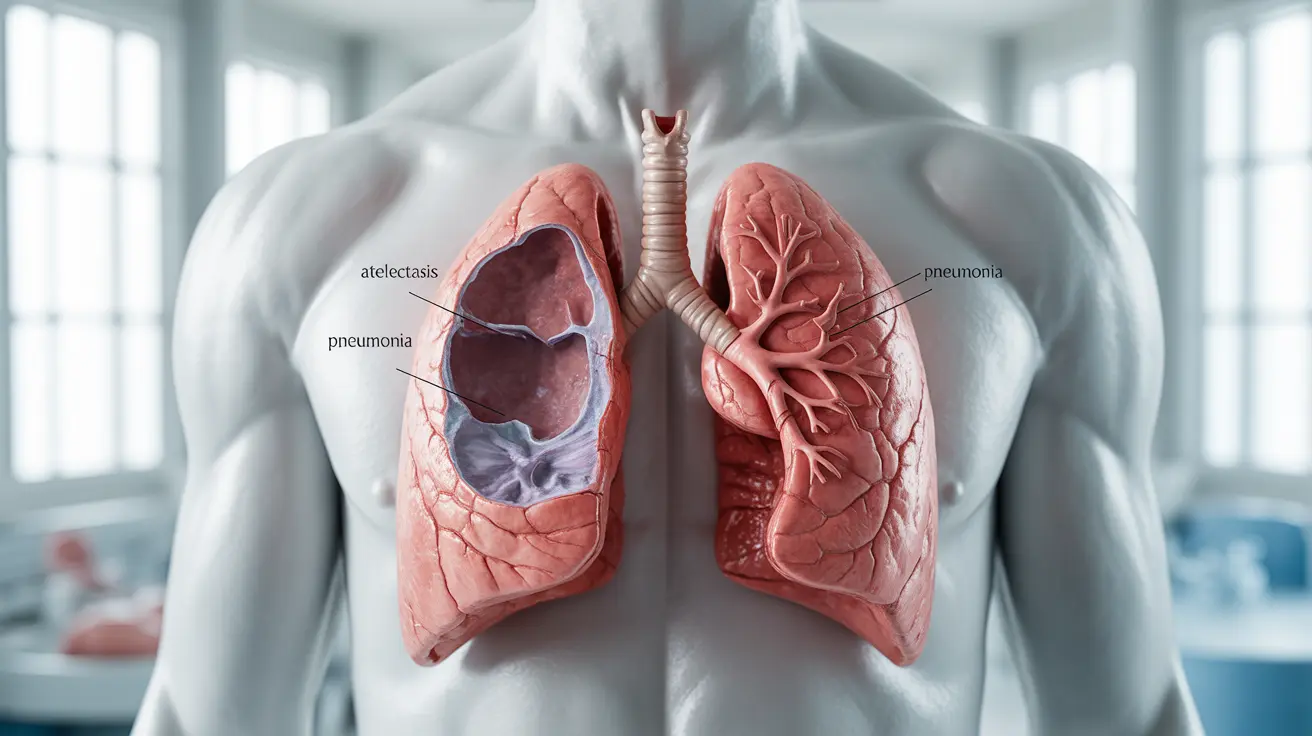
Atelectasis
Atelectasis, the most common post-surgical lung complication, occurs when portions of the lungs collapse or become compressed. This condition develops when air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs don't fully expand, often due to shallow breathing and reduced mobility after surgery.
Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion involves fluid accumulation between the lungs and chest wall. This condition can cause breathing difficulties and chest discomfort, requiring careful monitoring and sometimes medical intervention for resolution.
Pneumonia
Post-operative pneumonia is a serious concern that can develop when bacteria accumulate in the lungs. Patients with reduced lung function or those who cannot clear secretions effectively are at higher risk for this complication.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Key symptoms that may indicate lung complications include:
- Persistent shortness of breath
- Sharp chest pain when breathing
- Productive cough with colored sputum
- Fever or chills
- Rapid breathing
- Unusual fatigue during light activities
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Lung function typically improves gradually after open heart surgery. Most patients experience significant improvement within 6-8 weeks, though complete recovery may take several months. The timeline varies based on individual factors such as age, overall health, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Breathing Exercises
Regular breathing exercises are essential for preventing lung complications:
- Incentive spirometry as directed by healthcare providers
- Deep breathing exercises every hour while awake
- Controlled coughing techniques to clear secretions
Physical Activity
Gradual increase in physical activity helps improve lung function:
- Early mobilization as permitted by medical team
- Regular walking sessions
- Structured cardiac rehabilitation program participation
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can support better lung function:
- Maintaining good posture
- Avoiding smoking and second-hand smoke
- Staying well-hydrated
- Following a healthy diet
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the common lung problems that cause shortness of breath after open heart surgery? The most common lung problems include atelectasis (collapsed air sacs), pleural effusion (fluid accumulation), and pneumonia. These conditions can cause breathing difficulties and require proper medical attention and management.
2. How can atelectasis be prevented and treated following open heart surgery? Atelectasis can be prevented through regular deep breathing exercises, incentive spirometry, early mobilization, and proper positioning. Treatment includes continued breathing exercises, chest physiotherapy, and sometimes supplemental oxygen.
3. What symptoms indicate pleural effusion or pneumonia after open heart surgery? Symptoms include increased shortness of breath, chest pain when breathing, fever, productive cough with colored sputum, and decreased exercise tolerance. Any of these symptoms should be reported to healthcare providers immediately.
4. How long does lung function typically take to recover after open heart surgery? Most patients see significant improvement in lung function within 6-8 weeks after surgery. However, complete recovery may take 3-6 months, depending on individual factors and dedication to rehabilitation protocols.
5. What steps can patients take to reduce the risk of lung complications after open heart surgery? Patients should follow prescribed breathing exercises, maintain good posture, participate in early mobilization, stay well-hydrated, avoid smoking, and actively participate in their cardiac rehabilitation program to reduce complications.