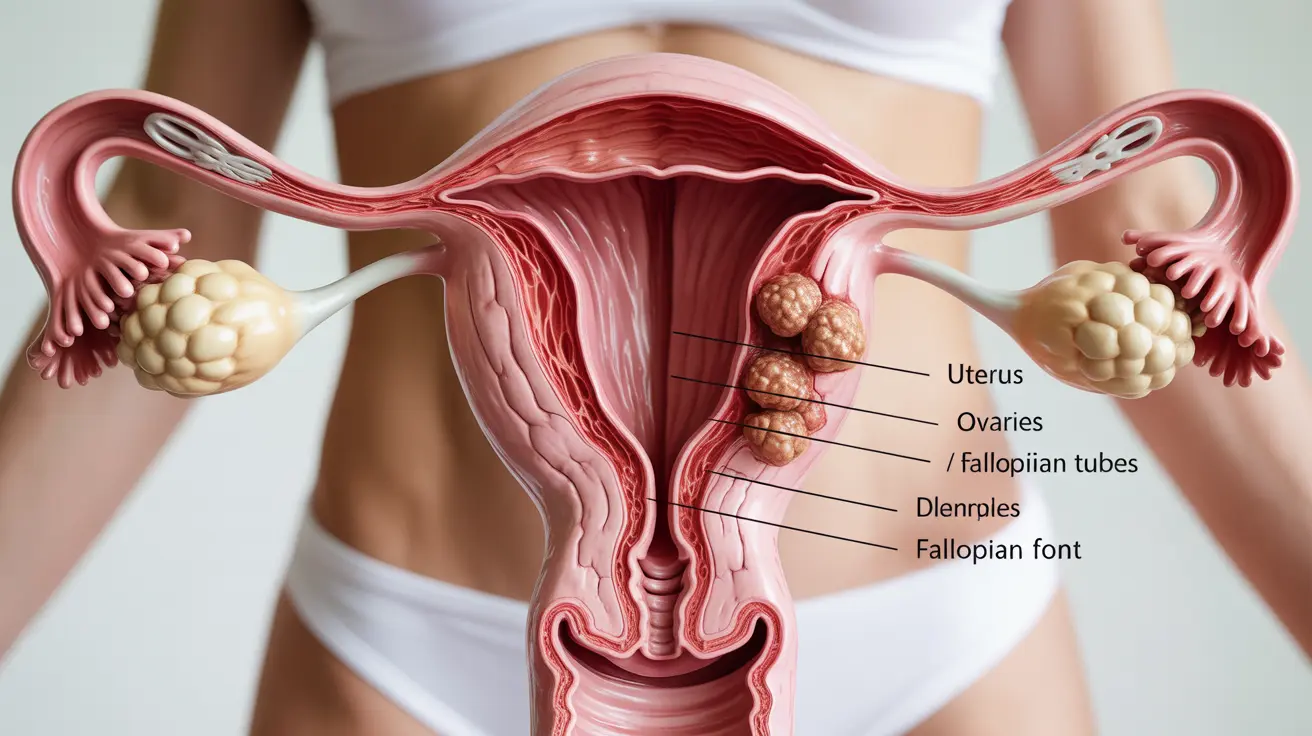
Living with menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding) combined with irregular cycles can be both physically and emotionally challenging. This condition affects many women and can significantly impact daily activities, causing anxiety about unpredictable bleeding patterns and concerns about underlying health issues.
Understanding the causes, getting proper diagnosis, and exploring effective treatment options are crucial steps in managing this condition. Let's dive deep into what you need to know about menorrhagia with irregular cycles and how to address these concerns effectively.
Common Causes of Menorrhagia with Irregular Cycles
Several underlying conditions can lead to both heavy bleeding and irregular menstrual patterns:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Uterine fibroids or polyps
- Endometriosis
- Thyroid disorders
- Bleeding disorders
- Certain medications
- Perimenopause
Understanding these potential causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment planning. Each condition may require different approaches to management and care.
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers typically use a comprehensive approach to diagnose menorrhagia with irregular cycles:
Physical Examination and Medical History
Your doctor will conduct a thorough physical exam and discuss your menstrual history, including:
- Bleeding patterns
- Duration of symptoms
- Family history
- Current medications
- Overall health status
Laboratory Tests
Common diagnostic tests may include:
- Complete blood count
- Hormone level testing
- Thyroid function tests
- Coagulation studies
- Pregnancy tests
Imaging Studies
Various imaging techniques help visualize the reproductive organs:
- Ultrasound
- Hysteroscopy
- MRI (in some cases)
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Treatment approaches typically depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Options may include:
Medical Treatments
- Hormonal birth control methods
- Tranexamic acid
- NSAIDs for pain management
- Iron supplements for anemia prevention
Hormonal Therapies
Hormonal treatments are often effective in managing both heavy bleeding and irregular cycles:
- Combined oral contraceptives
- Hormonal IUDs
- Progesterone-only options
- Hormone therapy for perimenopausal women
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatments aren't effective, surgical options might be considered:
- Endometrial ablation
- Myomectomy for fibroids
- Hysterectomy (as a last resort)
Prevention and Lifestyle Management
While some causes of menorrhagia with irregular cycles aren't preventable, certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Stress management
- Proper nutrition
- Tracking menstrual cycles
- Regular medical check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of menorrhagia with irregular menstrual cycles?
Common causes include hormonal imbalances, PCOS, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, thyroid disorders, and bleeding disorders. Certain medications and perimenopause can also contribute to these symptoms.
How is menorrhagia with irregular cycles diagnosed by doctors?
Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive approach including physical examination, medical history review, blood tests, hormone level testing, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or hysteroscopy.
What treatment options are available to manage heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding?
Treatment options include medical treatments (hormonal medications, tranexamic acid), hormonal therapies (birth control pills, IUDs), and surgical interventions when necessary. The chosen treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Can hormonal therapies like birth control pills or hormonal IUDs help regulate menorrhagia with irregular cycles?
Yes, hormonal therapies are often effective in managing both heavy bleeding and irregular cycles. Birth control pills and hormonal IUDs can help regulate menstrual patterns and reduce bleeding intensity.
What are the risks of leaving menorrhagia and irregular cycles untreated, and how can anemia be prevented?
Untreated menorrhagia can lead to iron-deficiency anemia, fatigue, and reduced quality of life. Anemia can be prevented through iron supplementation, proper nutrition, and treating the underlying cause of heavy bleeding. Regular medical monitoring is essential.