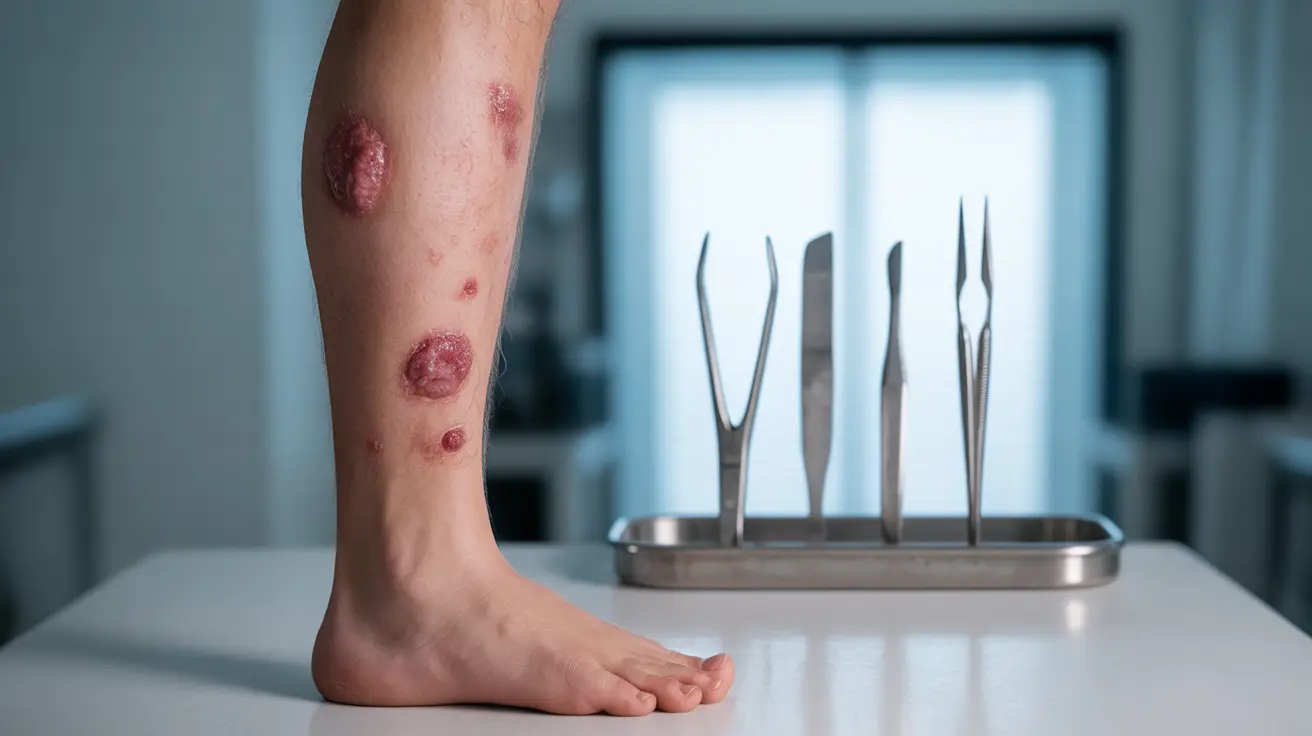
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections on the legs can be serious medical conditions requiring prompt attention and treatment. Understanding the signs, risks, and proper management of MRSA on legs is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring effective recovery.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about MRSA leg infections, including identification, treatment options, and essential prevention strategies.
Understanding MRSA Leg Infections
MRSA is a type of staph bacteria that has developed resistance to many common antibiotics. When it affects the legs, it typically manifests as skin infections that can range from mild to severe. These infections can occur in anyone but are particularly concerning in certain high-risk populations.
Signs and Symptoms of MRSA on Legs
MRSA infections on the legs typically present with several distinctive characteristics:
- Red, swollen areas that are warm to the touch
- Painful bumps that may resemble spider bites
- Fluid-filled blisters or boils
- Areas that may drain pus or other fluids
- Skin that appears deeply infected or abscessed
The infection site may also be accompanied by fever, fatigue, and general discomfort, particularly if the infection becomes more severe.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Medical Evaluation
Proper diagnosis of MRSA leg infections typically involves:
- Physical examination of the affected area
- Culture testing of drainage or tissue samples
- Assessment of symptoms and medical history
- Evaluation of risk factors and recent exposures
Treatment Options
Treatment for MRSA leg infections may include:
- Incision and drainage of boils or abscesses
- Specific antibiotics effective against MRSA
- Wound care and regular dressing changes
- Monitoring for signs of improvement or deterioration
- Follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing
Risk Factors and Prevention
High-Risk Groups
Certain individuals face increased risk of MRSA leg infections:
- Athletes and people who share equipment
- Healthcare workers and hospital patients
- People with weakened immune systems
- Individuals with recent surgeries or wounds
- Those living in crowded conditions
Prevention Strategies
Essential prevention measures include:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water
- Keeping cuts and scrapes clean and covered
- Avoiding sharing personal items like razors or towels
- Maintaining good personal hygiene
- Promptly cleaning and treating any skin injuries
Potential Complications
If left untreated, MRSA leg infections can lead to serious complications:
- Deep tissue infection
- Sepsis (bloodstream infection)
- Bone or joint infections
- Spread to other body parts
- Recurring infections
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs and symptoms of MRSA infection on the leg? The most common signs include red, swollen areas that are warm and painful to touch, boils or abscesses, pus drainage, and spider bite-like bumps. Systemic symptoms may include fever and fatigue.
How is MRSA on the leg diagnosed and treated? Diagnosis involves physical examination and laboratory testing of wound samples. Treatment typically includes proper wound care, specific antibiotics that target MRSA, and sometimes surgical drainage of infections.
Who is at higher risk of getting MRSA infections on the leg? Higher risk individuals include athletes, healthcare workers, people with weakened immune systems, those with recent surgeries or wounds, and individuals in crowded living conditions.
Can MRSA leg infections cause serious complications if untreated? Yes, untreated MRSA infections can lead to severe complications including deep tissue infections, sepsis, bone and joint infections, and spread to other parts of the body.
How can I prevent MRSA infections from developing or spreading on my legs? Prevention includes regular handwashing, keeping wounds clean and covered, avoiding shared personal items, maintaining good hygiene, and promptly treating any skin injuries.
Early recognition and proper treatment of MRSA leg infections are crucial for successful recovery. If you suspect a MRSA infection, seek medical attention promptly to prevent potential complications and ensure appropriate care.