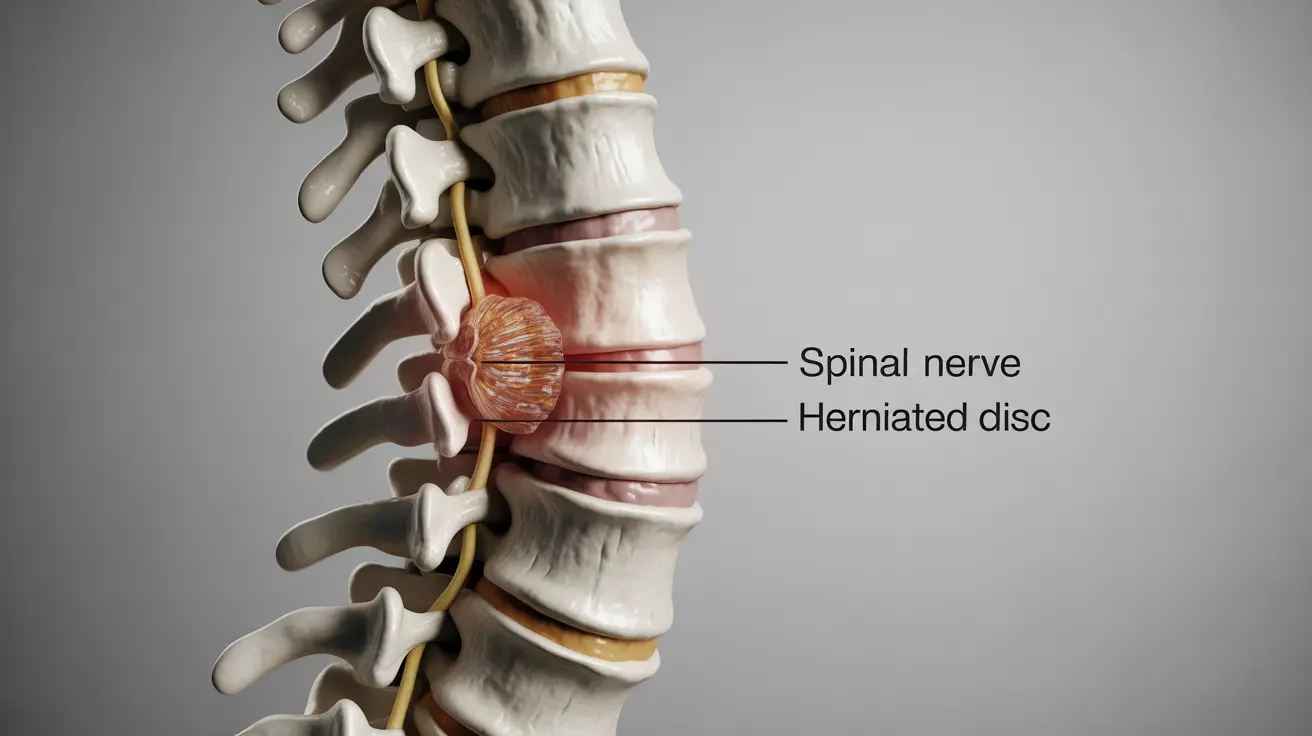
A slipped disc, also known as a herniated disc or disc prolapse, occurs when one of the cushioning discs between the vertebrae in your spine pushes out of position, potentially pressing on nearby nerves. This common spinal condition can cause significant discomfort and impact daily activities, but understanding its symptoms and treatment options is crucial for effective management.
While a slipped disc can be concerning, many people recover with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about managing this condition and preventing future occurrences.
Understanding Slipped Disc Symptoms and Effects
A slipped disc can manifest through various symptoms, depending on its location and severity. Common indicators include:
- Sharp, shooting pain that may radiate down arms or legs
- Numbness or tingling sensations in affected areas
- Muscle weakness
- Pain that worsens with certain movements
- Reduced range of motion
The location of the slipped disc determines which parts of the body are affected. For instance, a cervical (neck) disc herniation may cause symptoms in the shoulders and arms, while a lumbar (lower back) herniation typically affects the legs and feet.
Diagnosis and Medical Imaging
Healthcare providers typically begin with a thorough physical examination and medical history review. During the examination, they may:
- Test muscle strength and reflexes
- Assess pain levels and patterns
- Evaluate walking ability and posture
- Check for numbness in specific areas
While many cases can be diagnosed through physical examination alone, imaging tests may be necessary for confirmation or to rule out other conditions. MRI scans are particularly useful as they provide detailed images of the spine and can clearly show disc problems.
Conservative Treatment Approaches
Most slipped disc cases respond well to non-surgical treatments. Common conservative approaches include:
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design specific exercises to strengthen core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote proper posture. These exercises help reduce pressure on the affected disc and prevent future problems.
Medication Management
Various medications may help manage pain and inflammation:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Muscle relaxants (when prescribed)
- Short-term prescription pain medication (in severe cases)
Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief through complementary treatments such as:
- Acupuncture
- Chiropractic care
- Massage therapy
- Heat and cold therapy
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is typically considered only when conservative treatments fail to provide relief after several weeks or months, or when there are serious complications such as severe nerve compression or loss of bladder control.
Common surgical procedures include:
- Microdiscectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal fusion (in select cases)
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Several lifestyle changes can help prevent slipped discs and reduce the risk of recurrence:
- Maintaining good posture
- Regular exercise focusing on core strength
- Proper lifting techniques
- Weight management
- Ergonomic workplace setup
- Regular stretching routines
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a slipped disc and how do they affect the body?
Common symptoms include sharp, radiating pain, numbness or tingling in affected areas, muscle weakness, and pain that worsens with specific movements. The effects depend on the disc's location – cervical disc problems affect the upper body, while lumbar disc issues impact the lower body.
How is a slipped disc diagnosed and when is imaging like an MRI necessary?
Diagnosis typically begins with a physical examination and medical history review. MRI imaging becomes necessary when symptoms are severe, don't improve with initial treatment, or when surgery might be needed. It's also used to rule out other conditions or confirm the exact location and severity of the disc problem.
What nonsurgical treatments are effective for managing slipped disc pain and symptoms?
Effective nonsurgical treatments include physical therapy, pain medication, anti-inflammatory drugs, and alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care. Rest, combined with gentle exercise and proper posture, often provides significant relief.
When is surgery recommended for a slipped disc, and what are the common surgical options?
Surgery is recommended when conservative treatments fail after several months, or when there are serious complications like severe nerve compression or loss of bladder control. Common surgical options include microdiscectomy, laminectomy, and in some cases, spinal fusion.
How can I prevent a slipped disc or reduce the risk of recurrence through lifestyle changes?
Prevention strategies include maintaining good posture, regular exercise focusing on core strength, proper lifting techniques, weight management, and using ergonomic furniture. Regular stretching and avoiding prolonged sitting can also help reduce risk.