Meningitis, a serious infection affecting the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can be caused by different types of bacteria. Understanding whether meningitis is caused by gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria is crucial for proper treatment and patient outcomes.
This comprehensive guide explores the distinctions between gram-negative and gram-positive meningitis, helping you understand the characteristics, symptoms, and treatment approaches for each type.
Understanding Bacterial Classification
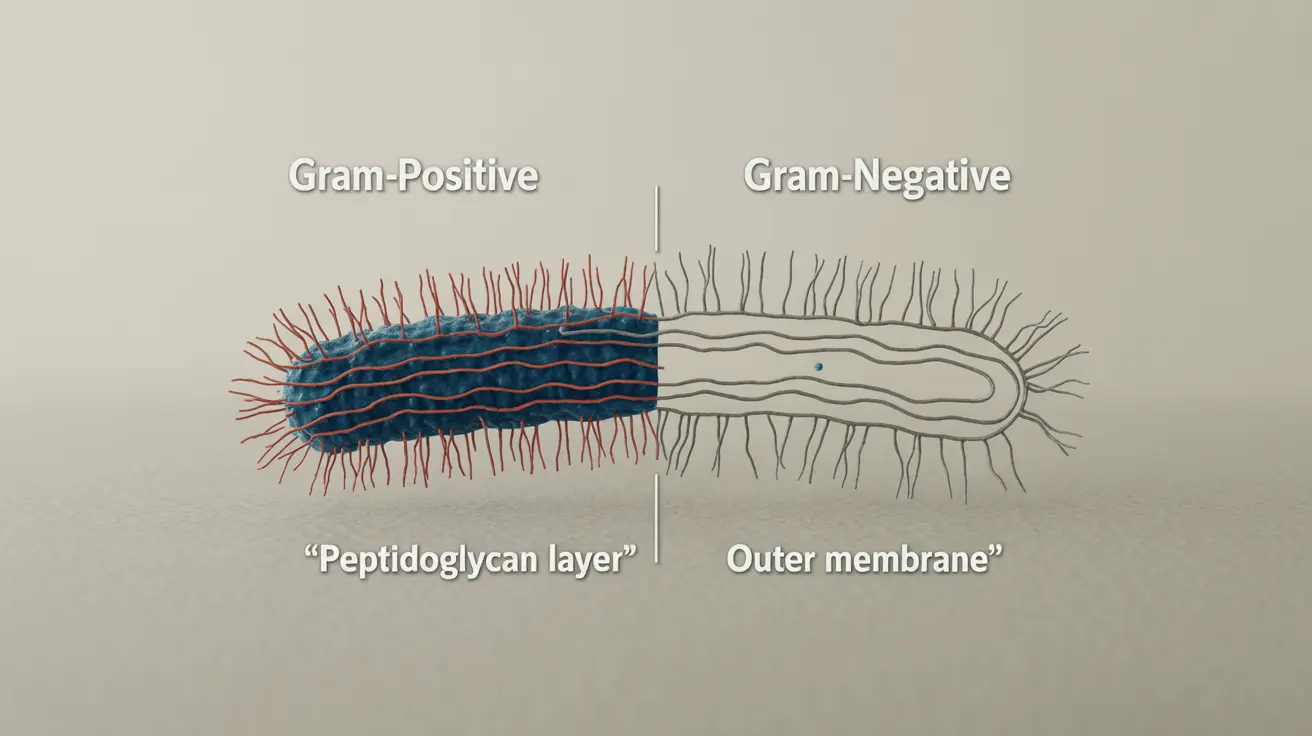
Bacteria are classified as either gram-positive or gram-negative based on their cell wall structure, which is determined through a laboratory staining process called the Gram stain test. This classification is crucial for determining appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Gram-Positive Bacterial Meningitis
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall. Common gram-positive bacteria that cause meningitis include Streptococcus pneumoniae and Listeria monocytogenes. These bacteria are generally more susceptible to certain antibiotics due to their simpler cell wall structure.
Gram-Negative Bacterial Meningitis
Gram-negative bacteria have a more complex cell wall structure with an additional outer membrane. Common causes include Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli. This sophisticated cell wall structure makes them more challenging to treat with antibiotics.
Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
While both types of bacterial meningitis can cause similar symptoms, there are some distinct characteristics in their presentation and progression:
Common Symptoms
- Severe headache
- Neck stiffness
- High fever
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Sensitivity to light
- Nausea and vomiting
Specific Features of Gram-Negative Meningitis
Gram-negative meningitis often presents with more severe symptoms and can progress more rapidly. Patients may experience:
- More pronounced neurological symptoms
- Higher risk of complications
- More severe inflammatory response
- Greater likelihood of septic shock
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Accurate diagnosis requires several medical procedures, including:
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
- Blood cultures
- Gram staining of cerebrospinal fluid
- PCR testing
Treatment strategies differ based on the bacterial type:
Treatment for Gram-Negative Meningitis
Gram-negative meningitis requires specific broad-spectrum antibiotics that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Treatment often involves:
- Third-generation cephalosporins
- Carbapenems
- Extended hospital stays
- Close monitoring for complications
Prevention and Risk Factors
Understanding risk factors and prevention strategies is crucial for both types of meningitis:
- Vaccination against specific bacterial strains
- Good hygiene practices
- Prompt treatment of other infections
- Regular medical check-ups for high-risk individuals
Frequently Asked Questions
Is meningitis caused by gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria?
Meningitis can be caused by both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Common gram-positive causes include Streptococcus pneumoniae, while common gram-negative causes include Neisseria meningitidis.
What are the main differences between gram-negative and gram-positive meningitis?
The main differences lie in the bacterial cell wall structure, treatment response, and prognosis. Gram-negative bacteria have a more complex cell wall, making them harder to treat, while gram-positive bacteria generally respond better to conventional antibiotics.
What symptoms should I look for if I suspect gram-negative meningitis?
Look for severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, confusion, light sensitivity, and nausea. Gram-negative meningitis often presents with more severe neurological symptoms and can progress more rapidly than gram-positive cases.
How is gram-negative meningitis diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis involves lumbar puncture, blood cultures, and gram staining. Treatment typically requires specific broad-spectrum antibiotics that can cross the blood-brain barrier, along with close monitoring in a hospital setting.
Why is gram-negative meningitis harder to treat than gram-positive meningitis?
Gram-negative bacteria have an additional outer membrane in their cell wall, making them more resistant to many antibiotics. This complex structure creates a stronger barrier against traditional treatments, requiring specific types of antibiotics and often resulting in longer recovery times.