Lupus affects different skin tones in unique ways, and recognizing its manifestations on black skin requires specific attention and understanding. For individuals with darker skin tones, lupus rashes can present distinct challenges in both identification and treatment, making it crucial to understand these differences for proper diagnosis and care.
This comprehensive guide explores how lupus-related skin conditions appear on black skin, effective treatment approaches, and why certain populations may be more vulnerable to this autoimmune condition.
Distinctive Features of Lupus Rash on Black Skin
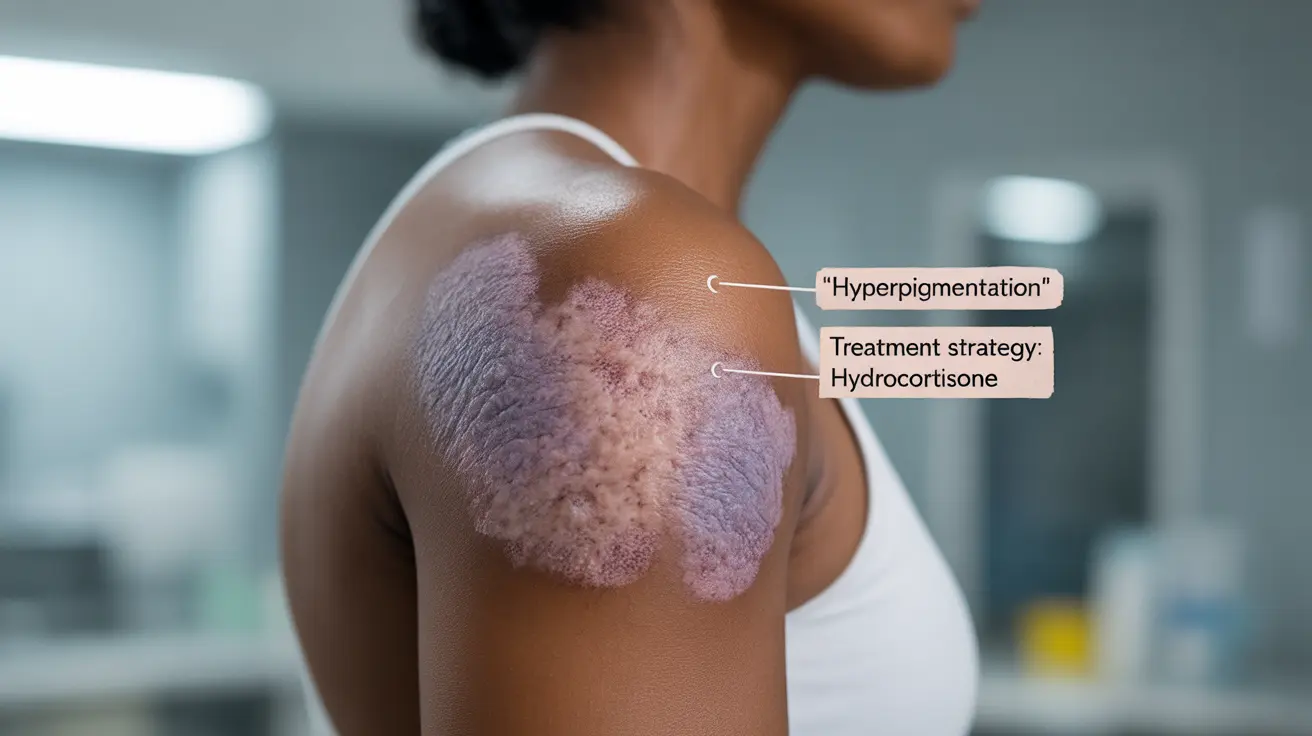
Lupus rashes on black skin often present differently than on lighter skin tones, which can sometimes lead to delayed diagnosis. The classic butterfly rash may appear as darker patches or have a violet-toned discoloration rather than the typical redness seen on lighter skin.
Key characteristics of lupus rashes on black skin include:
- Hyperpigmented (darker) patches
- Purple or violet-toned discoloration
- Less visible erythema (redness)
- More prominent scaling
- Increased risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
Impact of Sun Exposure on Dark Skin
While melanin provides some natural protection against UV radiation, people with darker skin tones are not immune to sun-triggered lupus symptoms. Sun exposure can still:
- Trigger new lupus rashes
- Worsen existing skin lesions
- Lead to hyperpigmentation
- Cause systemic flares
Protection from sun exposure remains crucial for all individuals with lupus, regardless of skin tone.
Types of Lupus Rashes and Their Presentation
Discoid Lupus
Discoid lupus on black skin typically appears as thick, scaly patches that may be darker than the surrounding skin. These lesions can lead to permanent scarring and changes in pigmentation if not treated promptly.
Acute Cutaneous Lupus
The butterfly rash characteristic of acute cutaneous lupus may appear as darker, violaceous patches across the cheeks and nose in individuals with black skin. These rashes are usually photosensitive and can worsen with sun exposure.
Treatment Strategies and Prevention
Effective treatment of lupus rashes on black skin requires a comprehensive approach:
- Topical corticosteroids for active inflammation
- Antimalarial medications for systemic control
- Careful sun protection measures
- Regular dermatological monitoring
- Early intervention to prevent scarring
Preventing Scarring and Discoloration
Special attention must be given to preventing long-term skin changes in darker skin tones. This includes:
- Prompt treatment of active lesions
- Use of appropriate skincare products
- Regular moisturizing
- Strict sun protection
- Early intervention for any new rashes
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a lupus rash look like on black skin compared to lighter skin tones?
On black skin, lupus rashes often appear as darker patches or have a purple/violet tone, rather than the red appearance typically seen on lighter skin. The scaling and texture changes may be more prominent, while traditional redness might be less noticeable.
How can lupus rashes on black skin be treated to prevent discoloration and scarring?
Treatment involves prompt use of topical corticosteroids, antimalarial medications, strict sun protection, and regular moisturizing. Early intervention is crucial to prevent permanent scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Why is lupus more common and severe in African American women?
The higher prevalence and severity in African American women may be linked to genetic factors, hormonal influences, and environmental triggers. Socioeconomic factors affecting access to healthcare can also impact disease outcomes.
How does sun exposure affect lupus rashes in people with darker skin?
Despite having more natural sun protection from melanin, people with darker skin can still experience sun-triggered lupus flares. UV exposure can worsen existing rashes and trigger new lesions, making sun protection essential.
What are the differences between discoid lupus and acute cutaneous lupus rashes on black skin?
Discoid lupus typically presents as thick, scaly patches that can lead to scarring and permanent pigment changes. Acute cutaneous lupus appears as darker, violet-toned patches, particularly in the butterfly rash pattern, and is more photosensitive but less likely to scar.