The male urethra plays a vital role in both urinary and reproductive health, serving as the essential passageway for both urine and semen. This remarkable anatomical structure extends from the bladder to the tip of the penis, with distinct regions that each serve specific functions in maintaining men's health.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the male urethra is crucial for recognizing potential health issues and maintaining optimal urological health. Let's explore the different parts of this important structure and how it contributes to everyday bodily functions.
Anatomical Structure and Location
The male urethra consists of four main segments, each with unique characteristics and functions:
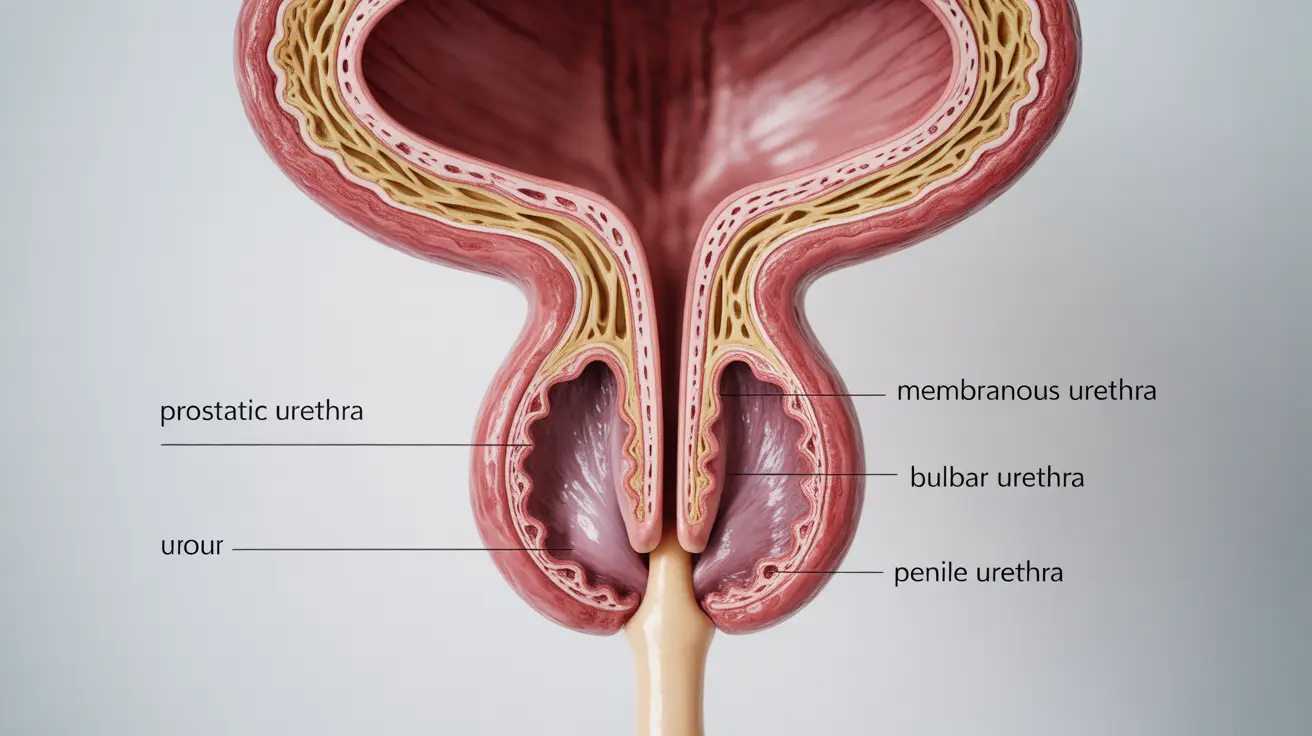
Prostatic Urethra
Located at the uppermost portion, the prostatic urethra passes through the prostate gland. This segment receives reproductive fluids from the prostate and serves as a crucial junction for both urinary and reproductive systems.
Membranous Urethra
This short but important segment passes through the urogenital diaphragm and is surrounded by the external urethral sphincter, which controls voluntary urination.
Bulbar Urethra
Beginning at the perineum, the bulbar urethra curves forward through the bulb of the penis. This segment receives secretions from the bulbourethral glands during sexual arousal.
Penile (Spongy) Urethra
The longest segment, running through the corpus spongiosum of the penis to the external urethral meatus at the tip of the penis. This portion is essential for directing both urine flow and ejaculation.
Functional Role in the Body
Urination Process
The male urethra works in conjunction with the bladder and sphincter muscles to control urination. The internal sphincter automatically prevents urine leakage, while the external sphincter allows for conscious control of urination.
Sexual Function
During sexual activity, the urethra transitions from a urinary passage to a reproductive conduit. Special mechanisms prevent the mixing of urine and semen, ensuring proper function during both processes.
Common Medical Conditions
Urethral Strictures
Narrowing of the urethra can occur due to injury, infection, or inflammation, leading to difficulty urinating and increased risk of urinary tract infections.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra, often caused by infections, can result in painful urination and discharge. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications.
Impact of Prostate Issues
Enlarged prostate (BPH) or prostate cancer can compress the prostatic urethra, leading to urinary symptoms and requiring medical attention.
Prevention and Maintenance
Maintaining urethral health involves several key practices:
- Adequate hydration
- Proper hygiene
- Regular medical check-ups
- Prompt attention to unusual symptoms
- Protection against sexually transmitted infections
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four main parts of the male urethra and where are they located?
The male urethra consists of the prostatic urethra (passing through the prostate), membranous urethra (through the urogenital diaphragm), bulbar urethra (in the bulb of the penis), and penile urethra (running through the penis to its tip).
How does the male urethra function in both urination and ejaculation?
The male urethra serves as a passage for both urine and semen, with specialized sphincters and timing mechanisms preventing the mixing of these fluids. During urination, it channels urine from the bladder, while during sexual activity, it conducts semen from the reproductive organs.
What common medical problems can affect different parts of the male urethra?
Common issues include urethral strictures (narrowing), urethritis (inflammation), urinary tract infections, and complications from enlarged prostate. These conditions can affect different segments of the urethra and require specific treatments.
What is the role of the sphincters in the male urethra and how do they control urine flow?
The male urethra has two main sphincters: the internal sphincter (involuntary control) near the bladder neck and the external sphincter (voluntary control) in the membranous region. These muscles work together to maintain continence and control urination.
How can issues like urethral strictures or prostate enlargement impact the function of the male urethra?
Urethral strictures can narrow the urinary passage, causing difficulty urinating and increasing infection risk. Prostate enlargement can compress the prostatic urethra, leading to reduced urine flow, frequent urination, and other urinary symptoms requiring medical attention.