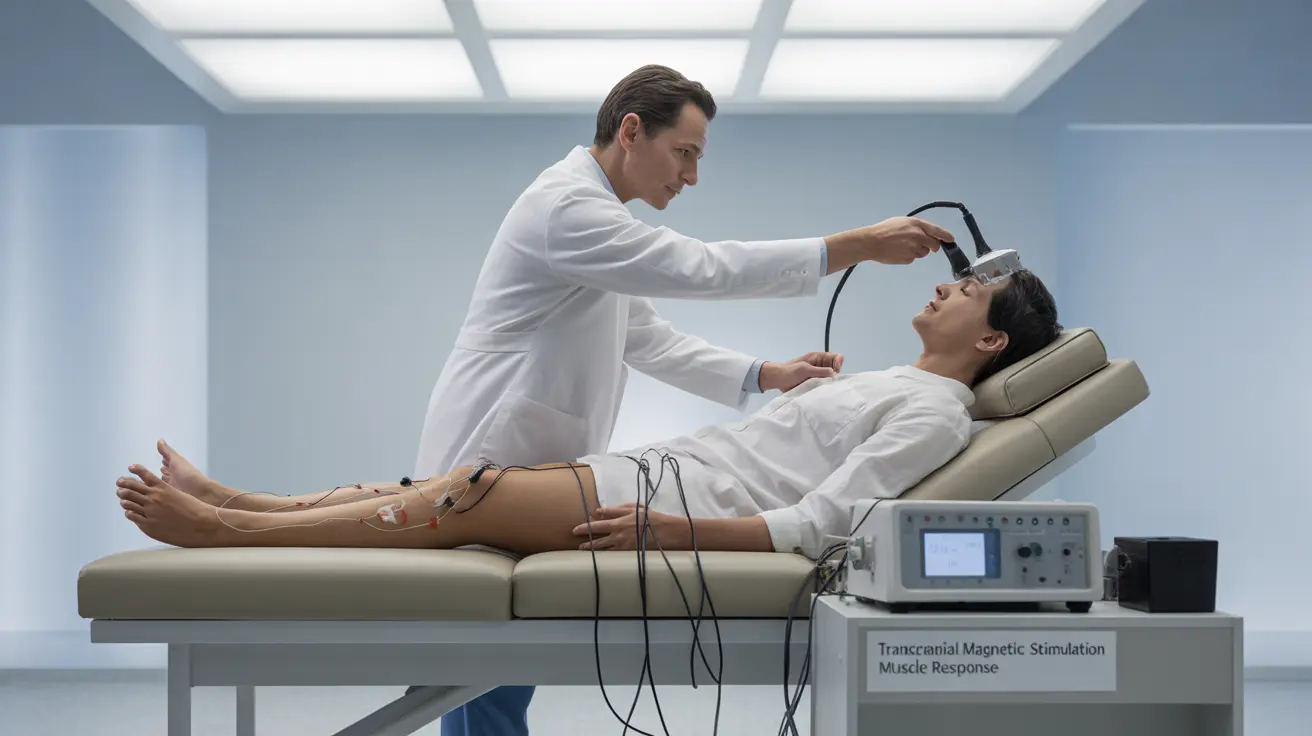
Motor evoked potential (MEP) tests are specialized diagnostic procedures that help doctors evaluate the function and health of your nervous system, particularly the pathways connecting your brain to your muscles. These tests are valuable tools in modern neurology, providing crucial insights into various neurological conditions and helping guide treatment decisions.
By using non-invasive magnetic stimulation, MEP tests measure how well electrical signals travel from your brain to your muscles, offering healthcare providers important information about your nervous system's functionality and identifying potential problems in nerve transmission.
How Motor Evoked Potential Tests Work
During a motor evoked potential test, medical professionals use transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to activate specific areas of your brain. This creates a brief magnetic pulse that stimulates nerve cells, generating electrical signals that travel through your nervous system to target muscles.
Special electrodes placed on your skin record these electrical responses, measuring both the strength of the signal and the time it takes to travel from your brain to the muscles. This information helps doctors assess the integrity of your nervous system pathways.
Medical Conditions Diagnosed Through MEP Testing
MEP tests are particularly useful in diagnosing and monitoring several neurological conditions, including:
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Spinal cord injuries
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Nerve compression disorders
These tests can detect problems in nerve transmission before physical symptoms become apparent, making them valuable tools for early diagnosis and intervention.
Preparing for Your MEP Test
Proper preparation is essential for accurate MEP test results. Your healthcare provider will typically provide specific instructions, which may include:
- Avoiding caffeine and certain medications before the test
- Getting adequate sleep the night before
- Wearing comfortable clothing
- Removing metal objects, including jewelry
- Informing your doctor about any medical devices or implants
The Testing Process
During the test, you'll be seated or lying comfortably while the medical team places small electrodes on specific muscles. A magnetic stimulator is then positioned over your head to deliver brief magnetic pulses. The entire procedure usually takes 30-60 minutes, depending on how many muscle groups need to be tested.
What to Expect During Testing
You may experience mild muscle twitches during the procedure, which is completely normal. The magnetic stimulation might cause some brief discomfort, but most patients find the procedure tolerable. Your healthcare provider will monitor you throughout the test and can adjust the stimulation intensity if needed.
Safety and Risk Considerations
MEP testing is generally considered safe, but like all medical procedures, it carries some risks. These are typically minimal and may include:
- Temporary headache
- Mild scalp discomfort
- Tingling sensations
- Slight muscle tension
Some patients should not undergo MEP testing, including those with certain types of metal implants or a history of seizures. It's crucial to discuss your medical history with your healthcare provider before the test.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a motor evoked potential (MEP) test and how does it work?
A motor evoked potential test uses magnetic stimulation to measure how well electrical signals travel from your brain to your muscles. It works by creating brief magnetic pulses over specific areas of your brain while electrodes record the response in your muscles.
- What conditions or neurological problems can an MEP test help diagnose?
MEP tests can help diagnose multiple sclerosis, ALS, spinal cord injuries, stroke, brain tumors, and various nerve compression disorders. They're particularly useful in detecting nervous system problems before physical symptoms appear.
- How should I prepare for a motor evoked potential test to ensure accurate results?
Prepare by avoiding caffeine, getting adequate sleep, wearing comfortable clothing, removing metal objects, and informing your doctor about any medical devices or implants. Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare team.
- What happens during a motor evoked potential test and is it painful?
During the test, electrodes are placed on your muscles while a magnetic stimulator delivers pulses to your brain. The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes and isn't usually painful, though you may feel mild discomfort or muscle twitches.
- Are there any risks or side effects associated with motor evoked potential testing?
While MEP testing is generally safe, possible side effects include temporary headache, mild scalp discomfort, tingling sensations, and slight muscle tension. Some patients with metal implants or a history of seizures should not undergo this testing.