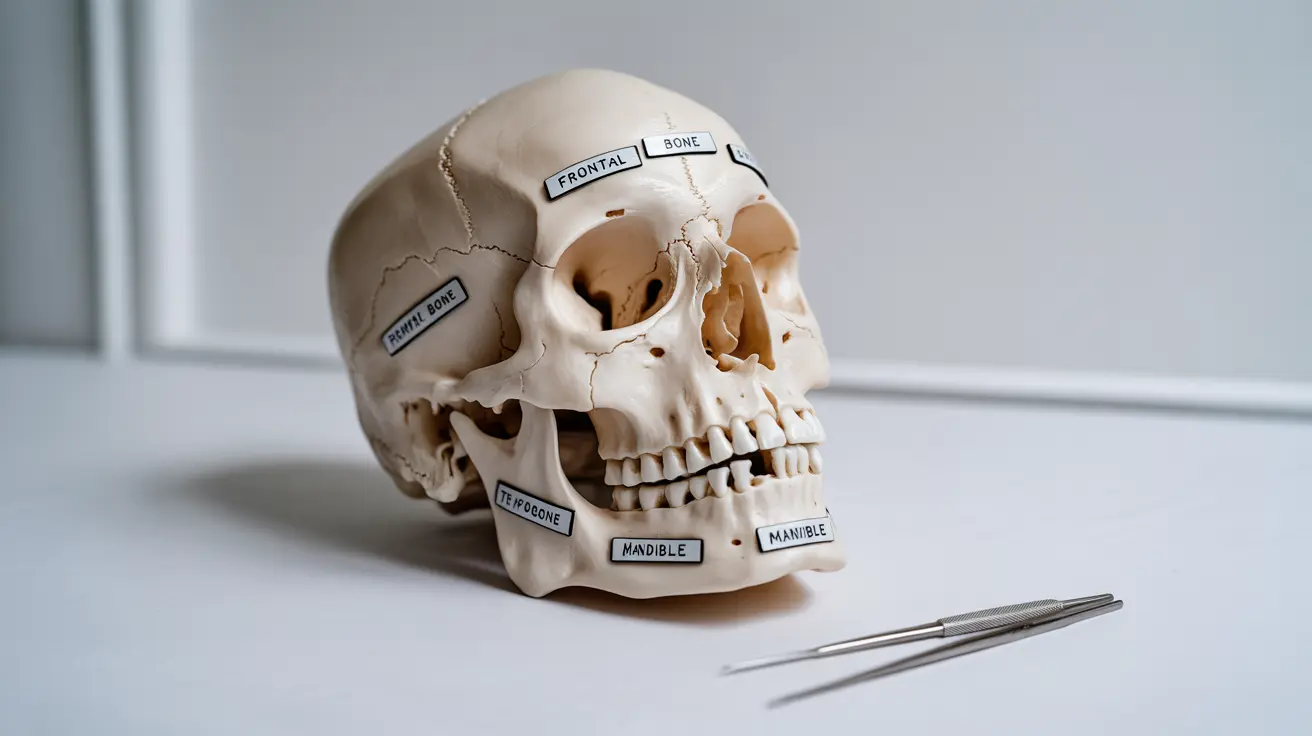
The human skull is a remarkable structure composed of multiple bones that work together to protect our brain and support vital sensory organs. This intricate assembly of bones not only safeguards crucial neural tissue but also provides the framework for our facial features and enables essential functions like chewing and speech.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various bones that make up the human skull, their unique characteristics, and their vital roles in maintaining our health and functionality.
The Two Main Components of the Skull
The human skull is divided into two primary sections: the cranium and the facial bones. Each section serves distinct purposes and contains specific bone structures essential for our survival and daily functions.
The Cranium: Nature's Protective Vault
The cranium, also known as the braincase, consists of eight major bones that form a protective shell around the brain. These bones include:
- Frontal bone (forehead)
- Occipital bone (back and base of skull)
- Two parietal bones (top and sides)
- Two temporal bones (lower sides)
- Sphenoid bone (central skull base)
- Ethmoid bone (between the eyes)
The Facial Skeleton: Framework for Features
The facial skeleton comprises 14 bones that create our unique facial features and support vital functions. Key facial bones include:
- Two maxillae (upper jaw)
- Two zygomatic bones (cheekbones)
- Two nasal bones
- Two palatine bones
- Two lacrimal bones
- Vomer
- Two inferior nasal conchae
- Mandible (lower jaw)
Critical Connections: Skull Sutures
Sutures are the fibrous joints that connect the skull bones. These unique connections allow for slight movement and growth during development while maintaining the skull's protective integrity. The major sutures include:
- Coronal suture
- Sagittal suture
- Lambdoid suture
- Squamous suture
Specialized Structures Within the Skull
The Orbital Cavity
The eye sockets, or orbital cavities, are formed by seven different bones working together to protect the eyes and associated structures. These include portions of the frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, lacrimal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones.
The Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a complex space formed by multiple bones, including the nasal bones, maxillae, palatine bones, and vomer. This structure supports respiratory function and our sense of smell.
The Unique Mandible
The mandible stands out as the only movable bone in the skull. This distinctive feature allows for essential functions like speaking, chewing, and facial expressions. It connects to the temporal bones through the temporomandibular joints (TMJ).
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the major bones that make up the human skull and what are their functions?
The human skull consists of 22 bones total: 8 cranial bones that protect the brain and 14 facial bones that form facial features. The cranial bones include the frontal, occipital, two parietal, two temporal, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones. The facial bones include the mandible, maxillae, zygomatic bones, and others that support sensory organs and enable functions like eating and breathing.
How are the cranial bones different from the facial bones in the skull?
Cranial bones form a protective case around the brain and are typically larger and more curved. Facial bones are generally smaller and more intricate, designed to support sensory organs and create facial features. Unlike cranial bones, some facial bones, particularly the mandible, are mobile to enable essential functions.
What role do sutures play in the structure of the human skull?
Sutures are fibrous joints that connect skull bones, allowing for minor movement and growth during development. They act as shock absorbers and permit the skull to expand during brain growth in childhood. The major sutures include the coronal, sagittal, lambdoid, and squamous sutures.
Which bones form the eye socket (orbit) and nasal cavity in the skull?
The eye socket is formed by seven bones: parts of the frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, lacrimal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones. The nasal cavity is primarily formed by the nasal bones, maxillae, palatine bones, and vomer, creating a complex structure for breathing and smell.
Why is the mandible unique compared to other bones of the skull?
The mandible is unique as it's the only freely movable bone in the skull. It connects to the temporal bones via the temporomandibular joints (TMJ), allowing for movement necessary in speaking, chewing, and making facial expressions. This mobility distinguishes it from all other skull bones, which are fixed together by sutures.