End-stage myasthenia gravis represents the most severe form of this chronic autoimmune condition, requiring careful monitoring and specialized medical management. Understanding the progression, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for patients and caregivers facing this challenging phase of the disease.
While myasthenia gravis can be serious, modern medical advances have significantly improved outcomes for patients, even in advanced stages. This article explores the critical aspects of end-stage myasthenia gravis, including warning signs, management strategies, and factors affecting prognosis.
Recognizing End-Stage Symptoms and Crisis Events
End-stage myasthenia gravis often manifests through increasingly severe symptoms that can signal a medical emergency. The most concerning symptoms include:
- Severe difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Extreme muscle weakness affecting multiple body regions
- Inability to swallow safely
- Speech difficulties or complete loss of speech
- Profound fatigue resistant to rest
- Weakened neck muscles affecting head control
These symptoms can rapidly progress to a myasthenic crisis, requiring immediate medical intervention to prevent life-threatening complications.
Critical Management Strategies
Managing end-stage myasthenia gravis requires a comprehensive approach involving multiple treatment modalities and careful monitoring:
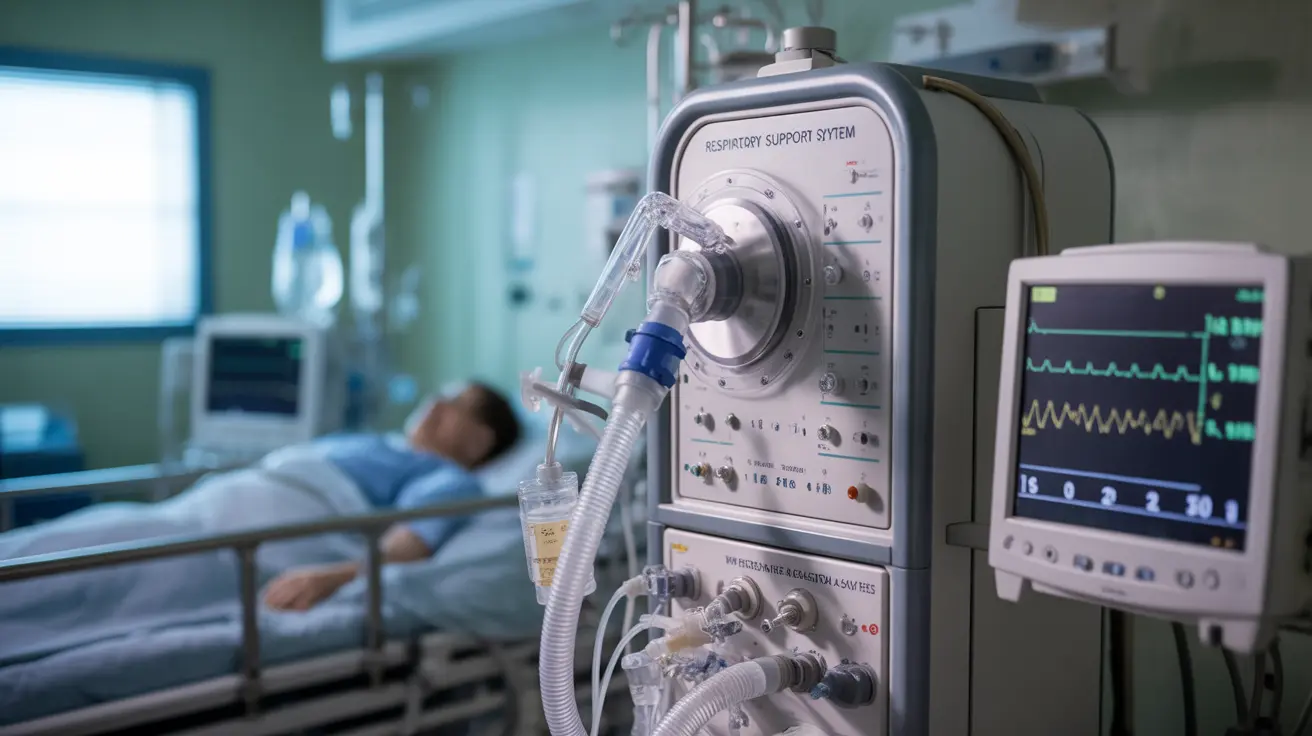
Respiratory Support
Respiratory care becomes paramount in end-stage disease. This may include:
- Regular pulmonary function testing
- Mechanical ventilation when necessary
- Specialized respiratory therapy
- Emergency protocols for sudden breathing difficulties
Medication Management
Advanced medication protocols typically involve:
- Carefully adjusted immunosuppressant medications
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- Targeted biological therapies
- Crisis intervention medications
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing severe or end-stage myasthenia gravis:
- Advanced age at disease onset
- Presence of thymoma
- Delayed diagnosis or treatment
- Concurrent autoimmune conditions
- Poor medication compliance
- Frequent infections
Modern Treatment Approaches
Current treatment options for managing end-stage myasthenia gravis and crisis situations include:
- Plasmapheresis for rapid symptom relief
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy
- Advanced immunosuppressive protocols
- Thymectomy in appropriate cases
- Targeted biological treatments
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
With proper medical care and management, many patients with myasthenia gravis can maintain a good quality of life. Modern treatments have significantly improved the prognosis, even for those with advanced disease. Regular monitoring, prompt intervention during crises, and adherence to treatment plans are essential for optimal outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What symptoms indicate that myasthenia gravis is reaching an end-stage or severe crisis? End-stage symptoms include severe respiratory difficulty, extreme muscle weakness, inability to swallow, speech problems, and profound fatigue that doesn't improve with rest. These symptoms can rapidly progress to a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention.
How is end-stage myasthenia gravis managed to prevent respiratory failure and other complications? Management involves close monitoring of respiratory function, aggressive medication protocols, and immediate intervention when symptoms worsen. This may include mechanical ventilation, immunotherapy, and specialized respiratory care.
What treatments are available for myasthenic crisis, and how effective are they in improving survival? Available treatments include plasmapheresis, IVIG therapy, mechanical ventilation, and aggressive immunosuppression. When implemented promptly, these treatments are highly effective, with survival rates exceeding 90% in specialized care settings.
What factors increase the risk of developing severe or end-stage myasthenia gravis? Risk factors include advanced age at onset, presence of thymoma, delayed diagnosis, concurrent autoimmune conditions, poor medication compliance, and frequent infections.
Can people with myasthenia gravis expect a normal life expectancy with proper medical care? Yes, with modern treatments and appropriate medical management, most people with myasthenia gravis can expect a normal or near-normal life expectancy. Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are essential for maintaining good outcomes.