Understanding safe melatonin dosage is crucial for anyone considering this popular sleep supplement. While melatonin is naturally produced by your body to regulate sleep cycles, supplemental melatonin requires careful attention to dosing to avoid potential adverse effects and ensure optimal benefits.
This comprehensive guide will explore safe melatonin dosages, signs of overconsumption, and important considerations for both adults and children. Understanding these factors is essential for using melatonin safely and effectively.
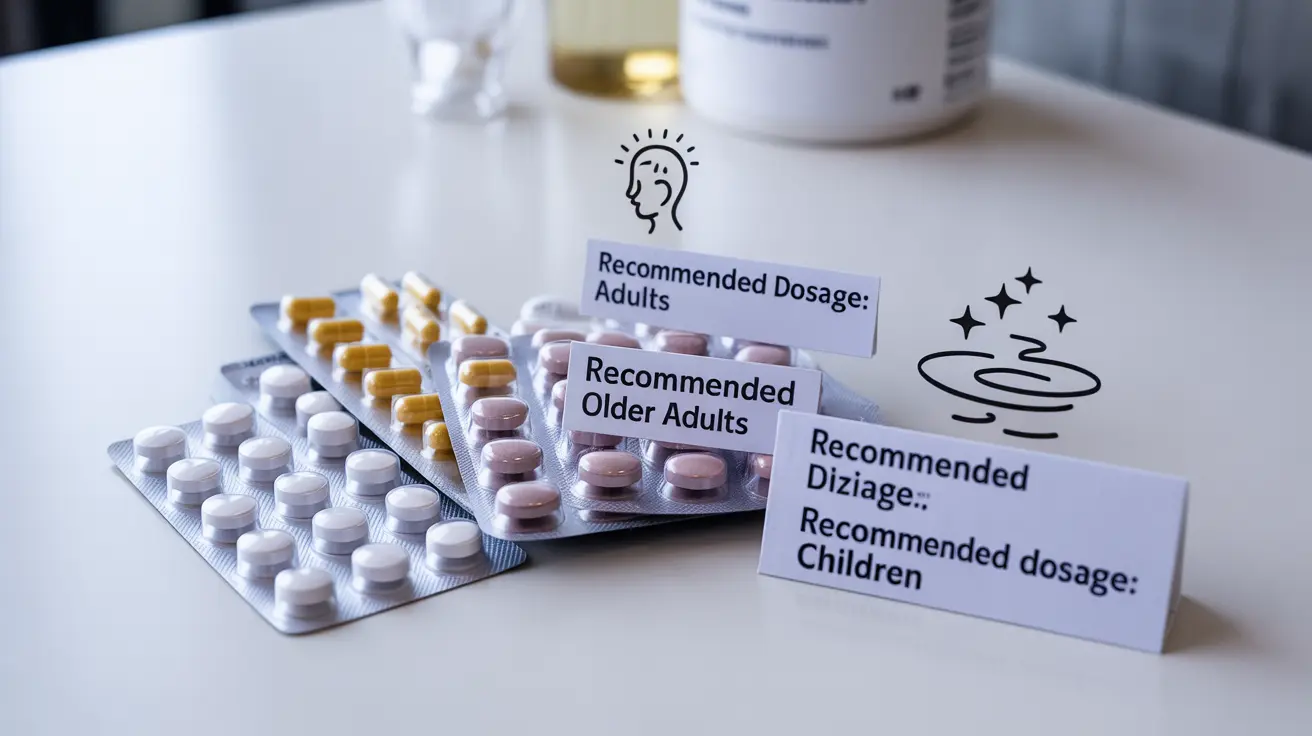
Safe Melatonin Dosage Guidelines
The appropriate melatonin dose varies significantly based on age, health status, and specific sleep concerns. Generally, it's recommended to start with the lowest effective dose:
- Adults: 0.5-5 mg
- Older adults: 1-2 mg
- Children (with physician approval): 0.5-3 mg
It's crucial to note that these are general guidelines, and individual needs may vary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting melatonin supplementation, especially for children or individuals with underlying health conditions.
Signs of Excessive Melatonin Use
Taking too much melatonin can lead to various uncomfortable symptoms. Common indicators include:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Changes in blood pressure
- Vivid or unusual dreams
- Mood changes
Short-term vs. Long-term Effects
While short-term effects of excessive melatonin typically resolve within 24 hours, regular overconsumption may lead to more persistent issues, including disrupted natural sleep-wake cycles and hormonal imbalances.
Risk Factors and Special Considerations
Certain individuals should exercise extra caution with melatonin use:
- Pregnant or nursing women
- People with autoimmune conditions
- Those taking blood-thinning medications
- Individuals with depression or anxiety
- People with diabetes or high blood pressure
Medication Interactions
Melatonin can interact with various medications, including:
- Blood pressure medications
- Diabetes medications
- Blood thinners
- Immunosuppressants
- Antidepressants
Emergency Response to Melatonin Overconsumption
If you suspect someone has taken too much melatonin, take these steps:
- Monitor their symptoms
- Keep them awake if possible
- Contact poison control or emergency services if severe symptoms develop
- Document the amount taken and timing
- Seek immediate medical attention if breathing difficulties occur
Frequently Asked Questions
- How much melatonin is too much to take safely for adults and children?
For adults, doses exceeding 10 mg per day are generally considered excessive. Children should not exceed 3-6 mg daily, and any supplementation should be supervised by a healthcare provider. The safest approach is to start with the lowest effective dose.
- What are the common symptoms or signs of a melatonin overdose?
Common signs include severe drowsiness, headaches, nausea, dizziness, anxiety, irritability, and disrupted sleep patterns. In some cases, individuals may experience changes in blood pressure and vivid dreams.
- Can taking too much melatonin cause serious health risks or complications?
While melatonin is generally considered safe, excessive amounts can lead to disrupted circadian rhythms, hormonal imbalances, and increased daytime drowsiness. Long-term overuse may affect natural melatonin production.
- How should I respond if I suspect someone has taken too much melatonin?
Monitor their symptoms closely, keep them awake if possible, and contact poison control or emergency services if severe symptoms develop. Document the amount taken and when it was consumed.
- Are there any medication interactions or risk factors to be aware of before taking melatonin?
Yes, melatonin can interact with blood thinners, diabetes medications, immunosuppressants, and blood pressure medications. People with autoimmune conditions, depression, or hormone-sensitive conditions should consult their healthcare provider before use.