When it comes to foot pain, understanding the specific condition affecting you is crucial for proper treatment. Two common forefoot conditions that often cause confusion are metatarsalgia and sesamoiditis. While both conditions affect the front part of the foot, they have distinct characteristics, causes, and treatment approaches.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key differences between these conditions, their symptoms, and how to effectively manage them. Whether you're an athlete experiencing foot pain or someone dealing with daily discomfort, knowing the distinctions between metatarsalgia and sesamoiditis can help you seek appropriate care.
Understanding the Location and Symptoms
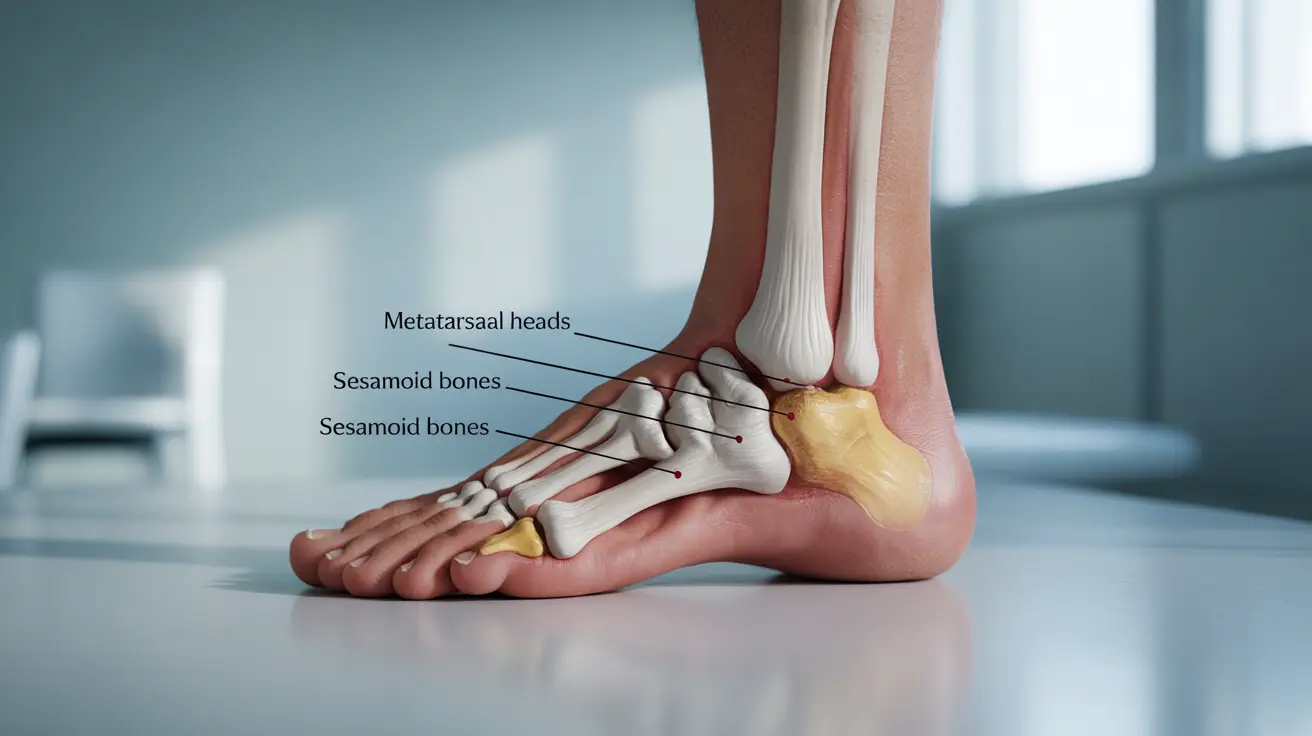
Metatarsalgia primarily affects the ball of the foot, specifically the area behind the toes where the metatarsal bones are located. The pain typically feels like you're walking on pebbles or having a burning sensation across the ball of your foot. It may worsen when standing, walking, or running.
Sesamoiditis, on the other hand, specifically affects the sesamoid bones beneath the big toe joint. These small, pea-shaped bones can become inflamed, causing sharp, focused pain directly under the big toe. The pain is usually more localized compared to metatarsalgia and may be accompanied by swelling.
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes of Metatarsalgia
- High-impact activities like running or jumping
- Ill-fitting shoes, particularly high heels
- Foot deformities such as bunions or high arches
- Being overweight or obese
- Aging and natural foot changes
Common Causes of Sesamoiditis
- Activities requiring repeated pressure on the big toe
- Dancing, particularly ballet
- Basketball and other sports involving jumping
- Sudden increase in activity level
- Wearing shoes with poor cushioning
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use different methods to diagnose these conditions accurately. For metatarsalgia, physical examination often includes checking for tender spots across the ball of the foot and assessing foot mechanics during walking. X-rays may be ordered to rule out stress fractures or other bone conditions.
Sesamoiditis diagnosis typically involves specific pressure tests on the sesamoid bones, along with imaging studies such as X-rays, bone scans, or MRI to evaluate the extent of inflammation and rule out fractures.
Treatment Strategies and Recovery
Treating Metatarsalgia
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice therapy for pain relief
- Proper footwear with metatarsal pads
- Custom orthotics to redistribute pressure
- Physical therapy exercises
- Anti-inflammatory medications when needed
Managing Sesamoiditis
- Immediate rest and ice application
- Padding or taping techniques
- Stiff-soled shoes to limit toe movement
- Custom orthotics with cutouts for sesamoid bones
- Gradual return to activities
- Possible immobilization in severe cases
Prevention Strategies
Preventing both conditions involves similar principles but with specific focuses. For metatarsalgia, emphasis is placed on proper weight distribution across the foot and wearing appropriate footwear. For sesamoiditis, protection of the sesamoid bones through proper technique in sports and adequate shock absorption is crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main differences between metatarsalgia and sesamoiditis in terms of pain location and symptoms? Metatarsalgia causes generalized pain across the ball of the foot, while sesamoiditis produces localized pain under the big toe joint. Metatarsalgia often feels like walking on pebbles, while sesamoiditis causes sharp, focused pain.
2. What causes metatarsalgia and sesamoiditis, and who is most at risk for these foot conditions? Athletes, dancers, and people who wear improper footwear are at risk for both conditions. Metatarsalgia is also common in people with foot deformities or excess weight, while sesamoiditis often affects those who put repeated pressure on their big toe.
3. How are metatarsalgia and sesamoiditis diagnosed by healthcare professionals? Diagnosis involves physical examination and pressure tests. Healthcare providers may use X-rays, MRIs, or bone scans to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
4. What are the most effective treatments and home remedies for metatarsalgia versus sesamoiditis? Both conditions respond to rest, ice, and proper footwear. Metatarsalgia often requires metatarsal pads and pressure redistribution, while sesamoiditis may need specific padding and immobilization techniques.
5. How can I prevent forefoot pain caused by metatarsalgia or sesamoiditis through footwear or lifestyle changes? Prevention includes wearing properly fitted shoes with good cushioning, gradually increasing activity levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and using appropriate protective equipment during sports activities.