A muscle contusion, commonly known as a bruised muscle, occurs when direct trauma or impact causes damage to muscle fibers and surrounding small blood vessels. Whether you're an athlete or someone who's experienced an accidental injury, understanding the nature of muscle contusions and their proper treatment is crucial for optimal recovery.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about muscle contusions, from identifying symptoms to implementing effective treatment strategies and recognizing when professional medical care is necessary.
Understanding Muscle Contusions and Their Symptoms
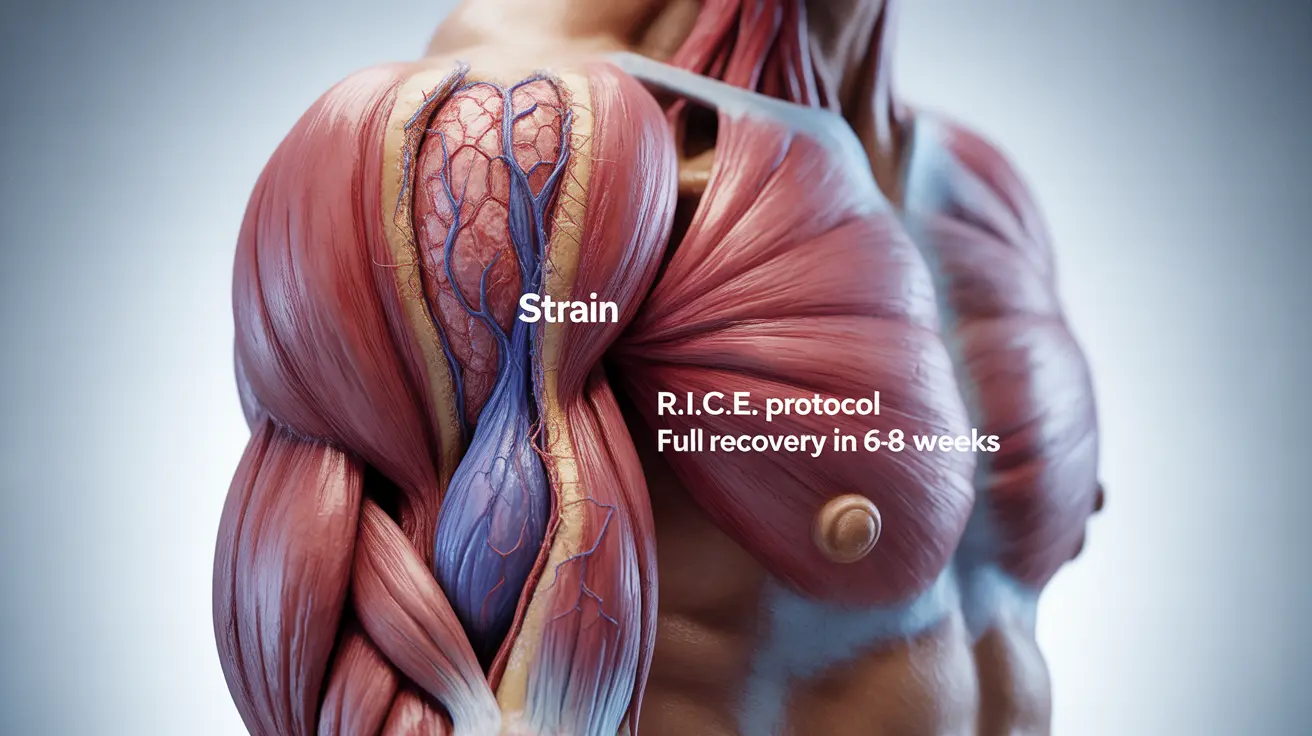
Muscle contusions occur when a direct blow or forceful impact damages the muscle fibers and blood vessels beneath the skin. The injury typically results in pain, discoloration, and limited range of motion in the affected area.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The primary indicators of a muscle contusion include:
- Immediate pain at the injury site
- Visible bruising or discoloration
- Swelling and tenderness
- Stiffness and restricted movement
- Weakness in the affected muscle
- Possible cramping or muscle spasms
Immediate Treatment and Home Care
The initial treatment for a muscle contusion follows the RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation), which helps minimize swelling and promote healing.
RICE Protocol Implementation
For optimal recovery, follow these specific steps:
- Rest the injured area and avoid activities that cause pain
- Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours
- Use compression bandages to reduce swelling
- Elevate the affected area above heart level when possible
Additional Home Care Measures
Beyond the RICE protocol, consider these supportive measures:
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers as needed
- Perform gentle range-of-motion exercises once initial pain subsides
- Maintain proper nutrition to support healing
- Get adequate sleep and rest
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many muscle contusions can be treated at home, certain situations require professional medical evaluation:
- Severe pain that doesn't improve with rest and ice
- Inability to move the affected limb
- Significant swelling that doesn't reduce
- Signs of infection (increased warmth, redness, fever)
- Numbness or tingling in the injured area
- Development of a hard lump at the injury site
Recovery Timeline and Return to Activity
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the contusion and the affected muscle. Mild contusions may heal within a few days, while severe cases can take several weeks or longer.
Gradual Return to Activity
Follow these guidelines when returning to physical activity:
- Begin with gentle stretching once pain allows
- Gradually increase activity intensity
- Listen to your body and avoid pushing too hard too soon
- Consider working with a physical therapist for proper progression
Prevention Strategies
To minimize the risk of muscle contusions:
- Wear appropriate protective gear during sports
- Practice proper technique in contact sports
- Maintain good muscle strength and flexibility
- Use padding in high-risk areas during activities
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a muscle contusion and how can I recognize it? A muscle contusion typically presents with immediate pain, visible bruising, swelling, and limited range of motion in the affected area. The skin may appear purple or dark red, and the muscle will feel tender to touch.
How is a muscle contusion treated and what are the best home care steps to promote healing? Treatment involves following the RICE protocol: Rest the injured area, apply Ice for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours, use Compression bandages, and Elevate the affected area. Over-the-counter pain medication can help manage discomfort.
When should I seek medical attention for a muscle contusion instead of treating it at home? Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain that doesn't improve, significant swelling, inability to move the affected area, signs of infection, numbness or tingling, or if you develop a hard lump at the injury site.
What complications can arise from a muscle contusion and how can they be prevented? Possible complications include myositis ossificans (bone formation in the muscle), compartment syndrome, and chronic pain. Prevention involves proper initial treatment, following recovery guidelines, and not returning to activity too quickly.
How long does it typically take to recover from a muscle contusion before returning to sports or physical activity? Recovery time varies from a few days for mild contusions to several weeks for severe cases. A gradual return to activity should only begin when pain has significantly decreased and range of motion has improved. Full recovery should be achieved before returning to intense physical activity.