Narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias are important cardiac conditions that affect the heart's electrical system, causing rapid heart rates with specific ECG characteristics. Understanding these arrhythmias is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment, as they can significantly impact a person's quality of life and require specific medical interventions.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various types of narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias, their distinguishing features, and the most effective approaches to diagnosis and management. Whether you're a patient or healthcare provider, this information will help you better understand these common cardiac rhythm disturbances.
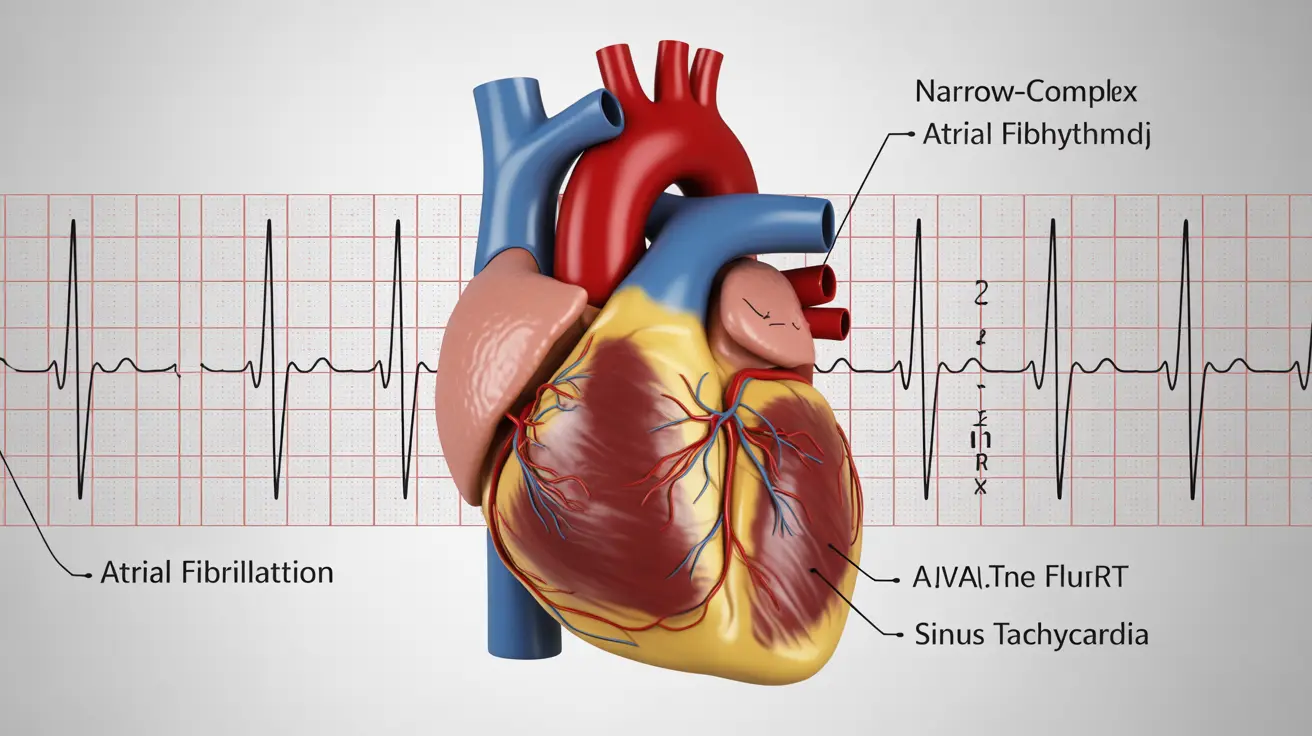
Types of Narrow-Complex Tachyarrhythmias
Narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias are characterized by their distinctive QRS complex width of less than 120 milliseconds on an ECG. The main types include:
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
The most common irregular narrow-complex tachyarrhythmia, characterized by chaotic electrical signals in the atria leading to irregular ventricular responses. This condition affects millions of Americans and increases the risk of stroke.
Atrial Flutter
A more organized form of supraventricular tachycardia where atrial rates typically range from 250-350 beats per minute, often conducting to the ventricles in predictable patterns.
Sinus Tachycardia
A normal response to exercise, stress, or other physiologic demands, characterized by a regular rhythm originating from the sinus node with rates above 100 beats per minute.
AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
The most common form of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, typically presenting with sudden onset and termination of rapid, regular heart rates.
Identifying Characteristics on ECG
Narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias have distinct features that help in their identification:
- QRS duration less than 120 milliseconds
- Heart rate typically above 100 beats per minute
- P waves may be visible, hidden, or absent
- Regular or irregular rhythm patterns
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Patients with narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias may experience:
- Palpitations or racing heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest discomfort
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias:
- 12-lead ECG
- Holter monitoring
- Event recorders
- Exercise stress testing
- Electrophysiology studies in selected cases
Treatment Options
Treatment approaches vary depending on the specific type of arrhythmia and may include:
Acute Management
Immediate interventions might involve vagal maneuvers, medications, or electrical cardioversion in certain cases.
Long-term Management
Chronic treatment options include antiarrhythmic medications, catheter ablation, and lifestyle modifications to prevent recurrence.
Prevention Strategies
Several lifestyle modifications can help reduce the frequency of episodes:
- Stress management techniques
- Regular exercise within prescribed limits
- Adequate sleep
- Avoiding triggers like caffeine or alcohol
- Maintaining proper electrolyte balance
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common types of narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias and how do they differ? Narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias primarily include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, sinus tachycardia, and AVNRT. They differ in their mechanism, regularity, and treatment approaches. AFib is irregular, while flutter and AVNRT typically maintain regular patterns.
How can I tell if my narrow-complex tachyarrhythmia is regular or irregular on an ECG? Regular rhythms show consistent intervals between QRS complexes, while irregular rhythms display varying intervals. This can be determined by measuring R-R intervals on the ECG strip.
What symptoms should I watch for if I have a narrow-complex tachyarrhythmia? Key symptoms include palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, chest discomfort, and fatigue. Severe symptoms like fainting or severe chest pain require immediate medical attention.
How are narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias diagnosed and treated? Diagnosis typically involves ECG monitoring, while treatment may include medications, cardioversion, catheter ablation, or a combination of these approaches, depending on the specific type and severity.
Can lifestyle changes or medications help prevent episodes of narrow-complex tachyarrhythmias? Yes, lifestyle modifications like stress reduction, regular exercise, and avoiding triggers can help prevent episodes. Medications may also be prescribed for long-term prevention, depending on the type and frequency of arrhythmia.