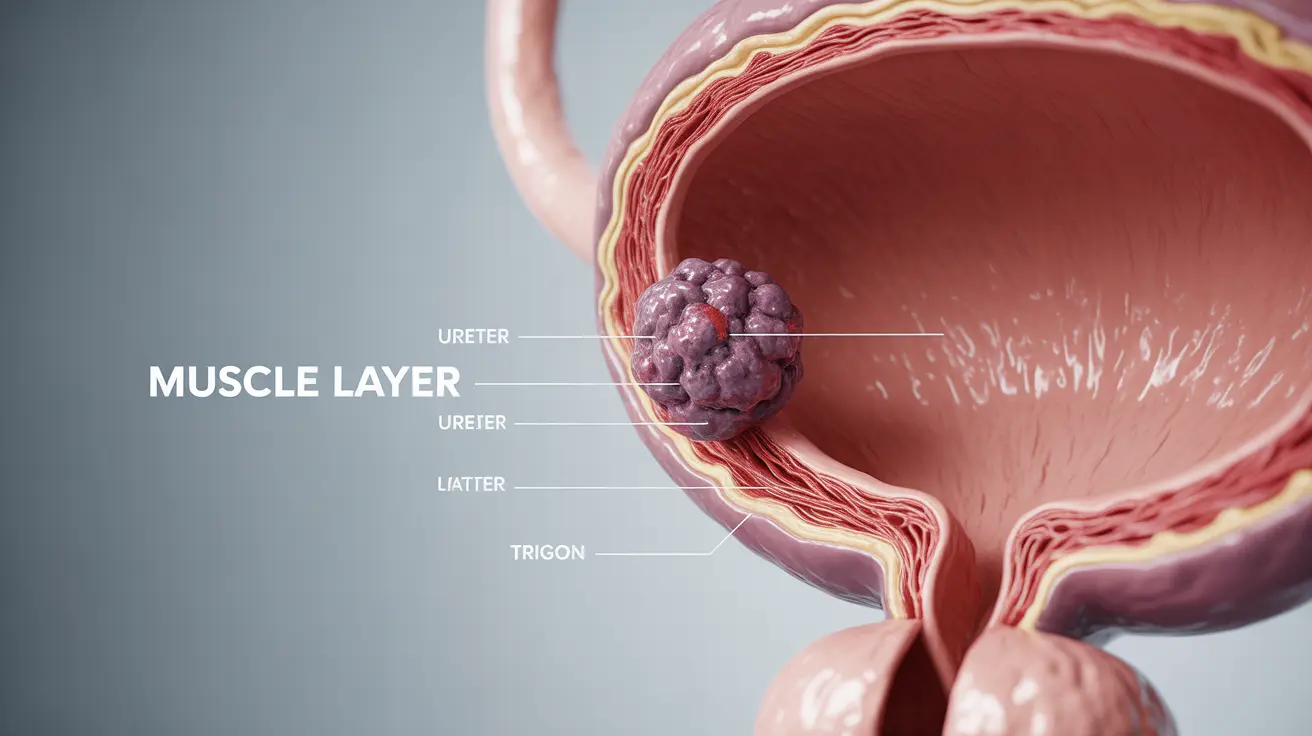
Muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is a serious form of bladder cancer that has grown into the muscle wall of the bladder. This aggressive type of cancer requires prompt medical attention and treatment to achieve the best possible outcomes. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis methods, and available treatments is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Early detection and appropriate treatment are vital factors in managing MIBC effectively. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of muscle invasive bladder cancer, including risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and current treatment approaches.
Signs and Symptoms of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of MIBC is crucial for early detection. Common signs include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination
- Urgent need to urinate
- Pain or burning during urination
- Lower back pain on one side
- Pelvic pain
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms can be similar to other conditions, but their persistence should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Diagnosis and Staging Process
Accurate diagnosis of muscle invasive bladder cancer involves several steps and procedures:
Initial Assessment
The diagnostic journey typically begins with:
- Detailed medical history
- Physical examination
- Urinalysis and urine cytology
- Blood tests to assess overall health
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
Confirming MIBC requires specialized tests:
- Cystoscopy with biopsy
- CT urogram or MRI
- Chest imaging to check for metastasis
- Bone scan if bone involvement is suspected
Treatment Approaches for MIBC
Treatment for muscle invasive bladder cancer typically involves a multi-modal approach:
Surgical Options
The primary treatment usually includes:
- Radical cystectomy (removal of the bladder)
- Lymph node dissection
- Urinary diversion surgery
Additional Therapies
Treatment may also involve:
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before surgery
- Adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery
- Radiation therapy in specific cases
- Immunotherapy for certain patients
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding risk factors is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Smoking is the most significant modifiable risk factor for MIBC, accounting for approximately half of all cases. Other risk factors include:
- Age (more common in older adults)
- Male gender
- Chronic bladder inflammation
- Exposure to certain industrial chemicals
- Family history of bladder cancer
Prognosis and Follow-up Care
The prognosis for muscle invasive bladder cancer varies depending on several factors:
- Stage at diagnosis
- Response to treatment
- Overall health status
- Access to comprehensive care
Regular follow-up care is essential for monitoring recovery and detecting potential recurrence early.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs and symptoms of muscle invasive bladder cancer?
The most common symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, pain during urination, lower back pain on one side, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms should not be ignored and require immediate medical attention.
How is muscle invasive bladder cancer diagnosed and staged?
Diagnosis involves multiple steps including cystoscopy with biopsy, imaging tests (CT, MRI), and staging procedures. Doctors use the TNM staging system to determine the extent of the cancer's spread and develop appropriate treatment plans.
What are the main treatment options available for muscle invasive bladder cancer?
The main treatment options include radical cystectomy (bladder removal), chemotherapy (before or after surgery), radiation therapy, and in some cases, immunotherapy. Treatment plans are typically individualized based on the cancer's stage and the patient's overall health.
How does smoking increase the risk of muscle invasive bladder cancer?
Smoking exposes the body to harmful chemicals that are processed and excreted through the urinary system. These carcinogens can damage the bladder lining over time, potentially leading to cancer development. Smoking is associated with approximately 50% of bladder cancer cases.
What is the prognosis and survival outlook for someone diagnosed with muscle invasive bladder cancer?
The prognosis varies significantly based on factors such as cancer stage, treatment response, and overall health. Early detection and appropriate treatment can improve survival rates. Five-year survival rates vary depending on the stage at diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatment.