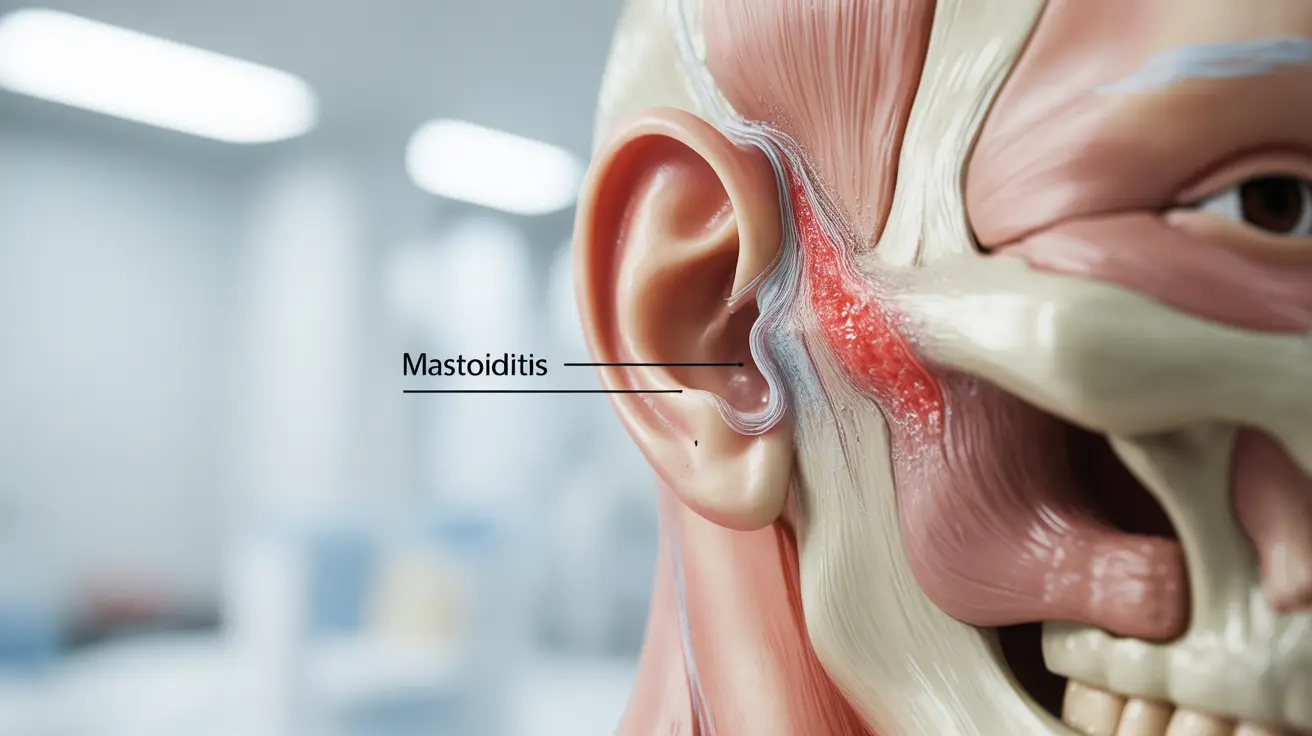
Mastoiditis in adults is a serious infection of the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. While less common in adults than children, this condition requires prompt medical attention to prevent potentially severe complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and successful management.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything adults need to know about mastoiditis, from recognizing early warning signs to understanding treatment approaches and potential complications.
Key Symptoms of Mastoiditis in Adults
Adult mastoiditis symptoms can be distinct and often develop after an untreated ear infection. The most common signs include:
- Severe ear pain that worsens over time
- Redness and swelling behind the ear
- Tenderness when touching the mastoid area
- Protruding ear from the affected side
- Persistent fever
- Drainage from the ear
- Hearing difficulties
Unlike typical ear infections, mastoiditis symptoms tend to be more severe and persist even with standard ear infection treatments. The pain is usually more intense and focused behind the ear rather than inside it.
Causes and Risk Factors
While acute otitis media (middle ear infection) is the most common cause of mastoiditis, other factors can contribute to its development in adults:
- Chronic ear infections
- Compromised immune system
- Previous ear surgery
- Cholesteatoma (abnormal skin cell growth in the middle ear)
- Upper respiratory tract infections
Risk factors that may increase susceptibility include:
- Smoking
- Allergies affecting the ears
- Anatomical abnormalities of the ear
- Regular exposure to water (swimmers)
- History of recurring ear infections
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing mastoiditis in adults involves several steps and specialized tests:
Physical Examination
Doctors will examine the ear canal, eardrum, and the area behind the ear for characteristic signs of infection and inflammation.
Imaging Tests
Several imaging options may be used:
- CT scan of the temporal bone
- MRI in certain cases
- X-rays of the mastoid area
Laboratory Tests
Additional testing may include:
- Culture of ear drainage
- Blood tests to check for infection markers
- Hearing tests to assess impact on auditory function
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for mastoiditis typically involves a comprehensive approach:
Conservative Treatment
Initial treatment usually includes:
- Intravenous antibiotics
- Pain management
- Regular monitoring of symptoms
- Ear cleaning and drainage care
Surgical Intervention
Surgery may be necessary when:
- Conservative treatment fails
- Complications develop
- There's extensive bone involvement
- Abscess formation occurs
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common mastoiditis symptoms in adults, and how do they differ from a regular ear infection? Adult mastoiditis symptoms include severe pain behind the ear, visible redness and swelling of the mastoid area, protruding ear, and fever. Unlike regular ear infections, these symptoms are more severe, focused behind rather than inside the ear, and often include visible external changes.
Can mastoiditis in adults be caused by something other than an ear infection, and what increases my risk of getting it? Yes, mastoiditis can be caused by cholesteatoma, chronic sinusitis, or traumatic injury to the mastoid area. Risk factors include compromised immunity, smoking, frequent swimming, and anatomical abnormalities of the ear.
How is mastoiditis diagnosed in adults, and what tests do doctors use to confirm it? Diagnosis involves physical examination, imaging studies (CT scan, MRI, or X-rays), and possibly laboratory tests including cultures of ear drainage and blood tests. Doctors may also perform hearing tests to assess any impact on auditory function.
What are the treatment options for mastoiditis in adults, and when is surgery needed? Treatment typically begins with intravenous antibiotics and pain management. Surgery becomes necessary when conservative treatment fails, complications develop, or there's significant bone involvement.
What serious complications can occur if mastoiditis in adults is left untreated, and when should I seek emergency care? Untreated mastoiditis can lead to serious complications including meningitis, brain abscess, facial nerve paralysis, and hearing loss. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe ear pain, fever, facial weakness, or changes in mental status.