For people living with asthma, medication choices require careful consideration, especially when it comes to beta-blockers like metoprolol. While this medication effectively treats various heart conditions, its use in asthma patients has long been a topic of medical discussion and concern.
Understanding the relationship between metoprolol and asthma is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients to make informed decisions about treatment options and manage potential risks effectively.
Understanding Metoprolol and Its Effects on Airways
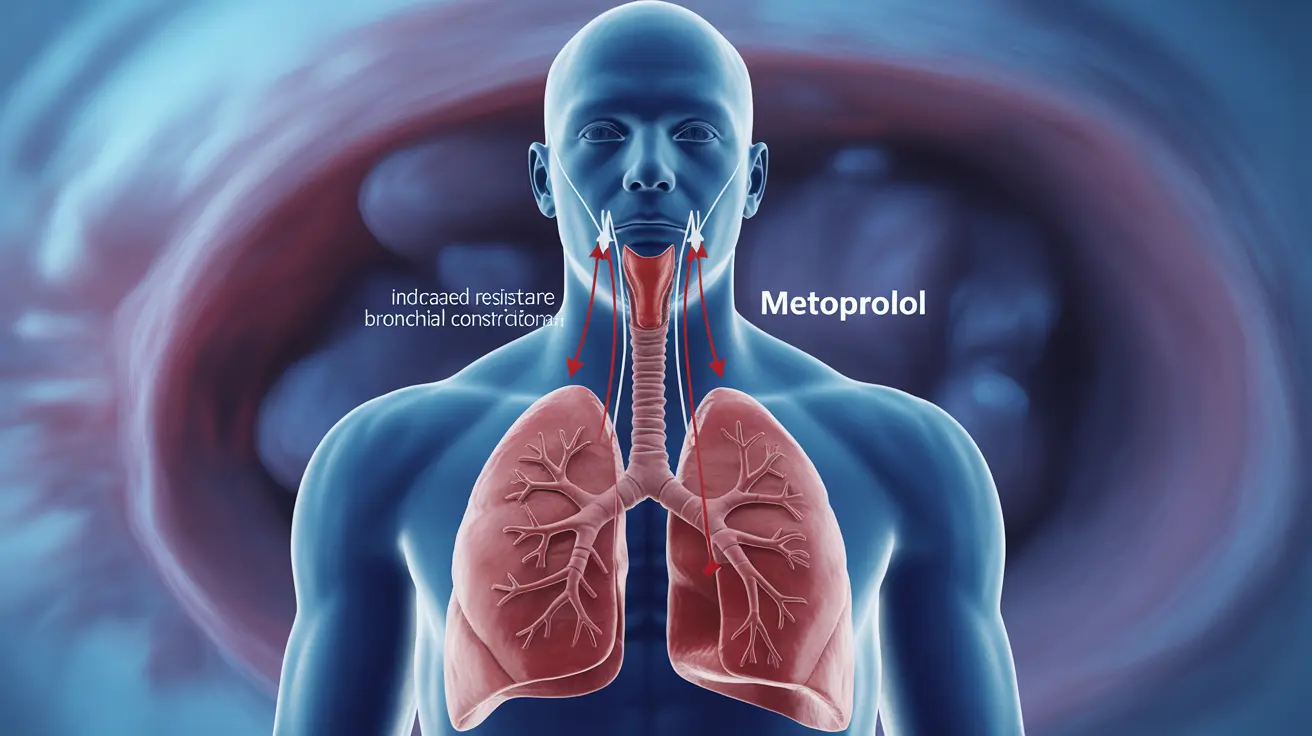
Metoprolol belongs to a class of medications called beta-blockers, which work by blocking certain receptors in the body. While these medications are excellent for treating conditions like high blood pressure and heart problems, they can affect the airways in ways that may concern asthma patients.
The medication works by blocking beta-1 receptors in the heart, but it can also partially affect beta-2 receptors in the airways, potentially impacting breathing in sensitive individuals.
Impact on Asthma Symptoms
When metoprolol interacts with the airways, several effects may occur:
- Increased airway resistance
- Reduced effectiveness of asthma rescue medications
- Potential bronchial constriction
- Changes in normal breathing patterns
These effects can be particularly concerning for individuals with severe or poorly controlled asthma.
Risk Assessment and Safety Considerations
The decision to use metoprolol in asthma patients requires careful evaluation of several factors:
- Severity of asthma symptoms
- Overall asthma control
- Presence of other medical conditions
- Available alternative treatments
- Individual response to medications
Monitoring and Prevention Strategies
For asthma patients who need to take metoprolol, several monitoring strategies can help ensure safety:
- Regular lung function testing
- Close observation of asthma symptoms
- Frequent communication with healthcare providers
- Maintenance of an asthma action plan
- Regular review of medication effectiveness
Alternative Treatment Options
When metoprolol isn't suitable, several alternative approaches may be considered:
- Cardioselective beta-blockers with less effect on airways
- Different classes of blood pressure medications
- Alternative heart medications
- Lifestyle modifications to support heart health
Managing Both Conditions Successfully
Successfully managing both asthma and conditions requiring metoprolol often requires a comprehensive approach:
- Regular medical check-ups
- Optimal asthma control measures
- Appropriate medication timing
- Emergency action plans
- Lifestyle modifications
Frequently Asked Questions
Is metoprolol safe to use if I have asthma?
The safety of metoprolol in asthma patients depends on individual factors, including asthma severity and overall health status. While some patients can safely use metoprolol, especially if their asthma is well-controlled, others may need alternative medications. This decision should always be made in consultation with a healthcare provider.
How does metoprolol affect asthma symptoms and lung function?
Metoprolol can affect lung function by partially blocking beta-2 receptors in the airways, potentially leading to increased airway resistance and reduced bronchodilation. This may result in decreased lung function and could affect the effectiveness of asthma medications.
Can metoprolol cause asthma attacks or worsen breathing problems?
Yes, metoprolol can potentially trigger or worsen asthma symptoms in some individuals, particularly those with severe or poorly controlled asthma. The risk varies among patients and depends on individual sensitivity to beta-blockers.
What are safer beta-blocker alternatives to metoprolol for people with asthma?
Highly cardioselective beta-blockers like bisoprolol or nebivolol may be safer alternatives for some asthma patients. Other medication classes, such as calcium channel blockers or ACE inhibitors, might also be considered depending on the condition being treated.
How can asthma patients manage their condition while taking metoprolol?
Successful management involves maintaining optimal asthma control, regular monitoring of symptoms, having an emergency action plan, and working closely with healthcare providers. Regular lung function testing and careful attention to any changes in breathing patterns are essential.