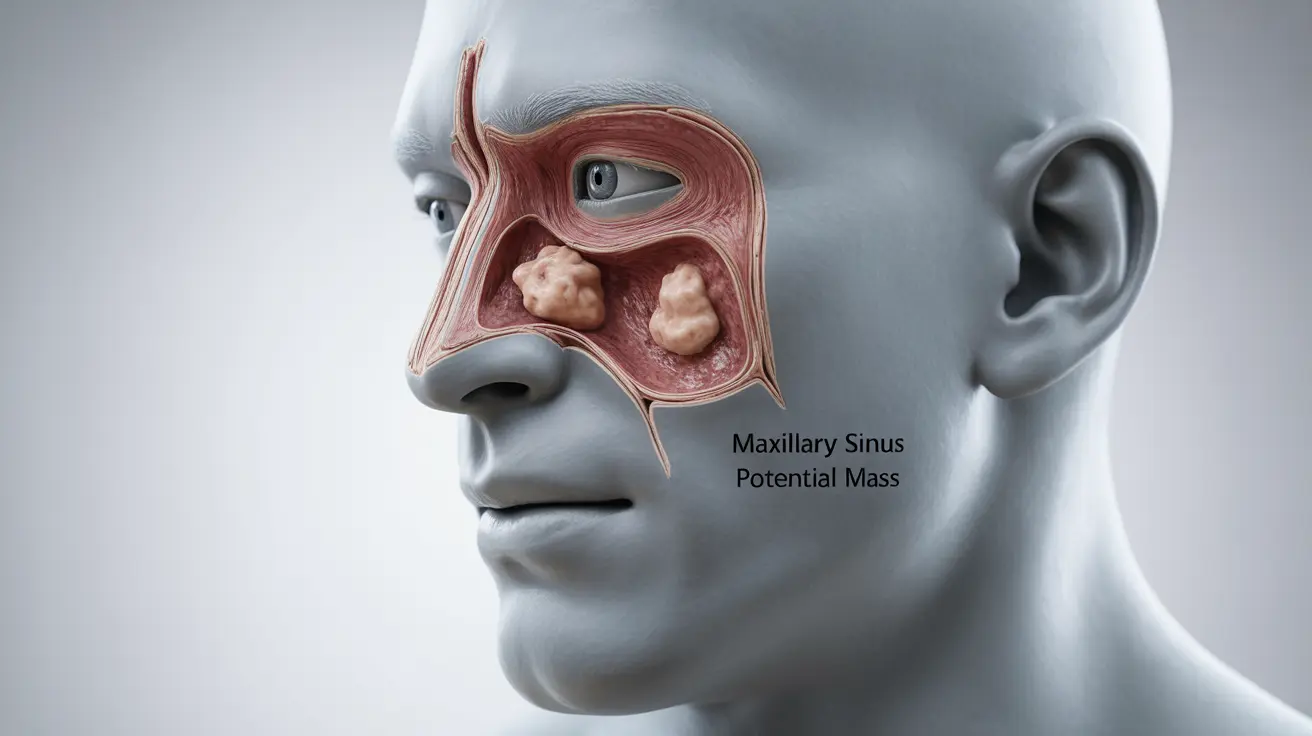
A maxillary sinus mass can be a concerning medical condition that develops in the maxillary sinuses, the largest of the paranasal sinuses located behind your cheekbones. These masses can range from benign growths to cancerous tumors, making early detection and proper medical evaluation crucial for optimal outcomes.
Understanding the signs, symptoms, and available treatment options for maxillary sinus masses is essential for anyone experiencing unusual symptoms in this area. This comprehensive guide will help you better understand this condition and know when to seek medical attention.
Signs and Symptoms of Maxillary Sinus Masses
Recognizing the early warning signs of a maxillary sinus mass is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent nasal congestion or blockage
- Recurring nosebleeds
- Facial pain or pressure
- Tooth pain in the upper jaw
- Chronic sinus infections
- Difficulty breathing through the nose
- Changes in sense of smell
More serious symptoms may develop as the mass grows, potentially indicating a more severe condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers use various diagnostic tools and procedures to identify and evaluate maxillary sinus masses:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will begin with a thorough physical examination of your face, nose, and mouth, looking for visible signs of abnormalities or asymmetry.
Imaging Studies
Several imaging techniques may be employed:
- CT (computed tomography) scans
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- PET (positron emission tomography) scans
- X-rays of the sinuses
Biopsy
A tissue sample may be necessary to determine if the mass is benign or malignant. This procedure is typically performed by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the type, size, and location of the maxillary sinus mass:
Conservative Management
For benign masses or mild cases, treatment may include:
- Monitoring through regular check-ups
- Medications to manage symptoms
- Nasal sprays or decongestants
Surgical Intervention
More severe cases may require surgical treatment:
- Endoscopic surgery
- Traditional open surgery
- Minimally invasive procedures
Additional Treatments
In cases of cancer, additional treatments might include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding risk factors can help in prevention and early detection:
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Exposure to industrial chemicals
- Chronic sinus infections
- Previous radiation exposure
- Family history of sinus cancers
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms that might indicate a maxillary sinus mass or cancer? Common symptoms include persistent nasal congestion, nosebleeds, facial pain, tooth pain in the upper jaw, and changes in sense of smell. Any persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
How is maxillary sinus cancer diagnosed and what tests are involved? Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, imaging studies (CT, MRI, or PET scans), and often a biopsy to determine the nature of the mass. Your doctor may also perform endoscopic examination of the sinuses.
What treatment options are available for maxillary sinus cancer at different stages? Treatment options vary by stage and may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches. Early-stage cancers might be treated with surgery alone, while advanced cases often require multiple treatment modalities.
Can a maxillary sinus mass cause facial numbness or changes in vision? Yes, as a mass grows, it can pressure nearby nerves and structures, potentially causing facial numbness, vision changes, or other neurological symptoms. These symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
What risk factors increase the likelihood of developing a maxillary sinus tumor? Key risk factors include smoking, exposure to industrial chemicals, chronic sinus infections, previous radiation exposure, and family history of sinus cancers. Avoiding these risk factors where possible can help reduce your risk.