Mild thrombocytopenia is a medical condition characterized by a moderately low platelet count in the blood. While not as severe as other forms of thrombocytopenia, understanding this condition is crucial for proper management and preventing potential complications. This comprehensive guide will explore the essential aspects of mild thrombocytopenia, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What Is Mild Thrombocytopenia?
Mild thrombocytopenia occurs when platelet counts fall slightly below normal levels but remain high enough to maintain adequate blood clotting. Normal platelet counts typically range from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. In mild thrombocytopenia, these levels usually fall between 100,000 and 150,000 platelets per microliter.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Mild thrombocytopenia often presents with subtle symptoms that may be easily overlooked. However, recognizing these signs is important for early detection and management:
- Easy bruising
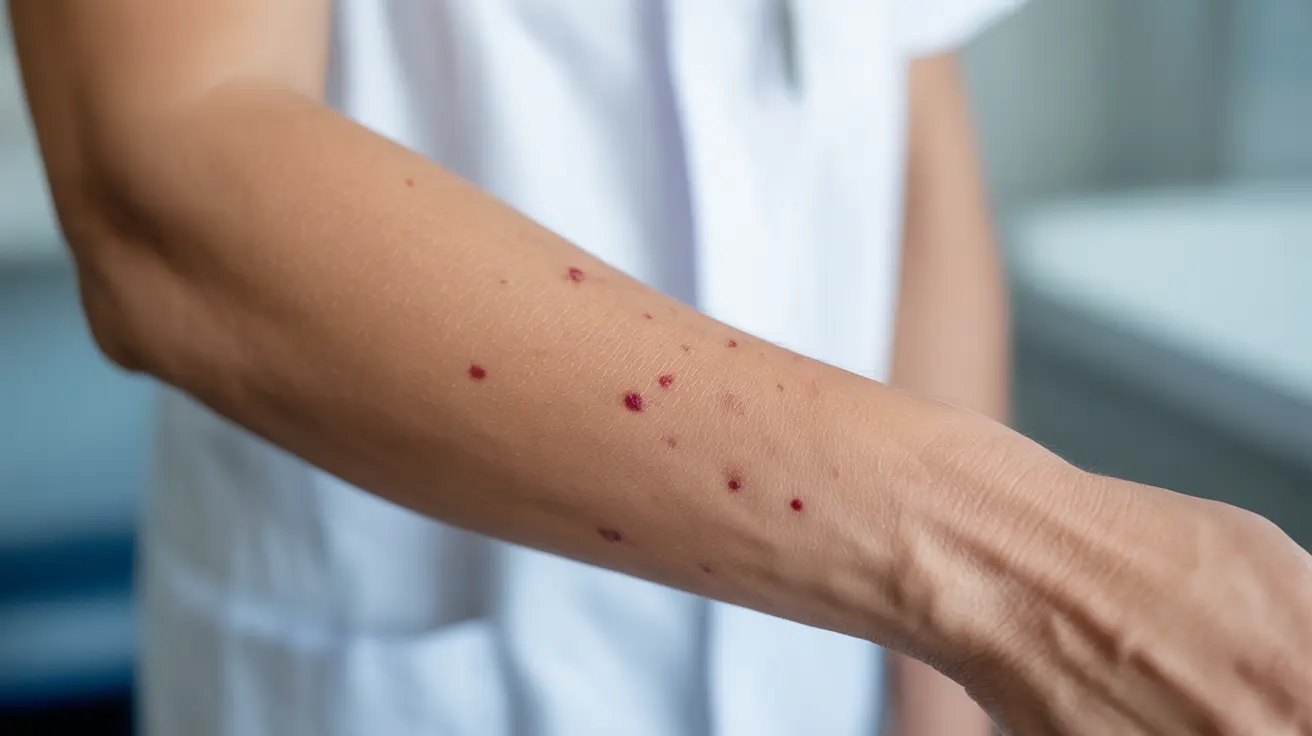
- Petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin)
- Slightly prolonged bleeding from minor cuts
- Occasional nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums during dental procedures
Many individuals with mild thrombocytopenia may remain asymptomatic, with the condition being discovered during routine blood work.
Understanding the Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of mild thrombocytopenia:
Medical Conditions
- Viral infections
- Autoimmune disorders
- Pregnancy
- Certain medications
- Bone marrow disorders
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- Alcohol consumption
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Exposure to certain chemicals
- Physical stress on the body
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Diagnosis typically begins with a complete blood count (CBC) test to measure platelet levels. Additional testing may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the condition.
Treatment Options
Treatment for mild thrombocytopenia varies depending on the cause and severity of symptoms. Common approaches include:
- Monitoring platelet counts regularly
- Treating underlying conditions
- Adjusting or discontinuing medications that may affect platelet counts
- Implementing lifestyle modifications
- In some cases, no immediate treatment may be necessary
Prevention and Management Strategies
Several lifestyle modifications can help manage mild thrombocytopenia:
- Avoiding activities with high risk of injury
- Maintaining good oral hygiene
- Following a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients
- Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption
- Regular medical check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of mild thrombocytopenia that I should watch for? Common symptoms include easy bruising, small red or purple spots on the skin (petechiae), slightly prolonged bleeding from cuts, occasional nosebleeds, and bleeding gums during dental care.
What causes mild thrombocytopenia and how can I identify the underlying reason? Mild thrombocytopenia can be caused by viral infections, autoimmune disorders, medications, pregnancy, or bone marrow conditions. A healthcare provider can determine the cause through blood tests and medical history evaluation.
How is mild thrombocytopenia typically treated and when is treatment necessary? Treatment depends on the underlying cause and symptom severity. Some cases may only require monitoring, while others might need specific treatments for underlying conditions. Treatment becomes necessary when symptoms are present or platelet counts continue to decrease.
Can lifestyle changes or diet help manage mild thrombocytopenia? Yes, lifestyle changes can help manage the condition. These include maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, avoiding alcohol, preventing injuries, and regular exercise as approved by your healthcare provider.
What precautions should I take to prevent bleeding if I have mild thrombocytopenia? Take precautions by avoiding contact sports or activities with high injury risk, using soft-bristled toothbrushes, being careful with sharp objects, and informing healthcare providers about your condition before medical procedures.